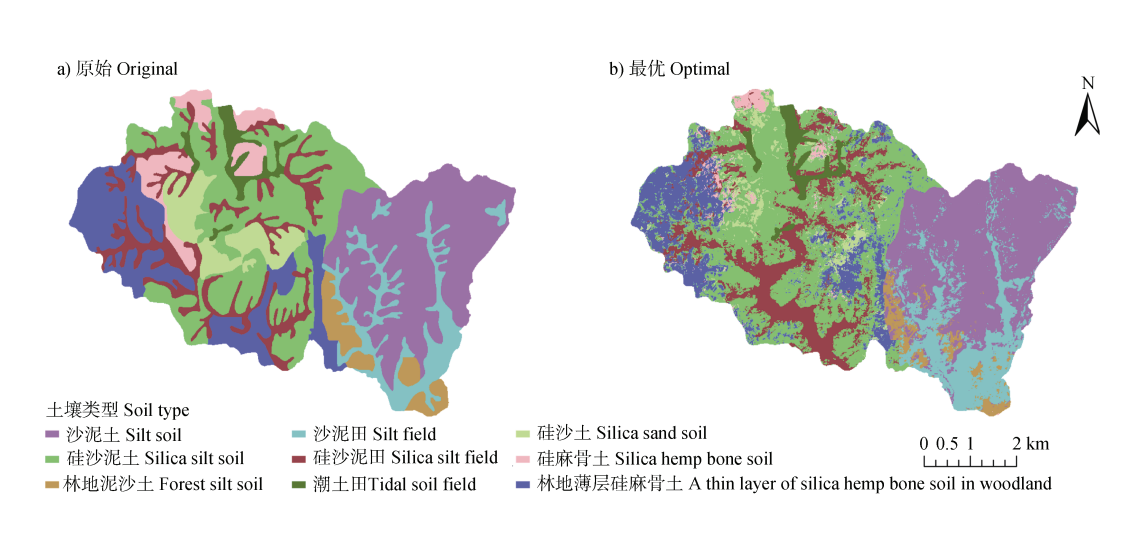
Comparison of Digital Soil Mapping Methods in Plain and Hill Mixed Regions
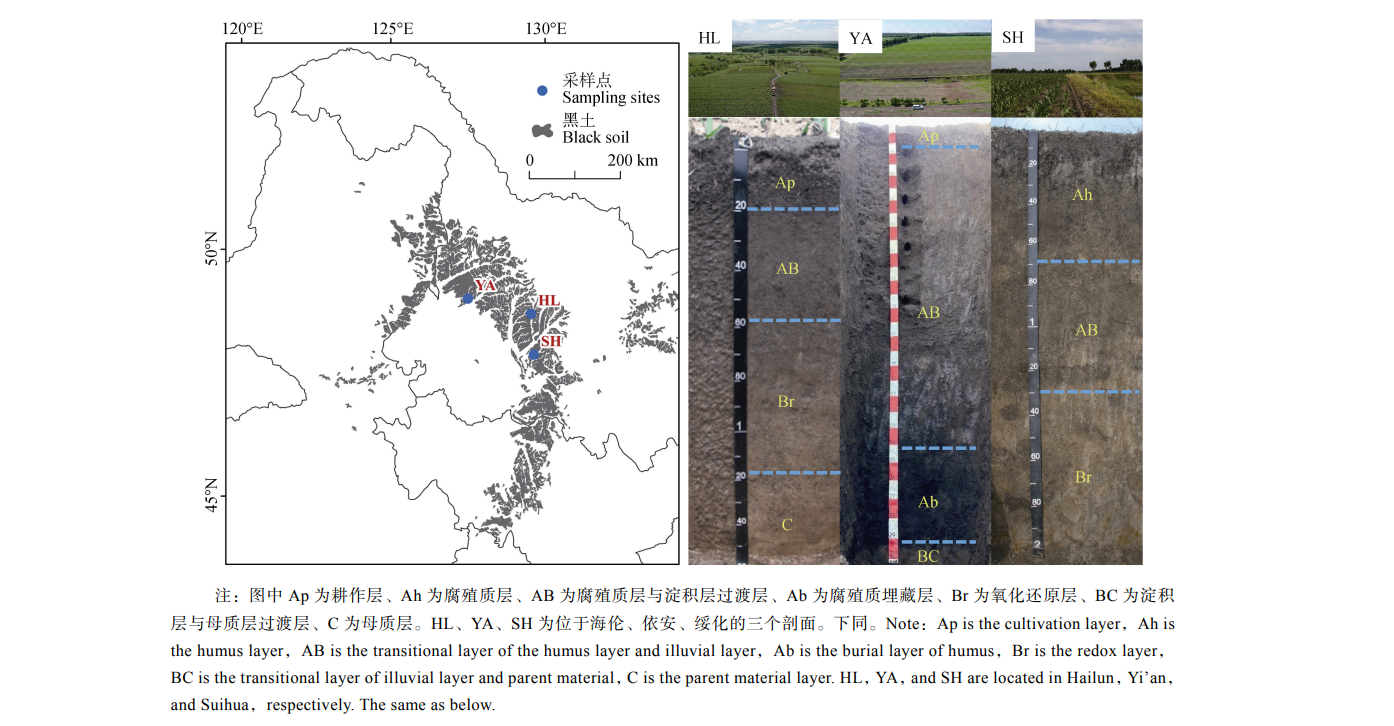
Distribution Characteristics of n-Alkanes and Compound-specific Carbon Isotopes in Black Soil of Songnen Plain and Their Implications
Effects of Sustained Low Level Organic Fertiliser and Chemical Fertiliser Blending on Soil Fertility and Multifunctionality in Oasis Farmland
Effects of Bacterial Residue Organic Fertilizer on Tomato Growth and Soil Antibiotic Resistance Genes Accumulation
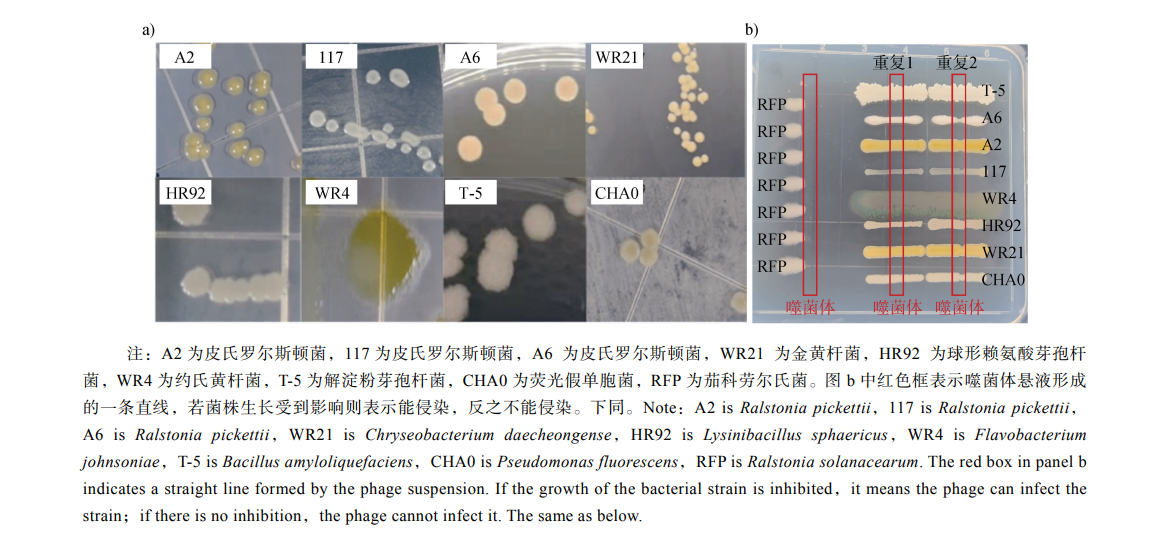
The Synergistic Effect of a Phage-Probiotic Combination on Suppressing Bacterial Wilt Disease
- Comparison of Digital Soil Mapping Methods in Plain and Hill Mixed Regions
- Distribution Characteristics of n-Alkanes and Compound-specific Carbon Isotopes in Black Soil of Songnen Plain and Their Implications
- Effects of Sustained Low Level Organic Fertiliser and Chemical Fertiliser Blending on Soil Fertility and Multifunctionality in Oasis Farmland
- Effects of Bacterial Residue Organic Fertilizer on Tomato Growth and Soil Antibiotic Resistance Genes Accumulation
- The Synergistic Effect of a Phage-Probiotic Combination on Suppressing Bacterial Wilt Disease
- Current Discuss
- First Published
- Album Paper
- Browser
-
Reconstructing the Micro-ecological Health of Arable Soil: Insights from Organic Co-Contamination Scenarios
HE Yan, LI Shuyao, YANG Xueling, SU Xin, LIU Meng, XU Jianming
2026,63(1):1-10, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506220299
Abstract:
The escalating organic co-contamination in arable soils poses a severe threat to soil microecological health and sustainable agricultural development, presenting an urgent challenge to synergistically enhance cropland productivity and maintain microecological function. This review systematically summarizes the ubiquity, complexity, and microecological risks associated with organic co-contamination in cultivated lands, delving into the significant challenges and opportunities for reconstructing the health of cropland soil microbiomes under such stress. Given the limitations of traditional remediation methods, which are often insufficient and costly for complex co-contamination, a frontier strategy is needed. Emphasis is particularly placed on the application potential of modern molecular biology techniques, specifically synthetic microbiomes (SynMicro), in restoring the health of contaminated soil microbiomes. The review elucidates cutting-edge strategies for constructing functionally defined and structurally simplified synthetic microbial communities by integrating advanced techniques including metagenomics (to understand community structure and potential function), culturomics and high-throughput screening (to accelerate the isolation of functional microbial resources), genome-scale metabolic modeling (to enable rational design and prediction of microbial interactions), and artificial intelligence/machine learning (to facilitate intelligent design and optimization of SynMicro consortia). This work forecasts the promising prospects of SynMicro engineering in achieving synergistic multiple objectives critical for soil health reconstruction under co-contamination, such as enhanced pollutant reduction, effective soil-borne disease control, and improved soil fertility through optimized nutrient cycling. By highlighting the potential of SynMicro-based strategies empowered by these frontier technologies and outlining the current challenges, this review aims to provide novel theoretical insights and practical technical pathways for the reconstruction of cropland soil microecological health, ultimately contributing to ensuring national food security and promoting sustainable agricultural development.
-
Effects of Atom/Ion Orbital Hybridization at the Soil Solid-Liquid Interfaces and Their Environmental Implications
LIU Xinmin, TANG Yuting, HU Feinan, TANG Ying, DU Wei, DING Wuquan, LI Hang
2026,63(1):11-24, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506230301
Abstract:
Soil is a unique “quantum mechanics” system, and significant orbital hybridization effects occur at soil solid-liquid interfaces. Orbital hybridization effects play a critical regulatory role in soil properties, processes, and functions. However, this concept has not been given much attention in the context of soil solid-liquid interfaces. In the present study, the structure and properties of soil solid-liquid interfaces were quantitatively described based on classical interfacial reaction theory, and atom/ion orbital hybridization in the electric field at the soil particle surfaces as well as its influence on ion-particle and particle-particle interactions were characterized. The intrinsic correlation and regulatory pathways were elucidated for different soil environmental processes, such as mineral weathering, soil acidification, heavy metal passivation/activation, soil water movement, and phosphorus transport. They reveal a multi-scale coupling and multi-process linkage mechanism spanning: subatomic orbital hybridization effects → microscale interfacial reactions → mesoscale soil particle interactions → macroscale soil processes and functions. This cross-scale research framework provides a crucial theoretical foundation for advancing soil system functionality, enhancing cultivated land quality, and strengthening agricultural environmental protection. The atom/ion orbital hybridization effects at the soil solid-liquid interfaces fundamentally arise from the interactions between the electric field and atoms. Future researches should prioritize advancements in the following domains: 1) Synergistic integration of modern analytical techniques and quantum mechanical theories to elucidate surface reaction mechanisms governed by orbital hybridization; 2) Development of precise predictive models for water-soil-solute transport dynamics; 3) Revealing multiscale coupling mechanisms between microscopic soil processes and macroscopic manifestations; and 4) Establishing a quantum mechanics-based core theoretical framework for soil science.
-
Research Progress on the Application of Synchrotron Radiation-Related Analytical Techniques in Soil Chemistry
CUI Chengyang, ZHANG Wannian, WANG Cheng, WAN Biao, WANG Xiaoming, YIN Hui, TAN Wenfeng, FENG Xionghan
2026,63(1):25-41, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507150347
Abstract:
Soil chemistry has developed rapidly over the past few decades and has formed a relatively complete theoretical system and technical system. Scientific apparatus represented by synchrotron radiation sources are playing an increasingly important role in the research of soil chemistry. The related technologies based on synchrotron radiation, with their unique advantages, can conduct in-situ analysis on the cycling of elements and substances in complex environments at the molecular level, providing more comprehensive technical support for the research covered by soil chemistry, such as soil mineral chemistry, soil organic chemistry, soil inorganic nutrient chemistry and soil pollution chemistry. Significant advances have been made in several areas, including the identification of poorly crystalline minerals, the structural and spatial resolution of organo(metal)-mineral complexes, and the characterization of the morphology and spatial distribution of heavy metals. In recent years, the combination of synchrotron radiation with other spectral and imaging techniques has been increasingly applied in soil research, greatly promoting the development of geochemistry. In this paper, it has been reviewed the progress made in the field of soil chemistry by related technologies based on synchrotron radiation sources and other combined technologies. Finally, prospects for the development of synchrotron radiation sources, for the further integration of complementary techniques, and for the application of related technologies based on synchrotron radiation to the actual soil environment are proposed.
-
Elimination of Organic Pollutants in Soil Basing on Synthetic Microbiome
WU Yiming, ZHANG Youai, XU Xihui, JIANG Jiandong, GAO Yanzheng
2026,63(1):42-52, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506230304
Abstract:
Polluted soils typically harbor a complex and widespread array of organic contaminants that seriously endanger ecological security and public health. The utilization of the microbiome to degrade organic pollutants in soil is regarded as a green, safe and cost-effective technique. Comparing with the traditional single-strain method, the bioremediation method based on the synthetic microbiome has obvious advantages. However, this method still has some problems and challenges concerning with the complex soil contamination with multiple organic pollutants. An in-depth investigation of the process and mechanism of the organic pollutant elimination in soil using synthetic microbiomes has become a research hotspot in bioremediation. This paper reviews the advantages and problems encountered in applying synthetic microbiomes to eliminate organic pollutants in soil, clarifies the methods for designing and constructing microbiomes for organic pollutant degradation, and analyzes the role and mechanism of synthetic microbiomes in eliminating soil organic pollutants. currently, synthetic microbiome is still at its early stage in the field of soil bioremediation, with more crucial data being needed. Future efforts must intensify research into synthetic-microbiome optimization, the combined use of synthetic microbiomes with other organisms, and multidisciplinary integration and technological innovation, thereby providing a robust foundation for developing safe, efficient, and feasible biological strategies for the remediation of soil organic pollution.
