2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049;
3. 中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所, 南京 210008;
4. 生态环境部环境工程评估中心, 北京 100012
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
3. Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing 210008, China;
4. Appraisal Center for Environment and Engineering, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Beijing 100012, China
稀土具有其他元素不可替代的光、电、磁等理化特性,被广泛应用于传统工业、高新技术产业、军事及新型农业等领域,是影响经济发展、技术进步、国家安全的重要战略资源[1-3]。中国是全球范围内稀土资源最丰富、种类最齐全的国家[4-5],其中南方离子型稀土矿富含稀缺的中、重稀土,因此受到高度关注[6-7]。
离子型稀土矿的开采工艺经历了池浸、堆浸及原地浸矿三个阶段[8-9],池浸和堆浸对山体破坏大且资源利用率低,已被列为淘汰工艺[10-11]。而原地浸矿是先将浸矿剂硫酸铵直接注入矿体内,利用铵根离子(
目前,我国南方存在大量的稀土尾矿[23]。虽然采用了防渗透及各种物理化学方法降低氮化物的排放量,但矿山废弃多年后,仍然可以在周围土壤及水体中检测到高含量铵态氮(
研究区位于江西省最南端的赣州市龙南县,该县占地面积1 641km2,地处亚热带丘陵地区,年均气温为19.5℃,年均降水量达1 507mm,降雨多集中在4到6月[26-27]。在地质构造上,研究区属于加里东隆起区,是由震旦系、寒武系和粤陶系组成的前泥盆纪地层,侵入岩极为发育,以酸性岩为主 [28]。该县主要土壤类型为红壤。龙南县矿产资源丰富,已探明稀土、钨、煤等40多种矿产,其中离子型重稀土储量占世界已探明储量的70%[29],且主要采取原地浸矿工艺开采[15],具有代表性。本次实验于2019年11月选取龙南县县城东南约10km一个采用原地浸矿工艺开采的离子型稀土矿山进行土壤采样,该矿山于2015年完成开采,此后一直未受人为干扰,局部有滑坡现象。矿山地处中低山区,所在区域多年平均径流系数为0.53[30],大气降水易通过地表径流沿陡坡汇入下游水系中,减少入渗水流。此矿山海拔352 m,整个矿区植被覆盖较好,坡度37°左右,以木本科植物为优势物种,主要的植物类型有马尾松、杉木、五节芒草等[31]。矿山顶部修筑有浸矿液池,山坡上均匀布设注液井(深度有差异,由含矿层埋深决定),山脚设有收液沟(深度以挖到基岩为准),其中GP1、GP2、GP3为采样剖面,表层为腐殖质层(图 1)。
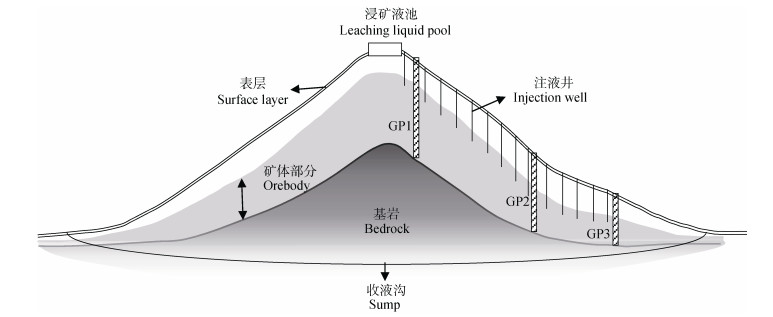
|
图 1 矿山结构、采矿设施布设及采样点位置图 Fig. 1 Mine structure, location of sampling points and layout of mining facilities |
自浸矿场地坡顶沿直线,于坡顶(GP1)、坡中(GP2)及坡底(GP3)各选择一个采样点(图 2)(坡顶至坡底的高程差为27 m)。每个样点均由表土采集至矿体底板(土体与基岩交界处)。矿体底板为新鲜的花岗岩岩体,透水性低。由于该地位于亚热带地区,花岗岩的半风化体深厚,因此稀土矿体较深。为使土壤样品尽量保持原始状态,使用洛阳铲来采集原状土柱。采样过程中,表层至1m土体的土壤按照发生层采样,1 m以下每50 cm混合均匀后采集一次样品。若在某一深度的50 cm厚度范围内土壤结构、颜色、紧实程度等形态和物理性质发生明显变化时则分为两段采样。GP1采样深度为9.7 m;GP2采样深度为8.0 m;GP3采样深度为5.5 m。