-
Research Progress on Soil Carbon Sequestration by Biochar
SUN Jiajing, HE Yuxiao, CHEN Yalan, SUN Ke
2026,63(1):53-64, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506250307
Abstract:
Soil is the largest organic carbon reservoir in terrestrial ecosystems. It serves as both a carbon source and a carbon sink and plays a critical role in achieving carbon neutrality goals. Biochar, a carbon-rich material, is produced by thermally cracking waste biomass or organic matter under oxygen-limited conditions. Due to its significant carbon sequestration effects and stability, biochar has become an important technical tool for improving and sequestering soil carbon. This review systematically elucidates the mechanisms of soil carbon sequestration mediated by biochar. It focuses on how the characteristics of the raw material(source, composition, and structure), the parameters of its preparation(pyrolysis temperature), and the conditions of its application(dose and duration of action) influence the efficacy of soil carbon sequestration. The review also analyzes the regulatory effects of environmental factors, such as nitrogen addition/deposition, temperature gradients, and soil texture, on biochar-mediated soil carbon sequestration. Based on the current state of research, future studies should focus on the dynamic response mechanisms of subsoil carbon pools, the evolution patterns of carbon stability under long-term application, and the interactive effects between biochar and inorganic carbon pools. This will provide the necessary theoretical support for developing a carbon-neutral application system based on biochar technology.
-
Research Progress on Multidimensional Ecological Functional Compensation and Metabolic Regulation of Soil Environmental Virome
YAO Keyu, CHEN Lin, ZHU Dong, MA Bin, CHEN Linxing, ZHOU Zhichao, LIU Peng, JIANG Xin, YE Mao
2026,63(1):65-75, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505300249
Abstract:
Soil viruses act as indispensable and invisible regulators in ecosystems, profoundly influencing virus-host interactions and soil health by encoding diverse auxiliary metabolic genes. Through key processes such as lysing host bacteria to release nutrients, facilitating the horizontal transfer of functional genes, and regulating microbial community structure and metabolic activities, they serve as critical drivers of functional succession and stability maintenance in soil ecosystems. This review systematically summarizes the multifaceted roles of soil viruses, including their contributions to nutrient compensation and elemental cycling (e.g., carbon fixation, nitrogen fixation, sulfur cycling, and phosphorus metabolism), improvement of the ecological environment (such as pH regulation and remediation of saline-alkali land), assistance in pollutant degradation, promotion of plant health, control of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and indirect modulation of human health. Furthermore, the paper highlights limitations in current research, such as the lack of in-depth functional analysis tools and methods, as well as insufficient coverage of diverse habitats. Future studies should focus on exploring viral genetic resources and promoting their safe and efficient engineered applications, so as to provide innovative solutions for sustainable agricultural development and environmental pollution remediation.
-
Occurrence Characteristics and Ecological Risk of Estrogens in Agricultural Soil Amended with Manure Fertilizer
WANG Junyue, ZHANG Zikang, CHEN Yang, LING Wanting
2026,63(1):76-85, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506230305
Abstract:
【Objective】 This study aimed to investigate the occurrence characteristics and ecological risks of manure-based fertilizer estrogens(estradiol [E2], estriol [E3], and bisphenol A [BPA])in different soil types(yellow-brown soil, brown soil, black soil, and red soil)in China. The research sought to elucidate the influence of soil physicochemical properties on estrogen speciation, degradation, and bioavailability, and to establish a framework for optimizing ecological risk models. 【Method】 Four representative agricultural soils were collected, air-dried, and sieved. Cattle manure containing E2(356.91 ± 0.27 μg·kg–¹), E3(227.58 ± 1.18 μg·kg–¹), and BPA(862.21 ± 0.42 μg·kg–¹)was mixed with soils at a 1: 10 ratio(manure: soil)and incubated for 0–60 d under controlled conditions. Estrogen speciation (organic solvent-extractable, water-soluble, humic acid-bound, and humin-bound forms) was quantified using sequential extraction and HPLC analysis. Soil properties(pH, organic matter, cation exchange capacity, etc.) were measured via standardized methods. Ecological risks were evaluated using risk quotients (RQ) based on predicted no-effect concentrations (PNEC) and estrogen equivalency (EEQ) models. 【Result】 The result revealed that soil type significantly influenced estrogen dynamics. Black soil, with high organic matter (59.73 g·kg–¹), exhibited the highest bound-state retention (humic acid-bound BPA: 33.92 μg·kg–1; bound-state total 17β-E2 equivalent: 11.35 μg·kg–¹), leading to low short-term risks (E2 RQ = 0.086)but potential long-term risks due to delayed release. In contrast, red soil, with low organic content (8.25 g·kg–¹) and acidic pH(5.02), showed elevated extractable state proportion, resulting in high immediate risks (E2 RQ=1.78; BPA RQ=0.73) despite faster degradation(only 6.63%, 6.36% and 1.76% extractable state of E2, E3 and BPA were transferred by day 60 respectively). In both yellow-brown soils and brown soils, the three target estrogens predominantly existed in bound states by day 60 of aging. E2 and E3 underwent significantly more biodegradation than BPA, while environmental risks were primarily contributed by E2 and BPA, presenting medium-to-high risk levels. Correlation analysis revealed extractable state estrogen content was negatively associated with pH and positively linked to organic matter(P<0.01). 【Conclusion】 This study highlights the critical role of soil-specific properties in modulating estrogen speciation and ecological risks. High-organic soils favored bound-state retention, delaying risks, while low-organic acidic soils amplified extractable state bioavailability, necessitating urgent mitigation. Current risk models, which prioritize extractable state concentrations, underestimate long-term hazards from bound-state reservoirs. The findings advocate for integrating speciation dynamics and soil heterogeneity into risk analysis to enable precision management of estrogen contamination in agricultural systems. This approach supports the transition from "total concentration control" to "speciation-targeted mitigation" for sustainable soil health and food safety.
-
The Mechanism of Micro-aerobic Habitat Alteration in Controlling Rice Cadmium and Phenanthrene Uptake
ZHANG Qiming, WU Chen, YI Shengwei, CHEN Mingjie, PENG Guanwei, WU Michuan, XIE Yunhe, WU Yujun, LI Feng
2026,63(1):86-96, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506220298
Abstract:
【Objective】The unique micro-oxygen environment of the rice rhizosphere constitutes a critical hotspot that governs the transport and transformation of pollutants. However, the chemical-microbial mechanisms for absorbing cadmium (Cd) and phenanthrene uptake by manipulation of the rhizosphere micro-oxygen environment are still unclear. 【Method】This study conducted a pot experiment using the mid-season rice cultivar 'Huanghuazhan'. The dissolved oxygen content in the rhizosphere was elevated by inserting plastic droppers to investigate the mechanisms by which this modulated micro-oxygen environment inhibits the uptake of Cd and phenanthrene in rice. 【Result】The results indicated that the increased rhizospheric oxygen content (up to 1.7-fold) led to reductions in the accumulation of Cd (24.2%–61.1%) and phenanthrene (26.1%–50.6%) in rice. First, the increased oxygen content in the rice rhizosphere promoted the formation of Amorphous Ferric Iron Phosphate (AFIP-Fe) on the root surface (up to a 1.5-fold increase). This enhancement thereby strengthened the adsorption and sequestration of Cd and phenanthrene, constructing a root barrier that effectively impeded pollutant uptake. Secondly, the aerobic environment reshaped the rhizospheric microbial community structure, forming a functional microbiota dominated by core functional flora such as Sphingomonas sp. and Mycobacterium sp. Consequently, the abundance of genes related to Cd resistance and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) degradation increased by 2.2 to 5.6-fold, which enhanced the microbial-mediated bio-immobilization of Cd and the biodegradation of phenanthrene. Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that dissolved oxygen was the key environmental factor driving microbial community succession and influencing the forms of pollutants. 【Conclusion】In conclusion, this study confirms that improving the micro-oxygen environment promotes the formation of root iron plaque and functional rhizosphere microbiota, which synergistically acted to inhibit the uptake of Cd and phenanthrene in rice. These findings provide a novel theoretical basis and a potential technical approach for the safe utilization of contaminated farmland.
-
Study of Soil Ecological Safety Threshold Values of Copper, Zinc, Lead and Cadmium
WU Tongliang, HUANG Yihang, QI Haitao, DING Changfeng, FAN Tingting, LIU Cun, ZHOU Dongmei, CHEN Huaiman, WANG Yujun
2026,63(1):97-109, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506220297
Abstract:
【Objective】Establishing ecology-based soil heavy metal thresholds is critical for accurately assessing regional ecological quality, managing contaminated sites effectively, and promoting the sustainable development of soil ecosystems. This study aims to derive such thresholds for copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), and cadmium (Cd) under different land use patterns by integrating extensive ecotoxicological data and accounting for key soil properties.【Method】It was systematically compiled and screened ecotoxicological data, yielding 118, 123, 61, and 100 valid entries for Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd, respectively. The dataset covered 29 terrestrial plant species, 4 terrestrial invertebrate species, and 10 soil ecological process indicators, with accompanying soil properties including pH, clay content (CL), organic matter (OM), and cation exchange capacity (CEC). The data were normalized, accounting for aging-leaching effects and soil property influences. Predictive models for 10% effect concentration (EC10) were developed based on soil properties. Species sensitivity distribution (SSD) was applied using weighted average models derived from multiple best-fitting distribution functions to reduce uncertainty related to reliance on a single distribution. 【Result】The result revealed that (1) Soil pH was the primary factor influencing the ecotoxicity of the heavy metals, with significantly higher thresholds observed in alkaline soils compared to acidic soils. (2) The order of ecotoxicity was Cd >> Cu > Zn > Pb. (3) Thresholds varied substantially across land use types: agricultural land and protected natural areas showed the lowest thresholds, reflecting the strictest ecological protection requirements. However, park and residential lands presented intermediate values, while commercial & service and industrial & mining lands had the highest thresholds. (4) The derived ecological thresholds based on land use and pH-specific categories differed notably from current standards in Europe and the United States, mainly due to differences in derivation methods, ecological receptor coverage, protection levels, and incorporation of soil properties. 【Conclusion】This study compiled extensive ecotoxicological data for Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd and developed toxicity threshold prediction models incorporating key soil properties (pH, CL, OM, CEC) following aging-leaching normalization and soil property normalization. The results provide a scientifically supported and practical framework for refining soil environmental quality standards and support differentiated ecological risk management based on land use and soil properties.
-
Mechanism of Humic Acid Regulated Fe(II)-Induced Ferrihydrite Transformation and Its Impact on Cadmium Sequestration
LIANG Bin, LIU Fu, ZHU Runliang, XING Jieqi, ZHANG Yekun, XIAO Zhifang, YE Qianting, WANG Wenxia, SHI Zhenqing
2026,63(1):110-119, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506230300
Abstract:
【Objective】Iron oxides play a pivotal role in the migration of heavy metals in natural environments, with humic acid (HA), a major organic component in soils and water bodies, potentially exerting significant regulatory effects on these processes. This study aims to systematically investigate the transformation kinetics of ferrihydrite (Fh) into crystalline iron oxides (lepidocrocite Lp, goethite Gt, and magnetite Mt)and its impact on cadmium (Cd) sequestration.【Method】Using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) coupled with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), this study conducted a controlled experiment involving Fh-Cd (control) and Fh-HA-Cd systems. Fe(II) was introduced as a catalyst to initiate the transformation, which was monitored over 168 h. The study examined the effects of HA (initial concentration 4.94 mmolŸL–1) and Cd (initial concentration 88.29–94.27 μmolŸL–1)on mineral phase evolution, Cd adsorption, and retention mechanisms. 【Result】The results revealed that in the Fh-Cd system, Lp (48.08%) and Gt (43.49%) formed rapidly within 6 h, with Lp continuing to transform into Gt by 120 h, and a small amount of Mt (4.82%) emerging by 168 h. In contrast, in the Fh-HA-Cd system, HA significantly inhibited the transformation rate, resulting in slower formation of Lp and Gt, with a final mineral composition at 168 h of Fh (2.63%), Lp (42.79%), and Gt (54.6%), and no detectable Mt. During the transformation, the solid-phase HA concentration decreased from 4.94 mmolŸL–1 to 4.49 mmolŸL–1, and Cd concentration in the solid phase dropped sharply after 6 h before stabilizing, with the Fh-HA-Cd system exhibiting 5%–10% higher solid-phase Cd than the Fh-Cd system. TEM-high angle annular dark field and EDS analyses showed that C and Cd were initially closely associated with Fh; post-transformation, Lp and Gt retained strong Cd adsorption but exhibited significantly reduced C adsorption. EELS line scans further indicated that C was primarily retained on Fh surfaces and within defects/porosities of Lp, with carbon functional groups (C-H, C=O, C-OH) desorbing during transformation, while Cd was retained through multiple mechanisms including adsorption, structural substitution, and physical encapsulation in the newly formed iron oxides.【Conclusion】This study demonstrates that HA significantly influences Cd’s geochemical behavior by suppressing iron oxide transformation and enhancing Cd adsorption. These findings provide valuable scientific insights into the interaction mechanisms among iron oxides, organic matter, and heavy metals, offering a theoretical basis for understanding and managing Cd contamination in natural systems.
-
Effects of Warming and Nitrogen Addition on Soil Phosphorus Bioavailability in China’s Mountains:Research Progress and Prospects
BING Haijian, Lü Jingyi, WU Yanhong, FANG Linchuan
2026,63(1):120-134, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411200447
Abstract:
Phosphorus (P) is a critical limiting nutrient in terrestrial ecosystems, and its bioavailability in soils is particularly important in influencing primary productivity and ecosystem carbon sequestration capacity. Mountain ecosystems are highly sensitive to climate changes and exhibit distinct responses to alterations in environmental conditions. The P bioavailability in mountain soils is thus a popular topic in ecological and environmental research, especially in the context of climate warming and increased atmospheric nitrogen (N) deposition. This review integrated a Meta-analysis method to synthesize findings of the response patterns and underlying mechanisms of soil P bioavailability to in situ simulated warming and N addition experiments in China’s mountain soils. This study found that single treatment of warming or nitrogen addition did not reduce the bioavailability of soil P, although there were still debates that were closely related to the initial environmental conditions of different ecosystems. Furthermore, the prospects of future research were provided, underscoring the necessity for long-term and multi-elevation in situ simulation experiments. These experiments are vital for understanding the variations in soil P bioavailability under the dual pressures of warming and N inputs. It is also essential to conduct controlled laboratory experiments to explore the effects of these factors on the transformation of soil P fractions across multiple spatial scales, such as landscape and ecosystem levels. Also, the molecular-level response mechanisms of soil P bioavailability to various climate change factors require further investigation. Additionally, there is a need to optimize the parameters in the P biogeochemical cycling models for predicting the effects of climate warming and varied atmospheric N deposition on soil P bioavailability in mountain ecosystems. These potential results will contribute to a far-reaching understanding of the processes and mechanisms of P biogeochemical cycling in mountains in the context of global climate change, which can become an important theoretical basis for the health and stability of mountain ecosystems.