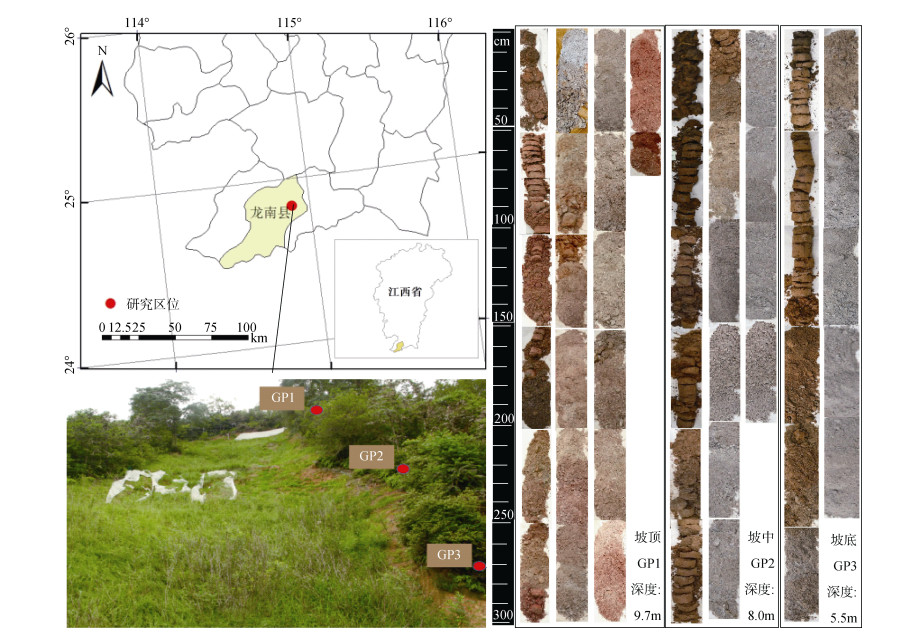
|
图 2 采样点位及土壤样品 Fig. 2 Sampling locations and the sampled soils |
采集完成的土壤样品在现场分成两份:一部分放入保温箱中低温保存,用于
土壤含水量的测定采用烘干法。全氮的测定采用硒粉、硫酸铜、硫酸钾消化-蒸馏法。有机质采用重铬酸钾-硫酸消化法测定。阳离子交换量选用乙酸铵-EDTA(pH7.0)交换法测定。颗粒组成采用激光粒度仪测定。pH采用pH计测定,电导率采用电导仪测定[32]。
2 结果与讨论 2.1 土壤铵态氮含量特征研究区土壤
|
|
表 1 样点土壤铵态氮含量描述性统计 Table 1 Descriptive statistics of soil ammonium nitrogen content |

|
图 3 土壤铵态氮含量频率分布图 Fig. 3 Frequency distribution of soil ammonium nitrogen content |
|
|
表 2 矿山总体土壤理化性质描述性统计 Table 2 Descriptive statistics of soil physicochemical properties in mine |
研究区内土体中
坡顶表层(腐殖质层,0~10 cm)

|
图 4 土壤铵态氮与硝态氮含量垂直分布 Fig. 4 Vertical distribution of soil ammonium nitrogen and nitrate content |
坡中表层(0~8 cm)
坡底土体中除靠近矿体底板外,土体中NH4+-N含量变化趋势与坡中相似(图 4 c)。表层0~10 cm的
从土壤物理化学性质来看,土壤pH与含水率是控制土壤硝化过程的关键因素[37],进而影响土壤
|
|
表 3 土壤理化特征之间的相关性 Table 3 Correlation coefficient between soil physicochemical characteristics |
研究中发现,矿区土壤
土壤中发生的自养硝化作用与异化还原作用共同影响着土壤
坡顶、坡中和坡底分别于200 cm、320 cm及150 cm深处明显出现稀土矿,而土壤
坡顶、坡中及坡底处土壤
根据采集的土壤样品的颜色、结构、风化程度等特征及开采过程对各层土壤铵态氮含量的影响将土壤剖面分为表层(腐殖质层)、中层(腐殖质层与半风化层中间的土体)、底层(半风化层,浸矿剂注入层)(表 4)。分层比较坡顶、坡中及坡底的
|
|
表 4 土层厚度 Table 4 Soil thickness |
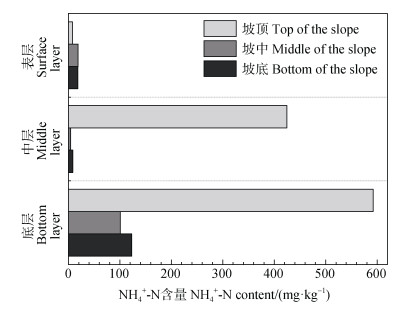
|
图 5 不同地形部位土壤铵态氮含量 Fig. 5 Soil ammonium nitrogen content in different terrain |
相较坡顶,坡中和坡底各土层
利用原地浸矿工艺开采稀土的闭矿区土壤
| [1] |
Zhu M Y, Cui Z N. Analysis of global rare earth market, and its future development, and demands (In Chinese)[J]. Journal of Shanghai Normal University(Natural Sciences), 2019, 48(6): 686-694. [朱铭岳, 崔中倪. 全球稀土市场分析及未来的发展和需求[J]. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 48(6): 686-694.]