-
Research Progress on the Mechanism and Related Application of Soil Bio-driven Aggregates Formation and Stability
MA Zheng, LI Zhenlun, YANG Yuran, LI Jiabing, ZHANG Xinlei, YANG Luyao, GUO Ruiting
2026,63(1):135-150, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202407270307
Abstract:
Soil aggregates are an important component and basic unit of soil structure, and their stability is crucial for maintaining soil health and crop productivity. The formation and stability of aggregates are the result of the joint action of biological and non-biological factors, and soil organisms (microorganisms and animals) play a crucial role in this process. A thorough understanding of the relationship between soil organisms and the formation and stability of aggregates is of great theoretical significance in elucidating the process and mechanism of soil quality change. However, systematic summaries of the driving mechanisms and current application status of soil organisms in aggregate formation and stabilization are still lacking. This paper reviews the effects of soil microorganisms and animals on aggregate formation and stabilization and clarifies the aggregate formation process and stabilization mechanisms driven by soil organisms. The study discovers that microorganisms mediate aggregate formation and stabilization through their physical characteristics, secretion of adhesive substances, and decomposition of organic matter, while animals mediate aggregate formation and stabilization through biological disturbance and feeding. Furthermore, the current status of using soil organisms and their products to increase aggregate stability is analyzed, emphasizing the potential application of novel soil biological structural modifiers. In conclusion, prospective research directions are outlined for future investigations. Researchers should concentrate on the following areas: (1) The formation and stabilization mechanism of soil aggregates driven by soil organisms on multi-scale interface processes; (2) The composition and genetic regulation mechanism of microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP); (3) The influence mechanism of soil archaea and viruses on the formation and stability of aggregates; (4) The formation process and stabilization mechanism of aggregates mediated by soil food web; and (5) Development and application of biological soil structure improvers. This paper aims to provide both theoretical insights and technical guidance for maintaining and improving soil quality.
-
Review and Prospects for Ecological Risk Assessments of Soil Heavy Metals Using Diffusive Gradient in Thin-Films Technology
LI Danyang, LI Hanbing, CHEN Bo, ZHAO Xiaohui, LIANG Yixuan, CHEN Sha
2026,63(1):151-163, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411140439
Abstract:
Extensive human activities, including industrialization, intensive agriculture, and urban construction, coupled with the accelerated pace of socio-economic development, have significantly precipitated and caused a measurable surge in heavy metal concentrations in soil environments. This environmental issue severely degrades the quality of natural environments, thereby engendering substantial threats to human health and ecological safety. Conventional risk assessment techniques have focused on quantifying the total content of heavy metals in soils. However, such approaches are inherently limited to capturing critical insights into speciation changes and bioavailable concentrations, which are essential for accurate ecological risk assessment of heavy metals. In recent years, the diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) technique has emerged as an innovative and promising tool for in-situ measurement of heavy metals in soils. DGT is recognized for its stable performance with minimal disturbance to the surrounding natural environment in real-world applications. Based on Fick's first law, the DGT technique facilitates the analysis of gradient diffusion and buffering kinetics of target pollutants, thereby providing valuable data on their speciation and bioavailability in diverse environmental settings. Furthermore, the integration of the DGT technique with the DGT-induced fluxes in soil/sediments (DIFS) model significantly enhances its applicability, enabling detailed investigations into the dynamic behaviors of heavy metals within soil matrices. This study provides a comprehensive review of the current advancements and prospects of utilizing the DGT technique for soil heavy metal risk assessments. By examining the severity and urgency of heavy metal contamination in soils, the technical advantages of DGT as a precise assessment tool are delineated, and the necessity of its application is emphasized. Through a critical analysis, the principal environmental factors influencing the ecological risks associated with soil heavy metals are identified, including soil composition, pollutant characteristics, and external environmental conditions. Additionally, this study provides an in-depth overview of the DIFS model's role in visualizing the minute-scale dynamic behaviors of heavy metals under varying soil functional scenarios, highlighting the differences in ecological risks that may arise. In the concluding section, strategic recommendations for advancing DGT applications are outlined, focusing on improving the analytical criteria, enhancing the preparation of binding layer materials, facilitating multi-contaminant enrichment, and integrating multiple analytical techniques. These improvements are crucial for advancing the detection and quantification of heavy metals in complex environmental media. Potential directions for future research are also discussed to further expand the capabilities of DGT and DIFS in the context of soil pollution monitoring and ecological risk assessment.
-
Patent Analysis on the Mitigation of Cultivated Land Obstacles Caused by Salinization, Acidification and Soil Erosion
YUAN Jie, XU Lingying, WANG Xiang, ZHAO Yanqiang, CHEN Yuqi, ZHAO Xu
2026,63(1):164-178, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501230040
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil constraints, including salinization, acidification, and erosion, have evolved into pressing global environmental crises. Salinization, triggered by improper irrigation and inadequate drainage, causes salt accumulation in the soil, rendering it inhospitable for most crops. Acidification, mainly attributed to excessive use of chemical fertilizers and acid rain, disrupts the soil's pH balance, impeding plants' nutrient absorption. Erosion, aggravated by deforestation and climate change, strips away the fertile topsoil, significantly reducing soil productivity. These issues not only severely threaten food security by limiting crop yields but also degrade soil health, undermining the long - term sustainability of agriculture. Consequently, mitigating soil constraints has become a central concern for the agriculture, environmental science, and policy - making sectors.【Method】This study conducted a quantitative analysis of 3 996 global patents related to soil constraint mitigation technologies(as of 2024)using the authoritative IncoPat patent database. Patents sourced from various regions and periods were meticulously selected. The analysis delved into aspects such as patent filing dates, applicant locations, technological classifications, and types of innovation entities, with the aim of uncovering research and development trends, technological distributions, and the characteristics of different innovators in this field.【Result】The findings revealed that global patent applications exhibit a "three - phase growth pattern". Since 2015, China has taken the lead in innovation activities. Technological advancements are characterized by a "triple - core - driven" structure, with soil salinization reduction technology at its core. Specialized soil conditioners for constrained land, accounting for 42.8% of the total patents, and upgrades to mechanized equipment have emerged as major research hotspots. Enterprises and universities serve as the primary innovation entities, with enterprises focusing on practical applications and commercialization, while universities contribute to fundamental research and technological breakthroughs. To address future challenges, it is essential to enhance research and development in bioremediation technologies, promote interdisciplinary collaboration, establish an integrated "monitoring-governance-evaluation" technical framework, and develop tailored full-chain mitigation models for different soil constraints. Additionally, continuous efforts in the development of novel technologies, materials, and products are vital for safeguarding soil health and ensuring agricultural sustainability.【Conclusion】This study offers a comprehensive overview of the global landscape of soil constraint mitigation technologies through patent analysis. It underscores the urgent need for collective action to address soil constraints, given their far-reaching impact on food security and agriculture. The identified trends and hotspots provide valuable insights for researchers, enterprises, and policymakers to strategically allocate resources. As the global population continues to grow, future research should prioritize sustainable and innovative solutions. By leveraging the strengths of different innovation entities and promoting international collaboration, significant progress will be made in safeguarding soil health and ensuring the long-term viability of agricultural systems.
-
Effects of Biocrusts on Soil Detachment Process Across Different Lithology Development in Karst Regions
YANG Yuanfeng, YANG Lanhui, ZHANG Shiqin, SHI Jingqin, XU Jingben, TAN Yongshi, WANG fang, DENG Yusong
2026,63(1):179-194, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501160034
Abstract:
【Objective】 The southwestern karst region is characterized by both geological fragility and sensitivity, with soil erosion being a significant concern. Biological soil crusts, as widely developed surface coverings, play a crucial role in regulating soil erosion. However, the underlying mechanisms of how biocrust coverages at varying levels influence soil detachment control under different lithological conditions remain unclear. Therefore, it is essential to investigate the effects of different levels of biocrust coverages on the process of soil detachment and the main factors influencing this under varying lithological conditions in the southwestern karst region. 【Method】 In this study, we selected moss-dominated biocrusts developed on dolomite and clastic rock, with undisturbed soil serving as a control. Biocrust growth characteristics were determined in situ at five levels of moss coverages (1%~20%, 20%~40%, 40%~60%, 60%~80%, 80%~100%). The soil samples, including undisturbed soil and loose soil, were collected, and scouring experiments were conducted under different hydrodynamic erosion conditions (shear force of water flow ranging from 1.68 to 12.87 Pa). Quantitative relationships between moss coverages, growth characteristics, soil properties, soil detachment capacity, and rill erodibility were established. The differences in soil resistance to water erosion under moss coverage of different lithologies were analyzed, and the main controlling factors influencing soil detachment and erosion resistance were identified. 【Result】 The results indicate that: (1) The overall thickness and biomass of mosses on dolomite were significantly lower than those on clastic rock, while the roughness was the opposite. The thickness, roughness, and biomass of mosses increased with their coverage, following either a power function or exponential growth model, and soil properties were significantly affected by both lithology and moss development (P<0.05). (2) Moss coverages significantly affected soil detachment capacity and rill erodibility (P<0.05). The rill erodibility under moss coverages on dolomite decreased by 54.57%~99.98%, and on clastic rock by 69.11%~99.93%. (3) Regression analysis revealed that soil detachment capacity and rill erodibility in dolomite mosses were controlled by water-stable aggregates and mean weight diameter, while those in clastic rock mosses were controlled by water-stable aggregates. 【Conclusion】 In conclusion, the development of biocrusts significantly improves soil erosion resistance, with variations in water-stable aggregates and mean weight diameter caused by lithology being critical factors influencing soil erosion resistance. The results provide important scientific insights for ecological restoration and biological crust-based soil erosion prediction in the southwestern karst region.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research Hotspots and Trends in Grassland Soil Quality
ZHAO Wen, HUANG Laiming, SHAO Ming'an
2026,63(1):195-209, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412200499
Abstract:
【Objective】Grasslands cover approximately 40.5% of the Earth’s terrestrial surface and play a crucial role in maintaining the global carbon cycle and regulating climate change. However, with the intensification of human activity and the growing impacts of climate change, grassland ecosystems are experiencing varying degrees of degradation worldwide, leading to a decline in grassland soil quality. Although numerous studies have examined changes in grassland soil quality and their influencing factors across regions and over time, bibliometric analyses exploring the research trajectory and development trends in this field remain limited.【Method】To fill this gap, the present study conducted a bibliometric analysis of 8 089 articles published between 1990 and 2022 in the Science Citation Index Expanded database of Web of Science. The literature retrieval was based on the research topic “TS= (grassland) OR TS= (rangeland) OR TS = (meadow) OR TS = (savanna) OR TS = (steppe) OR TS = (prairie) OR TS = (pasture) OR TS = (grazing land) AND TS = (soil quality)”, and the retrieval period was set from January 1, 1990 to December 31, 2022. The analysis was conducted using the Bibliometrix package in R 3.6.3, VOSviewer 1.6.20, and CiteSpace 5.7.R1 software, focusing on annual publication trends, evolving research themes, international collaboration networks, core contributing authors, and leading journals. In addition, CiteSpace 5.7.R1 was used to perform co-citation analysis and thematic clustering on the 8 089 published articles. The results were visualized using ArcGIS 10.6 and Scimago Graphica 1.0.43.【Result】The results revealed that: (1) The total number of publications on “grassland soil quality” has steadily increased from 1990 to 2022, and the development of the field can be divided into three phases, including the initial stage (1990-2005), the rapid development stage (2006-2010), and the increasing maturity stage (2011-2022); (2) The research hotspots of “grassland soil quality” have shifted from “the impact of soil carbon on grassland soil quality” to “the effects of human activities on grassland soil quality”, and the focal research regions have shifted from “areas with sustainable livestock development and relatively high soil quality” to “areas with severe grassland degradation and poor soil quality”; (3) The grassland soil quality research predominantly encompasses establishing assessment indicator frameworks, analyzing driving factors or key processes, and clarifying assessment purposes and ecological significance. Currently, global studies of grassland soil quality have transitioned from analyzing spatio-temporal patterns to exploring the underlying microscopic mechanisms; (4) The United States and the People’s Republic of China hold leading positions in this field, with extensive global collaboration; (5) Richard D. Bardgett has the highest average citation frequency among researchers, Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment has the highest number of publications, while Soil Biology & Biochemistry is the most frequently cited journal. 【Conclusion】This study elucidates the historical development and current status of research on grassland soil quality, which provides data-driven support for advancing global research on grassland soil quality, enhancing regional grassland management practices, and improving the resilience of grassland ecosystems.
-
Research Trends and Quantitative Analysis of the Impact of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Soil Quality
MA Shijie, XUE Jiaxiang, HAN Ji, HU Fengnan, LAI Shuijing, KONG Zhaoyu, LIU Hongguang
2026,63(1):210-220, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411290457
Abstract:
【Objective】 Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) are important beneficial microorganisms in soil ecosystems, and their ecological functions have been extensively studied. However, a comprehensive evaluation on the impact of AMF on soil quality is still lacking. 【Method】 In this study, we conducted a bibliometric analysis using CiteSpace and a meta-analysis based on 4, 854 articles retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection from 2003 to 2023, aiming to systematically summarize the research progress on the effects of AMF on soil quality and to quantify their comprehensive effects on soil physicochemical and biological properties across different ecosystems and environmental conditions. 【Result】 The results revealed a steady increase in the number of publications over the past two decades, indicating growing research interest in this field. The top ten contributing countries in terms of publication size were China, the United States, India, Germany, Brazil, Australia, Spain, Canada, Italy, and France. Notably, China experienced a sharp rise in publication output after 2016, significantly surpassing other countries and becoming a major driving force in the field. Research during this period primarily focused on soil properties, nutrient uptake, glomalin-related soil proteins, elevated CO2 concentrations, phytoremediation, and AMF colonization rates. The research emphasis has gradually shifted from enhanced plant nutrient acquisition by AMF to its broader implications for soil ecosystem sustainability. Meta-analysis results showed that AMF inoculation had stronger effects on biological properties than on physicochemical traits. Specifically, AMF significantly enhanced soil bacterial (including actinomycete) abundance, enzyme activities, and plant biomass, and increased soil organic matter and nutrient availability. In contrast, its effect on soil bulk density and pH was not significant. The positive impact of AMF on soil quality was modulated by factors such as fertilization, inoculum source, soil sterilization status, and inoculation timing. 【Conclusion】This study provides a systematic synthesis of the effects of AMF inoculation on soil physicochemical and biological properties, and offers insights into the development of comprehensive indicators for evaluating soil quality improvement by AMF. The findings serve as a scientific basis for promoting the application of AMF in sustainable agriculture and ecological restoration.
-
Characterizing the Fertility Level of Purple Soil by Electrical Conductivity Measured with a Water Quality Meter
ZHANG Lin, LIANG Lanyue, LI Zhongyi, ZHAO Jingkun, ZHOU Jia, JIANG Zongyi
2026,63(1):221-229, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502220079
Abstract:
A study was conducted to assess the feasibility of using an inexpensive water quality meter for rapid measurement of electrical conductivity (EC) of purple soils and determining fertility levels with EC. A total of 78 purple soil samples from the top layer (0-20 cm) were collected. With a soil-to-water ratio of 1: 2.5, the equivalent ECs, displayed in the form of equivalent total dissolved solids (ETDS), were measured using a water quality meter. The ECs of each soil sample were measured with a laboratory EC meter under the same soil-water ratio. Simultaneously, seven fertility indicators, including pH, organic matter, available nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, water-soluble calcium, and water-soluble magnesium, were determined. And the comprehensive fertility level of purple soils was evaluated based on these seven fertility indicators. The results revealed that the water quality meter exhibited good stability and accuracy. The ETDS obtained by the water quality meter had extremely significant positive correlations (P<0.01) with soil fertility indicators such as available nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, water-soluble calcium, and water-soluble magnesium. It could be inferred that the ETDS reflected the abundance and shortage of the soil nutrients to a certain extent. Besides, there was a close correlation between the ETDS and the comprehensive soil fertility index, allowing for direct characterization of soil fertility levels based on the ETDS value. Consequently, when the ETDS obtained by a water quality meter (soil-to-water ratio of 1: 2.5) ≥ 250 mg·L–1, it means that the fertility level of the purple soils is high; an ETDS value of 200~250 mg·L–1 indicates a relatively high fertility level; an ETDS value of 100~200 mg·L–1 suggests a medium fertility level; an ETDS value of 50~100 mg·L–1 indicates a lower fertility level; while the ETDS value < 50 mg·L–1 indicates a very low fertility level. However, when the ETDS value exceeds 400 mg·L–1, caution is advised due to potential excessive soil salt content from overfertilization or other factors. Therefore, the fertility level of purple soil can be characterized based on rapid EC measurements using a water quality meter, providing a new technical means for rapid assessment of soil fertility levels.