(  0) 0) |
| [2] |
Peng Y, He J G, Zhang Z M, et al. Eco-environmental dynamic monitoring and assessment of rare earth mining area in Southern Ganzhou Using Remote Sensing (In Chinese)[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(6): 1676-1685. [彭燕, 何国金, 张兆明, 等. 赣南稀土矿开发区生态环境遥感动态监测与评估[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(6): 1676-1685.]
(  0) 0) |
| [3] |
Liu J H, Chen L K, Liu C Y, et al. Pb speciation in rare earth minerals and use of entropy and fuzzy clustering methods to assess the migration capacity of Pb during mining activities[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 165: 334-342. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.007
(  0) 0) |
| [4] |
Zhang S J, Zhang L W, Zhang Y W, et al. Summarize on rare earth mineral resources and their distribution at home and abroad (In Chinese)[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(1): 9-16. [张苏江, 张立伟, 张彦文, 等. 国内外稀土矿产资源及其分布概述[J]. 无机盐工业, 2020, 52(1): 9-16.]
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
Chen J B, Huo W M, Li X F, et al. Comparative analysis of rare earth resources situation between China, the US and the EU (In Chinese)[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2020, 33(7): 8-12. [陈甲斌, 霍文敏, 李秀芬, 等. 中国与美国和欧盟稀土资源形势对比分析[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2020, 33(7): 8-12.]
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
Yan H S, Liang T M, Liu Q S, et al. Compound leaching behavior and regularity of ionic rare earth ore[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 333: 106-114. DOI:10.1016/j.powtec.2018.04.010
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
Xiao Y F, Gao G H, Huang L, et al. A discussion on the leaching process of the ion-adsorption type rare earth ore with the electrical double layer model[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 120: 35-43. DOI:10.1016/j.mineng.2018.02.015
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
Wang J P, Huang J, Wang H J. Problems and Countermeasures in Mining Technology of Ionic Rare Earth Ore (In Chinese)[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2019(11): 231-232. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1667.2019.11.143 [汪江萍, 黄金, 王慧娟. 离子型稀土矿开采工艺存在的问题与对策[J]. 中国金属通报, 2019(11): 231-232.]
(  0) 0) |
| [9] |
Yin S H, Pei J N, Jiang F, et al. Ultrasound-assisted leaching of rare earths from the weathered crust elution-deposited ore using magnesium sulfate without ammonia-nitrogen pollution[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2018, 41: 156-162. DOI:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.09.028
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
Zhao Y H, Zhang T, Cheng X X. Advance of ammonia nitrogen pollution and control techniques for soil and water environment in ion-adsorption rare earth mines (In Chinese)[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2020, 41(1): 124-132. [赵永红, 张涛, 成先雄. 离子吸附型稀土矿区土壤与水环境氨氮污染及防治技术研究进展[J]. 稀土, 2020, 41(1): 124-132.]
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
Guo Z Q, Zhao K, Jin J F, et al. Reviews on environmental assessment and pollution prevention of ion adsorption type rare earth ores (In Chinese)[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2019, 40(3): 115-126. [郭钟群, 赵奎, 金解放, 等. 离子型稀土矿环境风险评估及污染治理研究进展[J]. 稀土, 2019, 40(3): 115-126.]
(  0) 0) |
| [12] |
Li C. The generalization and application of new technology on lixiviating mineral at the original place for ionic rare earths (In Chinese)[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2011, 2(1): 63-67. [李春. 原地浸矿新工艺在离子型稀土矿的推广应用[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2011, 2(1): 63-67.]