-
Screening of Salt-tolerant Algae and Bacteria and the Role of Theirs Consortium in Salinized Soil Improvement
SHU Xue, ZHAO Chenyu, SHI Junqiong, WU Zhongxing
2026,63(1):230-240, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501240041
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil salinization can not only lead to the deterioration of soil physical and chemical properties, but also can seriously harm the growth and development of crops, causing severe harm to agricultural production and the ecological environment. Using microorganisms to improve the quality of salinized soil is a clean and efficient way, but there are also problems, such as the single function of microorganisms and the limited improvement effect. Nevertheless, and algae-bacterial consortium can fully exert the synergistic effect of algae and bacteria and enhance the effect of algae and bacteria on soil. However, at present, there are few related studies on the improvement of salinized soil using the algae-bacterial consortium.【Method】In this study, five microalgae and ten bacteria were isolated from salinized soil. After comparing the changes of biomass and specific growth rate in algae or bacteria under different salt stress, three salt-tolerant algae and four salt-tolerant bacteria were screened out. Afterwards, the three salt-tolerant algae and four salt-tolerant bacteria were combined into different algae-bacterial consortia. By comparing the changes in photosynthetic pigment content of algae in each algae-bacterial consortium, three salt-tolerant algae-bacterial consortia were further selected. Subsequently, the changes in EPS secretion and desalination effects were analyzed under different degrees of salt stress, and the optimal consortium of algae-bacteria was identified. Moreover, 18S-rDNA sequencing or 16S-rDNA sequencing was performed on algae-1 and bacteria-8, and the phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method, respectively. Finally, the algae1-bacteria8 consortium was applied to salinized soils to improve soil quality. 【Result】According to the constructed phylogenetic tree, algae-1 was identified as Borodinellopsis sp., and bacteria-8 belonged to Bacillus sp. After 10-day culture, the exopolysaccharide (EPS) secretion of algae and bacteria increased significantly by 44.56% and 43.19% at treatments of 15 g·L–1 and 20 g·L–1 salt stress, respectively. The soluble salt content of the solution decreased significantly, and the salt removal rate reached 57.89% and 57.55% at treatments of 15 g·L–1 and 20 g·L–1, respectively. When Borodinellopsis, Bacillus, and algae-bacterial consortium were respectively inoculated into salinized soil surface for 30 days, EPS content in soil was significantly increased by 51.72%, 8.20% and 185.88%, and the salinity of soil leaching solution decreased by 5.10%, 3.45% and 7.00%, respectively. Moreover, the salinity of the soil leaching solution inoculated with an algae-bacterial consortium was significantly lower than that of the soil inoculated with algae or bacteria alone. Concurrently, the total nitrogen content of soil in algae-bacterial consortium was significantly increased by 55.33% compared with the initial group, while no significant changes were observed in treatments of algae or bacteria alone.【Conclusion】Collectively, although both soil microalgae and bacteria can reduce soil salinity, algae-bacterial consortium have better effects on salinized soil than algae or bacteria alone. This study will provide an important theoretical basis for improving salinized soil with an algae-bacterial consortium.
-
Quantitative Inversion of Pb and Zn Content in Mining Area Soils Based on Direct Standardization Algorithm and Fractional Order Derivative
QI Yingtao, GAN Shu, YUAN Xiping, HU Lin, HU Jiankai, LU Chengzhuo
2026,63(1):241-250, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411180444
Abstract:
【Objective】Hyperspectral technology provides a novel solution for the rapid and accurate monitoring of heavy metal content in soils. However, models developed using laboratory spectra often have limited generalizability in practical applications. Additionally, directly estimating soil heavy metal concentrations from remote sensing imagery is often hampered by factors such as weather conditions and surface environment at the time of image acquisition, which leads to reduced model accuracy and limits the ability to accurately reflect the spatial distribution of heavy metals in the study area.【Method】In this study, a tailings area in Kuanshan Town, Huize County, Yunnan Province, was selected as the research site. A total of 56 surface soil samples were collected, and both ground-based and image-based hyperspectral reflectance, as well as Pb and Zn concentrations, were obtained. First, the Direct Standardization (DS) algorithm, combined with laboratory spectra, was used to correct the GF-5 imagery. Subsequently, the Box-Cox transformation was applied to normalize the skewed distributions of Pb and Zn concentrations. Then, fractional order derivative (FOD) was performed on the corrected spectra, and the Boruta algorithm was used to identify informative spectral bands. Finally, Random Forest and XGBoost models were developed for the inversion of heavy metal concentrations.【Result】The results indicate that the DS algorithm effectively mitigated the influence of soil particle size and moisture content on image spectra. The Box-Cox transformation resolved the skewness distribution problem of Pb and Zn content. FOD effectively enhanced detailed spectral features, and the optimal feature band combinations selected by the Boruta algorithm significantly improved the inversion accuracy. Furthermore, the XGBoost demonstrated superior predictive performance in handling complex feature interactions and nonlinear regression problems. 【Conclusion】The optimal inversion model for Pb content in the tailings area was a 0.8 Order-Boruta-XGBoost model, while for Zn content it was the 1.6 Order-Boruta-XGBoost model. Both models exhibited good robustness. This study provides a reliable reference method for using hyperspectral technology to invert Pb and Zn content in mining area soils.
-
Effects of Simulated High Temperature and Precipitation on CO2 Emissions and Dissolved Organic Matter in Fertilized Soil
WANG Senyuan, LI Xingyu, XIONG Weiliang, HUANG Yuzhu, WANG Changquan, LI Bing, HUANG Rong
2026,63(1):251-264, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502100053
Abstract:
【Objective】Organic fertilization is one of the most important measures to maintain the fertility level of agricultural soil. However, it is still unclear whether soil fertilization can effectively cope with the frequent occurrence of compound extreme weather events and maintain the stability of soil organic carbon (SOC). Moreover, soil dissolved organic matter (DOM) is an important indicator to measure the dynamic changes of SOC and also a core participant in the process of SOC accumulation and stability. Nevertheless, it is still unclear how extreme weather events may affect DOM and consequently its contribution to SOC accumulation and stability. 【Method】A short-term simulation experiment was conducted using rice paddy soils, and headspace gas sampling, gas chromatography, ultraviolet-visible absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy were applied to compare the effects of high temperature (32 ℃)-precipitation on the emission of CO2 and spectral characteristics of soil DOM in different fertilized soils (PK: phosphorus-potassium fertilizer; NPK: nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizer, LOM: low-volume organic manure; and HOM: high-volume organic manure). 【Result】The results revealed that (1) the variation range of cumulative soil CO2 emissions in the organic fertilization treatments (LOM and HOM) was relatively small, ranging from 8.92% to 14.17% during high-temperature or high-temperature after precipitation incubations. This effectively increased the resilience of organically fertilized soil in response to external high temperature-precipitation events. (2) Compared with the first day (Day 1) of high-temperature incubation, the soil DOM content in LOM and HOM treatments significantly increased by 7.81-14.74 mg·kg–1(P<0.05). However, the HOM treatment significantly reduced the soil DOM aromaticity (SUVA254), hydrophobicity (SUVA260), and various fluorescent substances, indicating that under high temperature stress, organic fertilization only changed the structural composition of soil DOM and did not promote the emission of CO2. (3) High temperature incubation after precipitation (Day 28) significantly reduced the soil DOM content by 64.05%-80.44% (P<0.05) when compared with Day 14. Also, organic fertilization significantly increased the SUVA254 and SUVA260 indices of soil DOM and the humification index (HIX) compared with other treatments, thereby reducing CO2 emissions. The increase in protein-like substances (fluorescence peaks B and T) caused by organic fertilizer itself did not lead to an increase in soil CO2 emissions.【Conclusion】Overall, organic fertilization, especially the organic substitution of 25%-50% nitrogen fertilizer, can improve the stability of soil organic carbon, enhance its agricultural adaptability in extreme weather events under the conditions of this study. The findings of this study provide a scientific basis for optimizing agricultural fertilization models, and promoting sustainable agricultural development.
-
Effects of Different Management Measures on Paddy Productivity and Phosphorus Balance in the Taihu Lake Basin
CHEN Guanglei, YUE Ke, YUAN Jiahui, ZHU Yiyong, KAI Lei
2026,63(1):265-277, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202408030317
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aimed to evaluate the impact of various phosphorus (P) fertilizer application rates and irrigation methods on rice yield, P uptake, P loss, and P balance in the Taihu Lake Basin. The goal was to optimize nutrient management and mitigate non-point source pollution by assessing the effects of different P levels and water management practices on rice paddies. 【Method】A two-year field experiment was conducted with three P application rates (P2O5 0, 45, and 90 kg·hm–2) and three irrigation strategies: continuous flooding, mild dryness, and severe dryness. Soil and rice samples were collected at harvest. Soil P fractions were analyzed using sequential extraction, and rice yield and P uptake were measured from grain and straw. Runoff and leachate samples were obtained to assess P loss. 【Result】Compared to the control (no P fertilizer), applying P fertilizer increased rice yield by 2.20% to 11.5%. The P2O5 90 kg·hm–2 treatment reduced P agronomic and P use efficiencies by an average of 34.9% and 29.4%, respectively, compared to the application of P2O5 45 kg·hm–2. P application significantly increased the soil Olsen-P and available P fractions (the sum of Resin-P, NaHCO3-Pi, and NaOH-Pi) by 19.1%~62.4% and 36.5%~101%, respectively, while also enhancing P loss from paddy fields by 79.1% to 292%, compared to the control. In addition, the mild and severe dryness strategies significantly reduced P loss, with average decreases of 27.0% and 35.6%, respectively, particularly in runoff, where reductions were 31.5% and 41.3%, compared to flooding. The P2O5 90 kg·hm–2 treatment maintained a P balance for the rice season, while the application of P2O5 45 kg·hm–2 was sufficient to meet rice demands due to the high availability of soil P and Olsen-P higher than 20 mg·kg–1. Structural equation modeling indicated that Olsen-P and NaOH-Pi were the main influencing factors for rice yield, while Resin-P was the main influencing factor of P loss. 【Conclusion】Moderate P fertilization at P2O5 45 kg·hm–2 effectively increased rice yield with minimal P loss. Mild dryness irrigation and appropriate P application based on crop P requirements and soil P levels are vital for maximizing crop yields while minimizing P loss. The findings provide a scientific basis for nutrient management in paddy fields and the control of non-point source pollution in the Taihu Lake Basin.
-
Effects of Conservation Tillage on Colloidal Phosphorus in Soil Profile of Black Land
ZHOU Sudan, LI Jianye, ZHU Xueqi, LIU Chunlong, LIANG Xinqiang
2026,63(1):278-288, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202408140327
Abstract:
【Objective】A long-term field experiment was conducted in a typical black soil area in Northeast China to study the changes in soil colloidal phosphorus content in the 0-100 cm profile under no tillage(NT)and traditional tillage(CT). The purpose was to explore the effect of conservation tillage on the content of colloidal phosphorus and analyze the distribution pattern of colloidal phosphorus in soil under different tillage measures. 【Method】 The research area is located at the National Field Science Observation and Research Station of Hailun Farmland Ecosystem, Chinese Academy of Sciences (47°26′N, 126°38′E), where corn soybean rotation is implemented. After the corn harvest, the soil profiles of farmlands were collected and divided into eight layers: 0-5, 5-10, 10-15, 15-20, 20-40, 40-60, 60-80 and 80-100 cm. The contents of colloidal phosphorus and soil physical and chemical indicators in each soil layer were determined to study the variations and distribution patterns of colloidal phosphorus content in the 0 - 100 cm soil profile under straw mulching no-tillage (NT) and conventional tillage (CT). 【Result】NT significantly increased the content of colloidal phosphorus (P < 0.05), with an average increase of 33.40%. In the same soil layer, NT significantly increased the contents of total phosphorus and available phosphorus, and the average contents of colloidal molybdate reactive phosphorus (MRP) and colloidal molybdate unreactive phosphorus (MUP) (P < 0.05). Among them, MRP increased by 18.44% and MUP increased by 49.19%, but NT significantly decreased the proportion of MRP in colloidal phosphorus in the surface soil by 12.21% (P < 0.05). Tpcoll (colloidal phosphorus) and colloidal MRP were mainly carried by fine particles of 1-220 nm. The average proportion of FPcoll(1-220 nm colloidal phosphorus)in each soil layer under NT treatment was 73.47%, and that under CT treatment was 74.34%. The proportion of FMRP (1-220 nm MRP) was 59.64% under NT treatment and 63.22% under CT treatment, and the average proportion of FMRP in the surface soil under NT treatment was 5.66% lower than that under CT treatment. The content of colloidal phosphorus was affected by soil physical and chemical properties, showing a significant negative correlation with bulk density and a significant positive correlation with field capacity, soil porosity, total phosphorus content, available phosphorus, total carbon, and total nitrogen. 【Conclusion】 In conclusion, conservation tillage generally increases the contents of colloidal phosphorus, total phosphorus, and available phosphorus in each soil layer. This change might be due to the influence of NT on soil physical and chemical properties, and the increase in colloidal phosphorus content might increase the risk of phosphorus loss.
-
Effect of Organic Amendments on Nematode Community Under Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Application at the Aggregate Scale in Red Soil of Dryland
YANG Jiani, ZHU Baijing, REN Zhuhong, WAN Bingbing, CHEN Xiaoyun, LIU Manqiang
2026,63(1):289-302, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501070013
Abstract:
【Objective】In order to adequately meet the growing population's demand for agricultural products, reducing the application of chemical fertilizers, investing in organic amendments, and improving the efficiency of nutrient use have been recognized as effective ways to guarantee food security. Different soil aggregate sizes exhibit significant variations in terms of water-heat conditions and nutrient distribution, which in turn influence nematode communities to varying extents. However, the impact of reduced chemical fertilizer application combined with different organic amendments on soil nematodes at the aggregate scale remains poorly understood. 【Method】This study investigated the interaction between reduced fertilizer application (2 levels: full chemical fertilizer NPK and 60% reduction in NPK) and organic amendment types (no organic amendment as control, straw, and biochar) in the red soil of dryland agriculture. Each treatment was further divided into four aggregate size classes (> 2 mm, 2-1 mm, 1-0.25 mm, < 0.25 mm). 【Result】The results indicated that the nematode abundance in all treatments with reduced fertilizer application was higher than that of the full chemical fertilizer treatment. Regardless of the fertilizer application, both straw and biochar significantly increased the total nematode abundance, and nematode numbers increased with the increase in aggregate size. Compared to straw application, biochar application generally decreased the abundance of bacterivorous nematodes while increasing the abundance of omnivorous nematodes. Notably, in the 2-1 mm aggregate size class, biochar addition decreased the abundance of bacterivorous and omnivorous nematodes compared to straw, but increased the abundance of fungivores nematodes. Nematode community analysis revealed that as aggregate size decreased, the nematode structure and enrichment indices tended to decrease, indicating greater environmental disturbance. Further analysis showed that, soil pH and moisture were key factors influencing nematode community structure at the larger aggregate scale, while soil organic carbon was the critical factor at the smaller aggregate scale (P<0.01). 【Conclusion】This study revealed that organic amendments, reduced fertilizer application, aggregate size, and their interactions significantly affected nematode communities. Therefore, the rational combination of organic amendment types and reduced fertilizer application should be considered to better protect soil health and guide agricultural production.
-
Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Soil Nematode Communities in Dry-Hot Valley Under Different Altitude Gradients
ZENG Xiaoling, JIANG Chuan, CHEN Yuanyang, FENG Defeng, CHEN Shujie, YANG Yana, JIN Yanqiang, LIU Chenggang
2026,63(1):303-314, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202407020268
Abstract:
【Objective】Vegetation restoration is one of the most effective approaches to improve the ecological environment of the dry-hot valley of the Jinsha River, Yunnan Province. Exploring the changes in composition and structure of soil nematode communities under artificial and natural vegetation restoration can provide a theoretical basis for the reasonable management of the forest ecosystem in this region. 【Method】 In dry-hot valley of the Jinsha River, Leucaena leucocephala plantation and natural shrub-grass with Phyllanthus emblica and mixed Terminalia franchetii + Pistacia weinmannifolia were selected at low (1 150 – 1 200 m), middle (1 350 – 1 400 m)and high (1 550 – 1 600 m) altitudes. The effects of the vegetation restoration approach under different altitudes on the functional structure of nematode communities were analyzed by using ecological indices, c-p life history, and nutritional structure indices. 【Result】 1) A total of 17 genera of bacterivores were captured, accounting for 37.3% of the total number, and omnivores-predators belonging to 21 genera, accounted for 53.2%. Also, Aporcelaimus, Acrobeles, and Microdorylaimus were the dominant genera. 2) Nematode trophic taxa were dominated by omnivores-predators and bacterivores, while plant-parasites and fungivores had relatively low proportions. However, the taxa were biased towards K-strategies. 3) The responses of nematode abundance, trophic taxa, and life history strategies to vegetation restoration varied across different altitudes. As the altitude increased, the diversity and stability of the nematode community under T. franchetii + P. weinmannifolia mixed shrub-grass increased gradually, while that under P. emblica shrub-grass showed the opposite trend. However, the L. leucocephala plantation showed the lowest "V" pattern with the middle altitude. Meanwhile, L. leucocephala plantation at the low altitude increased the metabolic footprints of bacterivores and omnivores-predators, implying that the food web was relatively complex and stable. 4) Soil nitrate nitrogen, available phosphorus, and moisture were the main driving factors of nematode community changes in artificial and natural vegetation restoration. 【Conclusion】 We recommend taking L. leucocephala as the main plantation at the low altitude area in the process of vegetation restoration and actively protect the pure and mixed natural shrub-grass at the middle and high altitudes to promote the ecological restoration of degraded soil in the dry-hot valley of the Jinsha River.
-
Differential Responses of Microbial Necromass to Warming in Topsoil and Subsoil
YANG Dongqiao, ZHANG Zihan, LU Mengya, DING Xueli
2026,63(1):315-328, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202407080274
Abstract:
【Objective】Microbial necromass carbon (MNC) is an important component of the soil organic carbon (SOC) pool and probing the response of MNC to climate change is key to a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of microbial-mediated regulation of SOC formation. There is still a lack of understanding regarding the impact of climate warming on topsoil and subsoil MNC accumulation dynamics in different ecosystems. 【Method】A meta-analysis was conducted to investigate the effect of warming of 8 sample sites on MNC in different soil layers and its contribution to SOC and on the response of topsoil and subsoil MNC to warming (41 for total amino sugars, 69 for glucosamine, 69 for muramic acid and 26 for galactosamine). 【Result】Warming promoted the accumulation of MNC in different soil layers as a whole, especially in the topsoil (14.3%). This may be related to the differences in plant-carbon input and the spatial heterogeneity of microbial communities in different soil layers under a warming background. However, due to the acceleration of the loss of SOC in the subsoil after warming, the proportion of MNC contribution to SOC in the subsoil (12.5%) was higher than that in the topsoil (11.3%). Furthermore, the positive effect of the accumulation of fungal necromass and their contribution to SOC in different soil layers was greater than that of bacterial necromass, suggesting that climate change can directly or indirectly regulated the composition of MNC by affecting carbon inputs. Moreover, the impact of warming on the accumulation of MNC in different soil layers is bound up with warming amplitude and years. Lower warming (≤2 ℃) promoted microbial anabolism to increase the accumulation of MNC in the topsoil by 17.2%, while the contribution of MNC to SOC in the subsoil was significantly promoted during higher warming(> 2 ℃). On the timescale of warming, long-term warming (> 5 a) changed the microbial activity pattern and had a greater impact on the ratio of MNC to SOC in subsoil (42.8%). Meanwhile, the contribution of microbial necromass to SOC was increased with soil depth in forest and cropland, whereas warming weakened the proportion of subsoil microbial necromass to SOC in grassland. 【Conclusion】Based on our analysis, it is suggested that future research on the dynamics of microbial-mediated organic carbon accumulation in specific ecosystems in response to warming should focus on the response of microbial necromass in both topsoil and subsoils. This would provide a huge boost to understanding and predicting the sensitivity of SOC dynamics to climate change and its feedback mechanisms.
-
Effects of Plant Growth Retardants on Rhizosphere Microbial Community in Hemerocallis citrina
MENG Lu, MA Tao, YUE Xinli, WANG Hui, LI Xiaoyu
2026,63(1):329-337, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503310149
Abstract:
【Objective】Hemerocallis citrina Baroni, an important cash crop in China, has become a pillar industry in Yunzhou District, Datong City, Shanxi Province. Plant growth retardants could effectively delay the flowering period of H. citrina and regulate its growth and development. However, the effect of plant growth retardants on soil microbiota remains unexplored. Thus, this study aimed to clarify the impact of plant growth retardants on soil microbial community structure. 【Method】 This study was conducted in 2023 in Datong City, Shanxi Province. Plant growth retardants uniconazole (S3307) and paclobutrazol (PP333) were sprayed on H. citrina with three treatments: uniconazole 500 mg L–1 and paclobutrazol 500 mg L–1, water was used as the control, and each treatment was repeated three times. The rhizosphere soil was collected from each plot at the full bud stage, and the fine roots, plant residues, stones, and other debris were removed through a 10-mesh sieve. Then the response of the rhizosphere bacterial community to plant growth retardants was analyzed using 16S rRNA and internal transcribed spacer (ITS ) amplicon sequencing technology. 【Result】The results showed that paclobutrazol and uniconazole treatments had no significant effect on the Shannon index and Chao 1 index of the rhizosphere microbial community. However, both treatments increased the total operational taxonomic units (OTUs ) and unique OTUs of the rhizosphere soil bacteria. At the phylum level, paclobutrazol treatment increased the relative abundance of beneficial microorganisms such as Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, and Ascomycota. Under the genus level classification, the relative abundance of Fusarium in soil after paclobutrazol treatment was significantly increased by 9.68%, whereas uniconazole treatment increased the relative abundance of Cyathus by 25.13% compared with the control. 【Conclusion】 Plant growth retardant treatments have the potential to improve the richness and diversity of rhizosphere bacterial communities as well as change the population structure of soil microorganisms in the rhizosphere of H. citrina.
Research Advances of Soil Chemistry and Environment
土壤化学与环境研究前沿进展
Research Advances of Soil Chemistry and Environment
土壤化学与环境研究前沿进展
Reviews and Comments
Research Articles
-
Effects of Three-year Biochar Application on Microbial Community Structure and Carbon-Nitrogen Distribution in Soil Aggregates of Wheat Fields
MENG Xiangrui, YANG Weijun, WANG Zi, ZHAO Lining, ZHANG Liyue, ZHANG Jinshan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502250084
Abstract:
The aim of this study was to explore the long-term effects of biochar on improving soil fertility in farmland in the northern Xinjiang irrigation area. A three-year field trial with three treatments: no biochar application (B0), low biochar application (10 thm-2, B1), and high biochar application (20 thm-2, B2), was conducted to systematically analyze the effects of biochar on soil aggregate carbon and nitrogen components, enzyme activities, and microbial community structure. The results showed that when the biochar application rate was 10 t·hm-2, it exhibited the optimal soil improvement effect. Specifically, the organic carbon content in aggregates larger than 2 mm and smaller than 0.25 mm demonstrated an upward trend with the application of biochar. Among them, in the aggregates larger than 2 mm, the organic carbon content in treatment B1 was significantly increased by 44.05% compared to treatment B0. In the aggregates smaller than 0.25 mm, the organic carbon content initially increased and then decreased with the application of biochar, reaching the maximum in B1. Also, the total nitrogen content in aggregates larger than 2 mm first increased and then decreased with the application of biochar, reaching the highest level in B1. Furthermore, the findings indicated that the application of biochar increased the microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in aggregates larger than 2 mm and in the range of 2~0.25 mm, while reducing the microbial biomass nitrogen in aggregates smaller than 0.25 mm. Meanwhile, the urease activity in all three types of aggregates showed an upward trend with the application of biochar. Under the three aggregate conditions, compared to B0, B1 increased the activity of urease by 14.53%, 5.43%, and 1.08%, respectively. In addition, catalase activity was highest under the B1 condition, increasing by 10.64%, 21.43%, and 23.4% compared to B0, respectively. Although sucrase activity slightly decreased, it still remained at a relatively high level, ensuring the supply of carbon sources. The application of biochar significantly enhanced the α-diversity (Shannon and Chao1 indices) of the soil bacterial community. This promoting effect was strengthened as the aggregate particle size decreased. Moreover, under the application rate of 10 t·hm-2 (B1), the improvement effect was relatively balanced. In contrast, the impact of biochar on the α-diversity of fungi was relatively weak. The Shannon index only increased slightly, and the Chao1 index showed no significant change, indicating that the fungal community was less sensitive to the application of biochar compared to the bacterial community. Under the conditions of this study, applying 10 t·hm-2 of biochar (B1) can increase the content of carbon and nitrogen components in soil aggregates of wheat fields while enhancing the abundance of beneficial microbial communities.
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Phoebe bournei Litter Input on Soil Priming Effect Based on Organ and Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio Differences
MAO Zixi, GAN Ziying, XIE Jiangtao, QIU Qingyan†, HU Yalin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507200353
Abstract:
【Objective】Litter quality is a key factor regulating the intensity and direction of the soil priming effect. However, it remains unclear whether inputs of litter from different organs of the same plant or litter with different carbon to nitrogen ratios (C/N) from the same organ differentially impact soil priming effect, as well as the underlying mechanisms.【Method】To address this gap, 13C-labeled seedlings of Phoebe bournei were used as study materials. Through fertilized and non-fertilized treatments, leaf, stem, and root tissues with low and high C/N ratios were obtained to investigate the effects of litter inputs with different C/N ratios on soil priming. Soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and soil available nitrogen contents (NH4+-N and NO3--N) were measured concurrently to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.【Result】After 180 days of incubation, the addition of high and low C/N ratio leaf litter and low C/N ratio root litter inhibited the mineralization of soil organic carbon (SOC) by about 11.09%, 9.05% and 8.07%, respectively, inducing a significant negative priming effect. However, the other treatments did not cause significant priming effects. The influence of different C/N ratios in the same organ of Phoebe bournei on soil priming effect was primarily observed within the first 8 days of incubation, with high C/N ratio litter inducing a stronger negative priming effect than low C/N ratio litter. The reason is that high C/N ratio litter input caused microbial nitrogen (N) immobilization, reducing soil available N content, which led to N limitation and suppressed microbial activity, thereby decreasing SOC decomposition. In the later stages of incubation, the effects of different C/N ratio litter on soil microbial biomass carbon and carbon metabolism-related enzyme activities were not significant, so the influence of C/N ratio on soil priming gradually diminished. Among different plant organs, leaf litter induced a stronger negative priming effect than root litter. Specifically, the negative priming effect induced by leaf addition weakened over time, while root addition continuously induced a negative priming effect. Stem addition caused a priming effect that fluctuated between positive and negative, but the cumulative effect offset, resulting in no significant change in SOC decomposition.【Conclusion】The impact of Phoebe bournei litter input on soil priming effect varied significantly among organs, whereas the influence of litter C/N ratio on soil priming effect was mainly concentrated in the early stages of litter decomposition. The main mechanism by which leaf litter induced a negative priming effect was through reducing soil available nitrogen, which inhibited microbial activity, thereby decreasing SOC decomposition. In contrast, the negative priming effect induced by low C/N ratio roots was because their high lignin content and low bioavailability, causing C limitation for microorganisms during decomposition, leading to reduced SOC decomposition.
-
Characteristics of Cultivated Land Soil Acidity and Main Controlling Factors in the Typical Black Soil Region of Northern Songnen Plain
LIN Ziyi, WU Huayong, SONG Xiaodong, ZHAO Yuguo, ZHANG Ganlin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202509040439
Abstract:
【Objective】 Soil acidification is a prominent issue in the typical black soil region of the northern Songnen Plain, which hinders the sustainable development of regional agriculture. Thus, exploring the characteristics of soil pH, exchangeable acidity, and their influencing factors in the cultivated soils of the typical black soil region can provide a scientific basis for the zoning and classification of soil acidification improvement measures. 【Method】 In this study, surface soils of cultivated land in Bei""an City and Wudalianchi City, Heilongjiang Province, were taken as the research object. Soil samples from 119 soil sites were collected to determine soil acidity and related soil properties, while data on relevant environmental and anthropogenic factors were collected. Pearson correlation analysis and random forest model were used, combined with the theory of soil acid-base buffering, to explore the main controlling factors affecting the spatial variation of soil pH, exchangeable H⁺, and exchangeable Al³⁺ contents. 【Result】 The results showed that the surface soils of cultivated land in the study area were dominated by strongly acidic and acidic soils. The spatial variability of soil pH was low, while the spatial variability of soil exchangeable acid content was high. There were no significant differences in soil pH and exchangeable acidity contents between dark brown soils, black soils, marsh soils, and meadow soils. Pearson correlation analysis indicated that soil pH was extremely significantly and positively correlated with the contents of exchangeable Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺, clay fractions, and mean annual temperature, and significantly negatively correlated with soil organic matter content, silt content, aluminum saturation, mean annual precipitation, and elevation. Soil exchangeable H⁺ and Al³⁺ contents were extremely significantly and positively correlated with soil organic matter content, silt content, aluminum saturation, mean annual precipitation, and elevation, and extremely significantly and negatively correlated with the contents of exchangeable Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺, clay fractions, and mean annual temperature. The random forest model showed that the 15 influencing factors explained 84.38% and 71.61% of the variations in soil pH and exchangeable acids, respectively. Among these factors, soil factors contributed the most (65.67% and 56.19%), followed by environmental factors such as annual average precipitation (18.57% and 13.87%), whereas the contribution of anthropogenic factors was negligible with respect to the spatial variation of soil pH and exchangeable acid (0.14% and 1.55%). 【Conclusion】 The typical black soil region in northern Songnen Plain has a high acid buffering capacity due to its high base saturation and abundant feldspar minerals, which is significantly different from the soil in typical red soil regions. The main controlling factors for the spatial variation of soil acidity are soil exchangeable base ions (Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺) contents, aluminum saturation, and annual average precipitation.