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
Zheng W Q, He Y, Sun P. Study on the in situ leaching mining method in application of main parameter setting problems of weathering crust ion adsorption type rare earth deposit (In Chinese)[J]. Southern Metals, 2015(5): 40-43. [郑伟强, 贺义, 孙鹏. 原地浸矿采矿法在风化壳离子吸附型稀土矿床应用中主要参数设定问题的研究[J]. 南方金属, 2015(5): 40-43.]
(  0) 0) |
| [14] |
Li G, Zhu Z C, Liang J, et al. Industrial experimental study on in situ leaching of a rare earth ore (In Chinese)[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019(21): 268, 270. [李刚, 朱志成, 梁健, 等. 某稀土矿原地浸矿工业试验研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019(21): 268, 270.]
(  0) 0) |
| [15] |
Liu F, Wu L L. Study on the characteristics of plant community in the unmined area of rare earth mine in Longnan (In Chinese)[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(S2): 138-140. [刘芳, 吴亮亮. 赣州龙南稀土矿场未开采区植被群落特征研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(S2): 138-140.]
(  0) 0) |
| [16] |
Ma G X, Zhu W Q, Wang X J, et al. Evaluation of ecological and environmental cost of rare earth resource exploitation in China from 2001 to 2013 (In Chinese)[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(7): 1087-1099. [马国霞, 朱文泉, 王晓君, 等. 2001-2013年我国稀土资源开发生态环境成本评估[J]. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(7): 1087-1099.]
(  0) 0) |
| [17] |
Liu W S, Liu C, Wang Z W, et al. Limiting factors for restoration of dumping sites of ionic rare earth mine tailings (In Chinese)[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(4): 879-887. [刘文深, 刘畅, 王志威, 等. 离子型稀土矿尾砂地植被恢复障碍因子研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(4): 879-887.]
(  0) 0) |
| [18] |
Ren F T, Zhang Q Y, Yang G, et al. Characteristics of ammonium nitrogen pollution in deep soil profile of ionic rare earth ore tailings and influencing factors (In Chinese)[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021. DOI:10.11766/trxb20200619031 [任富天, 张秋英, 杨广, 等. 离子型稀土尾矿深层土壤剖面铵态氮污染特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2021.]
(  0) 0) |
| [19] |
Tu T, Wang Y, An D, et al. Present situation, hazard and treatment technology of groundwater pollution in rare earth mining area of southern Jiangxi (In Chinese)[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2017, 7(6): 691-699. [涂婷, 王月, 安达, 等. 赣南稀土矿区地下水污染现状、危害及处理技术与展望[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2017, 7(6): 691-699.]
(  0) 0) |
| [20] |
Liu J, Li Z. The treatment technology of ammonia- nitrogen wastewater and its development (In Chinese)[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2007, 27(4): 54-60. [刘健, 李哲. 氨氮废水的处理技术及发展[J]. 矿冶工程, 2007, 27(4): 54-60.]
(  0) 0) |
| [21] |
自然资源部. 自然资源部关于进一步规范稀土矿钨矿矿业权审批管理的通知[M]. 2018. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Notice of the Ministry of Natural Resources on further regulating the approval and administration of the mining rights of rare earth tungsten mines[M]. 2018. (  0) 0) |
| [22] |
国土资源部. 国土资源部关于下达2014年度稀土矿钨矿开采总量控制指标的通知[M]. 2014. Ministry of Land and Resources. Notice of the Ministry of Land and Resources on issuing the total control index for rare earth mines and tungsten mines in 2014[M]. 2014. (  0) 0) |
| [23] |
Fan X, Xue Q, Liu S W, et al. The influence of soil particle size distribution and clay minerals on ammonium nitrogen in weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth tailing[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111663.
(  0) 0) |
| [24] |
Yang S, Xue Q, Chen H H. Enhanced recovery of water due to ammonia nitrogen contamination caused by mining processes[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(14): 1-9.
(  0) 0) |
| [25] |
郑先坤. 离子型稀土原地浸矿废弃地中残存浸取剂与稀土的垂直分布规律研究[D]. 江西赣州: 江西理工大学, 2019. Zheng X K. Vertical distribution of residual leaching agent and rare earth in in situ leaching wasteland of ionic rare earth[D]. Ganzhou, China: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2019. (  0) 0) |
| [26] |
Lu H Z, Cao L X, Liang Y, et al. Mineral-leaching chemical transport with runoff and sediment from severely eroded rare-earth tailings in Southern China[J]. Solid Earth, 2017, 8(4): 845-855.