-
Penetration Resistance Characteristic Model of Red Soils and Influencing Factors
WANG Jinqiang, CHENG Chaofan, TIAN Zhengchao, HE Yangbo, LIN Lirong, CHEN Jiazhou
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507150348
Abstract:
【Objective】High soil penetration resistance (PR) limits global crop growth and sustainable agricultural productivity. Heavy soil texture, low soil organic matter, and low topsoil water content during summer significantly increase PR under a subtropical monsoon climate in southern China. However, the specific mechanisms controlling these processes remain elusive. Thus, the objectives were to investigate the applicability of various penetration resistance characteristic models in red soils with different parent materials and identify key influencing factors, and assess the ameliorative effects of mechanical- and bio-tillage on PR in Ultisols. 【Methods】This study investigated four red soils derived from different parent materials in China’s humid subtropical climate, including granitic (GS), Quaternary red clayey (CS), argillaceous shale (AS), and red sandstone red soil (SS). Key parameters measured included soil PR, water content (SWC), bulk density (), organic matter (SOM) and texture. We evaluated the performance of five PR models (soil water content model, soil matric potential model, soil water content and bulk density model, soil matric potential and bulk density model, and saturated stress model) and identified their influencing factors in red soils, assessed the ameliorative effects of mechanical- and bio-tillage on PR in Ultisols, and determined the PR threshold for four red soils using the least limiting water range. 【Results】Among the five characteristic models of soil PR, the saturated stress model provided a better fit (lower SSE and higher R²) for the four red soils, followed by the soil water content model, the soil water content and bulk density model, and the soil matric potential model. PR in red soils increased with decreasing water content, exhibiting a sharp increase once the water content fell below a critical value (~ 0.32 cm³·cm-³). The PR of low bulk density soils (1.3 g· cm-³) experienced a sharp increase at low water contents, whereas that of high bulk density soils (1.5 g·cm-³) showed a dramatic increase at high water contents. Soil texture (clay content) was a primary factor influencing PR of different parent material red soils, while SOM had negligible effects. When the soil water content was 0.25 cm³·cm-³, mechanical tillage (deep tillage with 30 cm ploughing depth) reduced PR by ~1 034 kPa in the 0~40 cm depth compared to control treatment (no-tillage), whereas bio-tillage achieved a reduction of ~785 kPa in the same depth and reduced PR (~1 500 kPa) in the subsoil. The critical PR thresholds of the four red soils exceeded 2 500 kPa, and thresholds for clayey red soils were higher than those for sandy red soils. 【Conclusion】The saturated stress model proved highly effective for predicting red soil PR in of southern China. SWC, and texture played the primary factors influencing PR across different parent material red soils, with clayey red soils (CS and AS) exhibiting higher PR thresholds than sandy red soils (GS and SS). This research provides a scientific basis for identifying the occurrence of seasonal drought and rationally selecting tillage practices for drought prevention in subtropical red soil regions of China through the lens of soil penetration resistance.
-
Effects of Different Green Manure Plantations on Runoff and Sediment Yield in Sloped Citrus Orchards with Purple Soil and Their Underlying Mechanisms
ZHAO Yanting, WANG Xiaoyan, HE Hui, CHEN Zhanpeng, CHEN Fangxin, SHAN Qiao
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202508030377
Abstract:
【Objective】Green manure cultivation in orchards plays a positive role in improving soil physicochemical properties, such as soil structure, and in reducing soil erosion. However, the mechanisms by which green manures mitigate soil erosion in sloping orchard systems remain unclear. 【Method】This study was conducted using runoff plots in a citrus orchard to systematically monitor runoff and sediment yield under natural rainfall conditions in plots planted with ryegrass (Lolium perenne), hairy vetch (Vicia villosa), and white clover (Trifolium repens), compared with bare tilled (bare soil) control plots. The effects of green manure plant characteristics, stem thickness, plant height, root length, and vegetation cover, on soil structural properties (porosity, bulk density, average infiltration rate) and organic matter content, as well as their relationships with runoff and sediment production, were analyzed. 【Result】The results showed that (1) Green manure plant traits significantly improved from initial to peak flowering. Hairy vetch exhibited the greatest plant height and root length, ryegrass had the optimal stem thickness, and white clover achieved the highest vegetation cover. (2) Soil bulk density and porosity were closely correlated with green manure root length: more developed root systems were associated with lower bulk density and higher porosity (P < 0.05). At peak flowering, green manure plots showed a significant decrease in bulk density and notable increases in porosity and average infiltration rate compared to the seedling stage, whereas the bare tilled control exhibited opposite trends. Organic matter content increased in all plots from seedling to peak flowering, but the smallest increase occurred in the bare control. Among treatments, hairy vetch showed the greatest reduction in bulk density (–8.69%) and the largest increases in porosity (+8.22%) and organic matter (+45.88%). Also, ryegrass demonstrated the best infiltration performance, followed by white clover. (3) Root length exerted strong influences on subsurface flow (effect strength = 0.66) and sediment yield (0.71), while plant height and vegetation cover primarily affected surface runoff (0.62) and sediment yield (0.61) by dissipating rainfall energy and resisting overland flow. Over a full annual cycle, including growth, residue decomposition, and tillage periods, the average runoff and sediment yields followed the order: bare tillage > hairy vetch > white clover > ryegrass, clearly indicating the superior overall erosion control by ryegrass. Although the hairy vetch plots recorded the lowest sediment concentration in runoff, temporal analysis revealed distinct performance patterns. Specifically, white clover was most effective in reducing runoff and sediment during the early growth stages (seedling/initial flowering) due to its rapid establishment, whereas ryegrass performed best during peak flowering, decomposition, and the non-growing season, owing to its persistent biomass and robust root system. 【Conclusion】Intercropping ryegrass and white clover in sloping citrus orchards provides the most effective control of soil and water loss. These findings provide theoretical support for the strategic mixing and temporal scheduling of green manure species, tailored to specific ecological functions in different agroecological zones.
-
Effect of Soil Aggregates on Stoichiometry Characteristics Nutrient under Different Land Use Types
YANG Qian, LIU Muxing, XU Jiapan, YI Jun, WANG Chuantao, DING Shuting
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506030256
Abstract:
【Objective】 Land-use change is a primary driver of soil structure alteration and nutrient cycling in ecosystems. In subtropical hilly areas of China, which are ecologically fragile and experience significant land-use pressure, understanding the interplay between soil physical structure and biogeochemical cycles is crucial for sustainable land management. The stability of soil aggregates and the ecological stoichiometry of nutrients serve as critical indicators for evaluating ecological restoration and soil quality. Thus, this study aims to elucidate the mechanism by which typical land use practices in subtropical hilly areas influence nutrient variations through alterations in the distribution characteristics of soil aggregates. 【Method】 We examined soils from three representative land use types (forestland, tea garden, and cultivated land) in Yingshan County, Hubei Province. Key stability indices, including the mean weight diameter (MWD), geometric mean diameter (GMD), soil erodibility (K), and fractal dimension (D), were calculated. Utilizing both stoichiometric methods and multivariate statistical models, we analyzed the relationship between aggregate stability levels and the distribution patterns of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus. 【Result】 The results revealed that: (1) The content of >5 mm aggregates in forestland soils was 3.43 and 1.58 times higher than that in tea garden and cultivated land, respectively. Both the mean weight diameter (MWD) and geometric mean diameter (GMD) followed the order: forestland > cultivated land > tea garden. The tea garden soil exhibited the highest erodibility (K) value and fractal dimension (D) value. (2) The soil organic carbon content in forest land was significantly higher than in other plots, reaching 10.22 g·kg?1. Total nitrogen content followed the order of forest land > tea garden > cultivated land, while total phosphorus content exhibited the opposite trend. Both C:P and N:P ratios were highest in forestland soils, followed by cultivated land and tea garden. (3) Aggregate characteristics were significantly correlated with nutrient indicators (P < 0.05), with the macroaggregates (> 5 mm) playing a major role in shaping C:P and N:P ratios. Also, the partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM) showed good fit (goodness-of-fit > 0.61) and the path coefficients indicated that the influence pathways of aggregate particle size on nutrient stoichiometric ratios varied under different land use types, with the direct effect being most pronounced in forested areas. 【Conclusion】 This study illustrates that changes in land use significantly affect the relationship between soil structure and nutrient cycling. Forestland, which experiences minimal disturbance, encourages the creation of stable macroaggregates. This process enhances long-term nutrient sequestration and maintains a balanced stoichiometric environment. On the other hand, intensive management practices in tea gardens and cultivated lands can disrupt aggregate stability. This disturbance leads to structural degradation and a notable stoichiometric imbalance. Therefore, it is crucial to preserve forestland and implement sustainable soil practices in managed lands. This approach will significantly improve soil quality and promote ecological sustainability in subtropical hilly areas.
-
Effects and Driving Mechanisms of Leguminous Green manure on Soil Ecosystem Multifunctionality in Apple Orchards
WANG Ju, YU Jintao, LI Mingjun, YANG Peizhi, ZHAI Bingnian, LI Ziyan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202509110448
Abstract:
【Objective】Intensive orchard management in semi-arid regions has caused soil quality degradation and declining ecosystems’ multifunctionality, thereby threatening production sustainability. While green manure mulching shows promise for sustainable orchard management, the mechanistic impact on soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality remain unclear.【Method】This study investigated the impact of four green manure mulching treatments- no mulching, gramineae monoculture (ryegrass, Lolium perenne L.), legume monoculture (white clover, Trifolium repens L.), legume-gramineae mixture (1:1) on soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality in semi-arid orchards.【Result】The results revealed that green manure mulching substantially enhanced soil quality, with legume monoculture showing superior performance (89.0% and 88.5% increases versus grass and mixed systems, respectively). All treatments stimulated soil enzyme activities and alleviated microbial limitations (carbon: 5.8%-8.6%; nitrogen: 5.0%-14.7%), collectively increasing ecosystem multifunctionality by 87.4%-100.2%.【Conclusion】This study reveals that green manure mulching effectively enhances soil ecosystem multifunctionality in semi-arid orchards, with legume-based systems (monoculture or mixed) recommended for implementation.
-
Research Progress of Pelletized Straw Incorporation
WANG Xiquan, WANG Peixin, QIAN Chunrong, PANG Huancheng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202510100492
Abstract:
Straw incorporation poses a persistent challenge while remaining fundamental to soil fertility management in modern Chinese agriculture. However, traditional straw incorporation methods are characterized by slow decomposition, inefficient soil organic matter enhancement, and significant yield reduction. To combat these drawbacks, we proposed and developed straw pelletization technology as a novel alternative for efficient straw utilization over 14 years, providing a novel solution for land conservation and intensive utilization. This review synthesized the research progress in straw pelletization and incorporation, with the aim of providing a theoretical foundation and technical guidance for its high-quality development. This review commenced with a retrospective analysis of the conceptual foundation of straw pelletization and incorporation, which involves secondary crushing and pelletizing of straw to simultaneously tackle decomposition and field incorporation challenges. Subsequently, based on previous practices, the study delineated ten major advantages, such as markedly increased incorporation rates, rapid soil organic carbon sequestration, and stable yield improvements. It also identifies three salient scientific questions, the mechanism of accelerated decomposition, carbon turnover processes, and carbon sequestration thresholds, while envisioning the application potential of pelletized straw returning in intensive agriculture, organic agriculture, medium- and low-yield fields, and reserve croplands. Finally, to bridge the gap in large-scale and widespread adoption, two essential supporting measures were proposed: the optimization and widespread deployment of integrated straw crushing and pelletizing machinery, and the establishment and development of a straw pellet trading platform. In summary, straw pelletization and incorporation enable the simultaneous improvement of soil fertility and crop yield, thereby supporting the national strategies of the Two Stores (storing grain in the land and through technology) and the Dual Carbon (Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality).
-
Spatio-Temporal Variations of Soil Total Nitrogen and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Farmland of A Typical County in Cinnamon Soil Area
HE Ningbo, SU Xinyue, BAI Kaidong, WANG Hengfei, LI Jianhua, XU Minggang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202504130178
Abstract:
Abstract: 【Objective】 Optimizing nitrogen management of the farmland is critical to achieve the strategy of reducing fertilizer input and improving efficiency, as well as advance the agricultural green development. This study aims to explore the spatio-temporal variations of soil total nitrogen (TN) and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) in typical county of cinnamon soil region over the past four decades, which can provide the scientific basis for enhancing farmland nitrogen management. 【Method】 Based on the farmland soil properties (soil nutrients, etc.) in Shouyang County, Shanxi Province in 1983, 2010, and 2023, and the agricultural production statistical data (planting area, crop yields, fertilizer types and application rates, livestock breeding quantity, etc.) from 1980 to 2023, classical statistics and geostatistics were employed to analyze the spatiotemporal dynamics of TN. The farmland nitrogen balance model was used to estimate nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and nitrogen surplus. Random-forest analysis was applied to identify the key factors that affected the variations of TN. 【Result】 From 1983 to 2023, the farmland TN content in Shouyang County increased significantly, rising from 0.66 g·kg-1 to 1.02 g·kg-1. The most notable increase in TN occurred in Pingtou Town, Yinlingzhi Town, and the eastern part of Chaoyang Town. Over the past four decades, the NUE showed a pattern of first decreasing and then increasing, which declined from 48.63% in the 1980s to 33.08% in the 2000s and subsequently rose to 43.75% in the 2010s. Spatially, the farmland NUE value ranged from 30.66% to 50.99% among various regions during the 1980s to 2000s, which showed no significant difference. While in the 2010s, the NUE in the northern region (45.52%) was significantly higher than that in the central (36.84%) and southern regions (36.80%). The Random-forest analysis identified that soil organic carbon and nitrogen fertilizer amount were the key influencing factors to the changes of TN, with the relative importance of 33.95% and 10.57%, respectively. Currently, the farmland NUE and nitrogen surplus in Shouyang County were 45.78% and 97.2 kg·hm-2, respectively, which were still outside the optimal nitrogen management level. The northern region exhibited a relatively high NUE but a substantial nitrogen surplus, while Jingshang Town and Xiluo Town in the southern region recorded extremely low NUE and high nitrogen surplus. 【Conclusion】 Overall, although the farmland nitrogen management in Shouyang County has been improved over the past four decades, it still falls short of the optimal level. It is recommended that the entire Shouyang County, especially the Jiechou Town in the northern region, the Chaoyang Town in the central region, and the Jingshang Town and Xiluo Town in the southern region should prioritize rational nitrogen fertilizer amount to enhance farmland NUE, reduce nitrogen surplus, and ultimately achieve the optimal nitrogen management level.
-
Effects of Earthworms on Nitrogen Utilization and Loss with Different Fertilizer Applications
Cheng Yihan, Ouyang Yi, Zhao Jiaxin, Pei Xiangyu, Zhang Lin, Lu Yaoxiong, Wu Yupeng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503290146
Abstract:
【Objective】The application of organic fertilizers in agricultural soils increases the density of earthworms. However, it remains unclear how earthworms change the fate of soil nitrogen under different fertilizer applications. 【Method】Using a pot experiment, the present study explores the effects of earthworms on soil nitrogen utilization, loss, and nitrogen transformation processes under the application of chemical (urea) and organic (compost) fertilizers. 【Result】The results showed that earthworms significantly increased the fresh weight of plants and the amount of nitrogen uptake by plants by 12.14% and 15.24% under chemical fertilizers and 18.38% and 37.28% under organic fertilizers, respectively. Earthworms significantly increased the cumulative soil N?O emissions and the cumulative soil ammonia volatilization only under the application of chemical fertilizers. There was no significant difference in nitrogen leaching loss between the treatment with and without earthworms. Overall, earthworms increased the nitrogen loss by 6.31 and 1.69 mg·pot?1 under the application of chemical and organic fertilizers, respectively. Also, earthworms significantly increased the ratio of the total nitrogen utilization by plants to the total nitrogen loss under the application of organic fertilizers, but no significant difference was found under the application of chemical fertilizers. The soil nitrogen primary transformation rate model showed that earthworms affected more nitrogen transformation processes under the application of organic fertilizers than under the application of chemical fertilizers, significantly increasing the total primary nitrogen mineralization rate of the soil. 【Conclusion】Regardless of the type of fertilizer applied, earthworms played a dual role in promoting plant nitrogen utilization and increasing nitrogen loss. However, considering the ratio of nitrogen utilization to loss, the application of organic fertilizers provided a more conducive environment for achieving the beneficial effects of earthworms in the soil nitrogen cycle.
-
Effects of Biological Nitrification Inhibitor Application on Nitrification Rate and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Upland Soils Amended with Organic Fertilizer
guo qirui, zhang yinghua, chen meiqi, liu zihan, jing hang, wang jing, Ahmed S. Elrys, cai zucong, chengyi
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505210232
Abstract:
【Objective】Application of biological nitrification inhibitors (BNIs) is an effective strategy to suppress nitrification rates and mitigate nitrous oxide (N?O) emissions in agricultural soils. However, how the addition of BNIs affects soil nitrification rate and N?O emission under organic fertilizer application remains unclear. 【Method】The microcosm aerobic incubation experiment was conducted using upland red and black soils, with two levels of organic fertilizer (chicken manure: N 0 and 100 mg·kg?1 soil) and three levels of BNIs addition (1,9-decanediol: 0, 1,000, and 2,000 mg·kg?1 soil). During the incubation, concentrations of inorganic nitrogen (N) and N?O emissions were measured, and quantitative PCR was employed to analyze microbial gene abundances related to N transformation. 【Result】The addition of 1,9-decanediol significantly decreased the net nitrification rate in both soils regardless of organic fertilizer input (P<0.05), exhibiting a dose-dependent suppression effect. Specifically, with organic fertilizer input, high concentrations of 1,9-decanediol decreased the net nitrification rate in black soil by 79% and even shifted the net nitrification rate in red soil from positive to negative. In contrast to nitrification, the addition of 1,9-decanediol either low or high concentrations significantly elevated N?O emissions in both soils, irrespective of organic fertilizer input (P<0.05). Also, a dose-dependent stimulation of N?O emissions occurred only in black soil. In red soil with and without organic fertilizer input, 1,9-decanediol significantly reduced the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and bacteria (AOB) amoA genes (P<0.05), with greater suppression at higher doses. In contrast, the suppressive effect in black soil was significantly weaker than in red soil. Regardless of organic fertilizer application, only high dosage of 1,9-decanediol significantly reduced the abundance of key denitrifying genes in red soil. In addition, partial least squares regression analysis indicated that under organic fertilizer plus BNIs treatment, net N mineralization rate and AOA/AOB amoA abundances were identified as primary determinants of nitrification rates, while net nitrification and mineralization rates were key drivers of N?O emissions. Net nitrification rate was significantly negatively correlated with N?O emissions (P<0.05), suggesting that denitrification rather than nitrification is the major pathway of N?O production. 【Conclusion】Combined application of organic fertilizer with biological nitrification inhibitor significantly reduced nitrification rates in red and black soils, but significantly enhanced N?O emissions. Therefore, rational selection of BNIs types and application rates is critical to avoid paradoxically stimulating N?O emissions while suppressing nitrification in upland agricultural soils.
-
Legacy Effects of Biochar and Organic Fertilizer Application on Soil N2O Emissions
YANG Pizhen, JI Cheng, DONG Caixia, LI Shijin, DING Zihao, XU Cong, NING Yunwang, LIANG Dong, ZHANG Yongchun, WANG Jidong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507010318
Abstract:
【Objective】Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 296 times that of carbon dioxide (CO2). Microbial-driven nitrification and denitrification are major processes contributing to N2O production. While numerous studies have explored the combined effects of biochar and organic fertilizer, most have been short-term, and the legacy effects of aged biochar on soil N2O emissions remain poorly understood. The interactive effects of its combined application with organic fertilizers necessitate further investigation. 【Method】Soil samples were obtained from a seven-year field experiment comprising four distinct treatments: (1) control (urea application, F); (2) one-time basal application of biochar (FB); (3) annual application of organic fertilizer (OF); and (4) combined annual application of organic fertilizer and one-time basal biochar (OFB). In the organic fertilizer treatments, 25% of the urea nitrogen was substituted with organic fertilizer nitrogen. A laboratory incubation experiment was conducted to measure cumulative N2O emissions, quantify the abundances of key functional genes (including nirS, nirK, and nosZ), and partition the relative contributions of fungal and bacterial pathways to N2O emissions. 【Result】The result showed that compared to the control, cumulative N2O emissions were significantly reduced by 49.4% in the biochar treatment (FB), 38.4% in the organic fertilizer treatment (OF), and 59.3% in the combined treatment (OFB). Biochar significantly decreased the fungal contribution to N2O emissions (FDC) by 11.4% and increased the bacterial contribution (BDC) by 5.8%. Organic fertilizer reduced the contribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) by 15.3% but increased the bacterial contribution by 12.1%. The combined application of biochar and organic fertilizer decreased the fungal contribution by 9.7% and increased the bacterial contribution by 15.7%. Structural equation modeling (SEM) indicated that biochar directly reduced FDC and enhanced BDC, organic fertilizers significantly enhance BDC and reduce (nirS+nirK)/nosZ, thereby decreasing N2O emissions. 【Conclusion】These results demonstrate the sustained potential of biochar and organic fertilizer amendments in reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural soils and provide mechanistic insights into how these amendments regulate microbial processes governing N2O production. This research outcome provides scientific support for in-depth analysis of the legacy effects of biochar and organic fertilizer application on soil and their microbiological mechanisms offering scientific guidance for optimizing fertilization practices to achieve the goal of reducing N2O emissions from farmland soils.
-
Effects of Fertiliser Adjustment on the Physicochemical Properties, Bacterial Community Composition and Ion Transport in Saline-Alkali Corn Fields
LIU Weifan, LIU Hao, WAN Menghu, MA Fenglan, LI Yueqi, LI Qingyun, WU Na, LIU Jili
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507080335
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aimed to investigate the synergistic effects of different water and fertilizer treatments on the physicochemical properties, bacterial community structure, and ion transport function of saline-alkali maize fields, thereby providing a theoretical basis for their targeted improvement. 【Method】A field experiment was conducted in saline-alkaline land in Pingluo County, Ningxia. A split-plot design was used with two irrigation levels as main plots: conventional irrigation (w1, 6 000 m3hm-2) and water-saving irrigation (w2, 4 800 m3hm-2), and four fertilization modes as sub-plots: f1 (nitrogen fertilizer alone), f2 (nitrogen with controlled-release fertilizer), f3 (nitrogen with organic fertilizer), and f4 (controlled-release fertilizer with organic fertilizer). Soil physicochemical properties were measured. Bacterial community structure was analyzed by 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing, and the abundance of ion transporter genes was predicted using PICRUSt2 software. 【Result】Water-saving irrigation w2 exhibits no significant difference in its impact on soil physicochemical properties compared to conventional irrigation w1. Compared with w2f1 treatment, the w2f3 treatment significantly increased the contents of soil organic matter (SOM), total nitrogen, alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, and Ca2+ (P<0.05), while significantly decreasing pH, electrical conductivity, and Na+ content (P<0.05). The water-fertilizer interaction had highly significant effects on the contents of sodium, magnesium, potassium, and calcium ions (P<0.01). Microbial analysis showed that the w2f4 treatment significantly increased the Simpson diversity index and Pielou evenness index (P<0.05). At the phylum level, w2f3 and w2f4 significantly increased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria, while decreasing the relative abundance of Acidobacteria (P<0.05). At the genus level, Kaistobacter and Lysobacter were the dominant genera, and their abundance was significantly increased by the w2f3 treatment (P<0.05). Linear discriminant analysis effect size analysis identified 32 biomarker species across five phyla, with w2f3 significantly enriching Proteobacteria and Bacteroidota. Prediction of ion transporter genes indicated that the w2f3 treatment simultaneously activated the magnesium transporter gene CorA and the Na+/H+ antiporter gene nhaA. The ecological dominance of Proteobacteria was positively regulated by KefB and CorA. Mantel test confirmed that SOM and pH were the core environmental factors driving the evolution of the microbial community structure.【Conclusion】Under water-saving irrigation, the combined application of nitrogen fertilisers with organic fertilisers (w2f3) achieves systematic restoration of ecological functions in saline-alkali soils by synergistically enhancing soil fertility, optimising bacterial community structures, and activating ion homeostasis networks. This provides both theoretical and technical underpinnings for the efficient remediation of saline-alkali land.
-
Gross Nitrogen Transformation Rates and Their Regulation in Soils of Three Typical Ecosystems in China
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507290364
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil gross nitrogen (N) transformation processes are fundamental and critical components of terrestrial N cycling. However, the mechanisms controlling gross N transformation rates and their controlling factors across soils with contrasting properties and land uses remain underexplored.【Method】Seven typical soils from three major ecosystems in China were selected: forest (Changsha, Linzhi, Chongqing), grassland (Duolun, Bayanbulak), and upland (Shangzhuang, Quzhou). A short-term incubation experiment was conducted using the?1?N isotope dilution technique combined with a numerical N tracing model. Ten key gross N transformation processes were quantified. 【Result】 Mineralization, immobilization, and autotrophic nitrification were identified as the dominant gross N transformation pathways. No significant differences in gross transformation rates were found among land use types. The means (±S.D.) of gross mineralization rates were 1.40±1.31, 2.07±1.46, and 1.83±0.01 mg·kg?1·d?1 for forest, grassland, and upland soils; corresponding to gross immobilization rates of 4.24±3.04, 6.93±3.79, and 5.54±2.00 mg·kg?1·d?1, and gross nitrification rates of 1.47±1.30, 3.75±1.86, and 5.26±2.52 mg·kg?1·d?1, respectively. Significant differences were observed between individual soils in most gross N transformation rates, indicating spatial heterogeneity in soil N supply and retention capacity. Correlation analysis showed that gross mineralization rates were positively correlated with soil organic carbon and negatively correlated with bulk density, whereas gross nitrification rates were positively correlated with soil salinity. 【Conclusion】These results demonstrate that soil properties and environmental factors jointly regulate the gross N transformation process. Under the context of global change, a multi-scale and multi-factor integrative framework, explicitly accounting for land use type, soil characteristics, and environmental conditions, is essential for improving the accuracy of ecosystem N dynamics modeling and predicting nitrogen loss risks.
-
Quantifying Pedoturbation with Luminescence Dating Techniques: Principles and Progress
ZHANG Aimin, LONG Hao, YANG Fei, ZHANG Jingran, PENG Jun, ZHANG Ganlin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202508180402
Abstract:
Pedoturbation is a ubiquitous surface dynamic process that profoundly influences soil development, nutrient and contaminant transport, soil erosion, and geomorphic evolution. Traditional investigation methods primarily rely on field observations, morphological analysis, or spatial distribution characteristics of short-lived radionuclides, which, while providing valuable information, are often labor-intensive, predominantly qualitative, and limited to short-term quantitative studies. Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating, a well-established Quaternary dating method used to determine the last sunlight exposure of mineral grains, has recently demonstrated unique advantages in quantifying pedoturbation through technological advancements, particularly by single-grain OSL dating techniques. This review examines the fundamental principles of OSL dating, elaborates its methodological framework for pedoturbation quantification, and systematically synthesizes its recent applications in analyzing soil formation processes, reconstructing bioturbation history, and investigating soil erosion-landform evolution relationships. Finally, the review discusses the technique’s strengths and limitations, aiming to demonstrate its potential for addressing pedological questions and promoting interdisciplinary innovation between Quaternary geochronology and soil science.
-
The Effects of Magnetically Treated Water Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community Characteristics and Functions in Three Types of Greenhouse Vegetables
WANG Qi, JING Ruyan, WU Yifei, BAI Yuqian, YAN Tianlong, DING Xinjing
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505200231
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil bacterial communities constitute fundamental drivers underpinning the maintenance of key ecosystem functions within facility agriculture systems. However, the specific regulatory mechanisms and functional outcomes of magnetically treated water (MTW) irrigation on the structural composition and functional dynamics of these soil bacterial communities in protected cultivation environments remain inadequately char-acterized.【Method】 This research investigated soil from cultivation plots of eggplant, cucumber, and pepper. The experimental design comprised irrigation treatments using magnetically treated water and non-magnetized water (NMTW). Employing high-throughput sequencing technology combined with functional prediction analysis (FAPROTAX), the study systematically evaluated the impact of magnetically treated water irrigation on bacterial community composition, diversity, and key environmental driving factors.【Result】Results demon-strated that magnetically treated water irrigation significantly increased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria in cultivated soils across all vegetable plots by 7.43%~61.94% and 1.95%~11.79%, respec-tively. Conversely, it decreased the abundance of Chloroflexi and Gemmatimonadetes by 3.98%~27.42% and 7.89%~9.62%, respectively. At the genus level, magnetically treated water irrigation increased the relative abundance of Streptomyces and Chryseolinea in plot soils across all vegetable cultivation systems. Alpha di-versity analysis revealed that magnetically treated water irrigation significantly enhanced the Chao1, ACE, and Shannon indices of bacterial communities in pepper cultivation plots by 21.27%, 26.74%, and 12.22%, re-spectively. No significant changes in these diversity indices were observed in eggplant or cucumber cultivation plots. Redundancy analysis (RDA) demonstrated that magnetically treated water irrigation altered key envi-ronmental drivers of soil bacterial communities, identifying soil pH, available phosphorus (AP), and total phosphorus (TP) as primary factors regulating dominant phylum abundance. Functional annotation further indicated that magnetically treated water irrigation markedly enriched cellulolysis and nitrification-related functional groups while suppressing human pathogen-associated functionalities.【Conclusion】This study elucidates the multidimensional impacts of magnetically treated water irrigation on soil bacterial communities in facility agriculture systems, specifically addressing compositional, functional, and ecological network charac-teristics. The findings establish a theoretical foundation for regulating soil bacterial structure and metabolic functions, optimizing microbial ecological networks, and promoting sustainable soil management in protected cultivation.