(  0) 0) |
| [27] |
Qie H M, Wen B Y, Wang J Q, et al. Safety evaluation of heavy metal contents in selenium-rich soil in the Zishan area, Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province (In Chinese)[J]. East China Geology, 2017, 38(3): 234-240. [郄海满, 文帮勇, 王继强, 等. 江西赣州梓山地区富硒土壤重金属元素安全性评价[J]. 华东地质, 2017, 38(3): 234-240.]
(  0) 0) |
| [28] |
吴澄宇. 赣南粤北地区风化壳离子吸附型稀土矿床研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 1988. Wu C Y. The study of ion-adsorbed type of rare earth deposits in weathering crust from south Jiangxi and north Guangdong provinces[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1988. (  0) 0) |
| [29] |
Xiong T W, Jiang F, Qi S H. Remote sensing dynamic monitoring on rare earth mining area and its vegetation restoration of 6 counties in southern Jiangxi (In Chinese)[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2018(1): 40-44. [熊恬苇, 江丰, 齐述华. 赣南6县稀土矿区分布及其植被恢复的遥感动态监测[J]. 中国水土保持, 2018(1): 40-44.]
(  0) 0) |
| [30] |
郭强. 土地利用变化对赣江流域水文过程的影响分析[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020. Guo Q. Impact of land use change on hydrological processes in Ganjiang River basin[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2020. (  0) 0) |
| [31] |
温春云. 稀土尾矿化学污染物空间分布及治理效果研究[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2013. Wen C Y. The research on the spatial distirbution and treatment effect of chemical contaminants in rare earth tailings[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2013. (  0) 0) |
| [32] |
Zhang G L, Gong Z T. Soil survey laboratory methods (In Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 2012. [张甘霖, 龚子同. 土壤调查实验室分析方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.]
(  0) 0) |
| [33] |
Wu H Y, Song X D, Zhao X R, et al. Accumulation of nitrate and dissolved organic nitrogen at depth in a red soil Critical Zone[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 337: 1175-1185.
(  0) 0) |
| [34] |
Gao Z Q, Zhou Q X. Contamination from rare earth ore strip mining and its impacts on resources and eco-environment (In Chinese)[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(12): 2915-2922. [高志强, 周启星. 稀土矿露天开采过程的污染及对资源和生态环境的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(12): 2915-2922.]
(  0) 0) |
| [35] |
Li D C, Huang J, Ma C B, et al. Soil organic matter content and its relationship with pH and bulk density in agricultural areas of China (In Chinese)[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(6): 252-258. [李冬初, 黄晶, 马常宝, 等. 中国农耕区土壤有机质含量及其与酸碱度和容重关系[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(6): 252-258.]
(  0) 0) |
| [36] |
李宇, 梁音, 曹龙熹, 等. 离子型稀土矿区小流域氨氮污染物地表迁移特征研究[J]. 土壤, 待刊 Li Y, Liang Y, Cao L X, et al. The transport of ammonia nitrogen pollutant in an ionic rare earth mining small watershed[J]. Soils, Accepted. (  0) 0) |
| [37] |
Zhang J, Cai Z, Müller C. Terrestrial N cycling associated with climate and plant-specific N preferences: A review[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 69(3): 488-501.
(  0) 0) |
| [38] |
李慧. 氨氮在黄土包气带中吸附解吸特征和影响因素探讨[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014. Li H. The characteristic and influence factors of ammonia-nitrogen adsorption desorption in the loess[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2014. (  0) 0) |
| [39] |
Di H J, Cameron K C, McLaren R G. Isotopic dilution methods to determine the gross transformation rates of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur in soil: A review of the theory, methodologies, and limitations[J]. Soil Research, 2000, 38(1): 213.
(  0) 0) |
| [40] |
Taylor A A, De-Felice J, Havill D C. Seasonal variation in nitrogen availability and utilisation in an acidic and calcareous soil[J]. New Phytologist, 1982, 92: 141-152.
(  0) 0) |
| [41] |
Li Q, Zhou L B, Zhu Y B, et al. Prediction method for ammonia nitrogen pollution in the soil of ionic rare earth mine (In Chinese)[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2017, 39(6): 56-59. [李青, 周连碧, 祝怡斌, 等. 离子型稀土矿山土壤氨氮污染预测[J]. 环境影响评价, 2017, 39(6): 56-59.]
(  0) 0) |
 2023, Vol. 60
2023, Vol. 60