-
Effects of Precipitation Change on Soil Microbial Biomass and Their Stoichiometric Ratios in an Alpine Meadow
PU Zhongyu, HUANG Yuchen, TIAN Shasha, WANG Changting, LIU Dan, LIU Yang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202504070161
Abstract:
【Objective】The increase in global CO2 concentration and climate warming has accelerated changes in the global water cycle and led to changes in global precipitation patterns. The Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP) is highly sensitive to global climate change, and its precipitation patterns have also shifted in response to the global precipitation pattern. Soil microorganisms constitute an important part of the underground ecosystem and play key roles in the soil carbon and nutrient cycle. An in-depth understanding of the response of soil microorganisms to precipitation changes is vital for analyzing the internal mechanism of the impact of global climate change on ecosystem carbon and nutrient cycles. However, it is still unclear how precipitation changes affect soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC), nitrogen (MBN), phosphorus (MBP), and their stoichiometric ratios in the alpine grassland ecosystem of the QTP. Therefore, the current study aims to investigate the response mechanisms of soil microbial biomass and their stoichiometric ratios to precipitation changes in an alpine meadow of the QTP. 【Method】A field manipulation experiment simulating precipitation variations was conducted in an alpine meadow of Hongyuan County, Sichuan Province. Five precipitation gradient treatments were established: a 90% decrease in precipitation (0.1P), a 50% decrease in precipitation (0.5P), a 30% decrease in precipitation (0.7P), a control (1P), and a 50% increase in precipitation (1.5P). Rhizosphere soil was collected in each precipitation gradient treatment. Soil MBC, MBN, and MBP content were determined by the chloroform fumigation method. Soil microbial biomass stoichiometric ratios were calculated by the soil MBC, MBN, and MBP content. At the same time, soil physicochemical properties, including soil water content (SWC), soil pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), and available phosphorus (AP) were also determined. 【Result】The results showed that: (1) Soil MBC and MBN contents were increased with the increase of precipitation; however, MBP was not changed along the precipitation gradient. Compared with the control (1P), soil MBC and MBN content were significantly reduced in the 0.1P treatment; (2) Soil MBC∶MBN and MBC∶MBP showed an increasing trend with the increase of precipitation. The 0.1P treatment significantly reduced the MBC∶MBP ratio when compared with control; (3) Pearson correlation analysis showed that soil MBC, MBN, and MBP content were significantly positively correlated with SWC, and the MBC and MBN content were also significantly positively correlated with NO3−-N and negatively correlated with DOC. The MBC∶MBP and MBN∶MBP were significantly positively correlated with soil C∶N; (4) Multiple linear regression analysis showed that DOC had a significant negative effect on MBC and MBN, while TP and soil N∶P had significant positive effects on MBC and MBN. SWC showed a significant positive effect on MBN and MBP, while the soil C∶N showed a significant negative effect on MBP. Soil DOC and SWC had significant negative effects on MBC∶MBN, and soil C∶N had significant positive effects on MBC∶MBP and MBN∶MBP. 【Conclusion】Our study demonstrates that soil moisture and soil nutrients drive the dynamic response of soil microbial biomass to precipitation changes in the alpine grassland ecosystem of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. By understanding the response mechanism of soil microbial biomass to precipitation changes, we can better predict and respond to the potential impacts of climate change on alpine ecosystems, and develop more effective ecological protection and management strategies to maintain the balance and sustainable development of alpine ecosystems. Therefore, this study provides a microbiological theoretical basis for the management of alpine ecosystems in the context of climate change.
-
Analysis of Research Progress and Development Trends of Land Reclamation at Home and Abroad Based on CiteSpace
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202504020154
Abstract:
【Objective】Through CiteSpace, this study conducted a comprehensive visual analysis of domestic and foreign homestead reclamation literature from the aspects of publication volume, keyword co-occurrence, clustering, etc., aiming to reflect the research progress in the field of homestead reclamation and the existing problems in this field, with a view to providing references for homestead reclamation research.【Method】With "homestead reclamation" and "homestead soil reconstruction" as search terms, literature screening was carried out in CNKI and WOS core collection, and visualization analysis was performed using CiteSpace.【Result】The increase in the number of papers published at home and abroad reflects the increasing research popularity and attention in this field. Domestic scholars focus on land use optimization, urban-rural integration, ecological protection and market circulation, while foreign literature is more inclined to case analysis and technological breakthroughs. In addition, domestic research on homestead reclamation focuses on the interaction between homestead reclamation and policies, while many international literatures discuss reclamation programs and their effects based on case studies and technical practice. 【Conclusion】Both domestic and foreign researches have recognized that soil quality is the key to the success of reclamation, but the domestic emphasis is more on the practice of "problem-countermeasure" closed loop, and the international emphasis is more on the scientific analysis of "mechanism - impact". Future research should prioritize addressing the low efficiency, high costs, and poor regional adaptability of soil reclamation technologies. Targeting soil constraints in rural homestead reclamation, interdisciplinary integration of environmental engineering, land science, ecology, sociology, and economics should be employed to develop a full-chain technical system covering diagnosis, reclamation, and maintenance. Concurrently, efforts must focus on enhancing the operability of these technologies to advance the transition of rural homestead reclamation from mere land leveling to multifunctional ecosystem reconstruction.
-
Manganese Speciation in Hangzhou’s Agricultural Soils: Distribution Patterns and an Artificial Neural Network Predictive Model
YI Zun, MA Jun, ZHENG Panrui, ZENG Huili, CHEN Baoliang, XIAO Xin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506100271
Abstract:
【Objective】The speciation of metal elements in soil determines their environmental functions and effects. Developing predictive models for element speciation based on soil properties is an important approach to enrich the informational value of such data and reduce the number of required analytical indicators. This is of great significance for data mining under conditions of limited information. Most metal elemants, as important trace elements in soils, are widely present and affect crop growth and soil ecosystem health. Their forms and valence state have significant effects on their migration and transformation mechanisms on the surface and underground. Therefore, studying the metal forms in soil helps to understand their geochemical cycles and facilitate the evaluation of their impact on soil electronic networks, providing scientific basis for developing natural soil remediation methods and supporting the green, efficient, and sustainable use of soil. 【Method】This study selected manganese (Mn), a representative trace metal and redox-active element in soils, as the target. A total of 29 surface agricultural soil samples from different locations in the urban area of Hangzhou were collected and analyzed. The samples were characterized for their physicochemical properties, including total organic carbon (TOC), pH, total Mn content, and cation exchange capacity (CEC). The classical Tessier sequential extraction method was used to determine five Mn fractions in the soil: exchangeable, carbonate-bound, Fe–Mn oxide-bound, organic matter and sulfide-bound, and residual, and their correlation with soil physicochemical properties was evaluated. A neural network-based weight analysis method was then applied to predict Mn using soil physicochemical properties as input variables. 【Result】The results show that the soil pH was mainly alkaline, with abundant CEC and organic matter content. However, CEC exhibited high variability and was probably unevenly distributed and may be easily affected by external factors. Further analysis revealed that the average total Mn content in Hangzhou soils was 1.46 g·kg?1, higher than the background value for Zhejiang Province. Among the Mn fractions, Fe–Mn oxide-bound and residual forms were dominant, followed by organic/sulfide-bound, while exchangeable and carbonate-bound forms were the least abundant. Spatial distribution showed a layered pattern for exchangeable and carbonate-bound Mn, decreasing from north to south. Significant positive correlations were observed among most Mn fractions, except for the residual form. Among the physicochemical factors, pH showed the strongest correlation with Mn speciation, particularly a highly significant negative correlation with the exchangeable and carbonate-bound species. CEC was positively correlated with carbonate-bound and organic-bound Mn, while soil organic matter showed no significant correlation with any Mn fraction. Also, the neural network modeling demonstrated that using three parameters: total Mn, pH, and CEC, yielded the best prediction performance, with the coefficient of determination (R2) improving from 0.41 to 0.85, and prediction error reducing from 65% to 16%. 【Conclusion】The findings of this study provide theoretical support for predicting metal speciation in soils based on the observed distribution patterns of Mn and its relationships with soil physicochemical properties. The neural network-based modeling approach proposed herein offers a feasible strategy for deep mining of conventional soil survey data and enables rapid estimation of specific metal species. This contributes to a better understanding of the behavior of Mn in the soil redox network.
-
Effects of Straw Incorporation Combined with Decomposition Agent on Soil Erosion Resistance in Medium-low Yield Purple Soil Sloping Farmland
WANG Dingbin, CHEN Xiaoyan, LIAO Congyun, CHEN Libo, ZHANG Shenghui, ZHANG Qiujie, ZHU Pingzong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506180290
Abstract:
【Objective】 Straw return is vital for improving soil structure, controlling erosion, and mitigating degradation. Nevertheless, the low straw decomposition efficiency under natural conditions greatly limits its widespread application. As a critical measure to promote straw decomposition, investigating the impacts of straw returning combined with decomposition agents on soil erosion resistance of medium-low yield sloping farmland, as well as the underlying mechanisms, holds significant importance for applying soil and water loss control measures that integrate the resource utilization of agricultural waste.【Methods】 A field in-situ monitoring experiment was conducted under the condition of full straw return. With no decomposition agent application as the control, four straw decomposing agents were co-applied with straw at rate of 1, 2, 3, and 4 kg·hm-2 and designed based on the viable bacterial count of the decomposer. The differences in soil erosion resistance and their dominant influencing factors under varying decomposer application rates were clarified.【Results】 The application of straw decomposition agent significantly promoted straw decomposition efficiency and improved soil structure. The straw decomposition amount and efficiency increased significantly with the increase in the application rate of the decomposition agent. Also, application of decompositing agent significantly reduced soil silt and clay contents, while significantly increasing soil sand content, saturated water content, field capacity, and organic matter content. Moreover, the soil erosion resistance was significantly improved with the application of straw decomposition agent. Compared to the control, the comprehensive soil resistance index (CSRI) increased by 43.24% ~ 360.77%. In addition, the results of PLS-SEM showed that the increase of CSRI was mainly governed by the direct binding and consolidation of residual straw (path coefficient 0.43) and the indirect effect of straw decomposition on the increase in soil organic matter content (path coefficient 0.40).【Conclusion】 Straw return combined with straw decomposition agents significantly increased soil erosion resistance of medium-low yield purple sloping farmland. Moreover, the direct effects of residual straw in enhancing soil erosion resistance slightly outweigh its indirect effects in increasing soil organic matter content via decomposition. However, a significant increase in CSRI was only detected when the application rate exceeded 3 kg·hm-2. This indicates that effective enhancement of erosion resistance requires a threshold application rate exceeding 3 kg·hm-2 for decompositing agents. These findings provide scientific guidance for the sustainable utilization of medium- low-yield purple soil sloping farmland and the green and high-quality development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
-
Effect of Tillage Practices and Straw Management on Soil Pore Structure Characteristics in Fluvo-aquic Soil
XIA Hao, WANG Guangshui, XIE Kun, QIAN Yongqi, JIANG Fahui, PENG Xinhua, YAO Shuihong, ZHANG Zhongbin, ZHANG Yueling, BI Lidong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506300317
Abstract:
【Objective】The plough layer of fluvo-aquic soil is shallow, while the subsoil is hard and compacted, exhibiting significant structural obstacles. Tillage and straw return are key measures for improving soil structure; however, the mechanism through which the combination of these agricultural practices affects soil structure remains elusive. 【Method】Undisturbed soil columns (20 cm height × 10 cm diameter) were collected from a fluvo-aquic soil experimental site at the Shangqiu Station of the national field Agro-ecosystem experimental network. The samples represented plots under rotary tillage (RT), deep ploughing (DP), and biennial deep ploughing (BDP), with and without straw returning. X-ray computed tomography (XCT) scanning, ImageJ software, and machine learning techniques were employed to perform three-dimensional reconstruction and visualization of the soil pore structure. The effects of different tillage methods and straw treatments on macroporosity, pore size distribution, pore morphology, network characteristics, saturated hydraulic conductivity, and air permeability were quantitatively analyzed. 【Result】Without straw return, deep ploughing and biennial deep ploughing increased macroporosity by 31.5% and 5.7%, respectively, compared to rotary tillage. With straw return, deep ploughing significantly increased macroporosity by 92.9% and 68.4% compared to rotary tillage and biennial deep ploughing, respectively (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the hydraulic radius increased significantly by 53.8% and 42.9%, respectively. Compactness increased significantly by 1.5 and 2.9 times, and global connectivity increased significantly by 12 times. Both saturated hydraulic conductivity and air conductivity were significantly enhanced (P < 0.05). 【Conclusion】 Deep ploughing increased the hydraulic radius of soil pores, improved connectivity, and enhanced pore network complexity, thereby constructing a relatively favorable soil pore morphology and network structure. This enhanced hydraulic and air conductivity, significantly reducing the structural obstacles in fluvo-aquic soil.
-
Effect of Phenolic Acid Accumulation and Microbial Community Response in Strawberry Continuous Cropping Soil
YANG Tongyi, ZHANG Li, WANG Xiujie, DONG Xiaona, JIA Qianqian
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202509290480
Abstract:
【Objective】Continuous cropping obstacles (CCOs) represent a critical constraint on the sustainable development of the strawberry industry, with core mechanisms involving soil phenolic acid accumulation, microbial community imbalance, and functional degradation. Although existing studies have demonstrated close correlations between phenolic acid autotoxic substances and microbial community changes, the dynamic evolution patterns and causal relationships of phenolic acid-microbiome interactions at the field scale remain unclear. Thus, this study aims to reveal the dynamic changes of phenolic acids, enzyme activity responses, and microbial community structure evolution in strawberry soil under long-term continuous cropping conditions. Also, the results will clarify the driving mechanisms of phenolic acid-microbiome interactions in CCO formation, and provide theoretical basis for developing precise regulation strategies. 【Methods】Greenhouse strawberry continuous cropping soils (0, 2, 5, 15, and 18 years) were selected as research objects to measure soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activities (urease, catalase, acid phosphatase, and sucrase), and phenolic acid contents (p-hydroxybenzoic acid, ferulic acid, and p-coumaric acid). Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technology was employed to analyze bacterial and fungal community structures, and redundancy analysis (RDA) was innovatively combined with structural equation model to construct causal networks of phenolic acid-microbiome-soil function interactions. 【Results】The results revealed that long-term continuous cropping resulted in significant soil acidification (pH decreased from 7.35 to 6.20), with continuous accumulation of phenolic acids reaching 247.3 mg·kg-1 at 18 years. Soil enzyme activities exhibited “increase-then-decrease” nonlinear dynamics, peaking at 5 years of continuous cropping (urease activity reached 1 527 U·g-1h-1), followed by a significant decline at 15 and 18 years. In addition, microbial community analysis revealed that continuous cropping led to a 23.6% reduction in bacterial Shannon diversity, a 43.3% decrease in the bacteria/fungi ratio, and an increase in the relative abundance of pathogenic fungi (e.g., Fusarium). Redundancy analysis first confirmed that p-coumaric acid (p-CA) was the dominant factor explaining bacterial community variation (18.9%), while ferulic acid (FA) was the key factor explaining fungal community variation (21.2%). Structural equation model further revealed that phenolic acids affected microbial communities through dual pathways of direct inhibition (path coefficient = -0.85) and indirect regulation (via soil acidification), with phenolic acids serving as the direct dominant factor inhibiting bacterial communities, while fungal community structure was primarily directly regulated by soil acidification. 【Conclusion】This study elucidated the formation mechanism of CCOs through the “phenolic acid accumulation-soil acidification-microbial imbalance” cascade, revealing the specific effects of phenolic acid as key factors at the field scale. These findings provide a theoretical foundation for developing green prevention and control strategies for CCOs based on microbiome regulation, offering technical support for the sustainable development of the strawberry industry.
-
Research on Soil Salinity Inversion and Mapping Based on UAV Imaging Spectroscopy Data and Machine Learning Algorithms
shizefeng, xumingxing, zhaochengyi, jiaocaixia, chentong, cengrong, LU Jing, ZHENG Guanghui
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502140060
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil salinization seriously restricts the sustainable development of agriculture, and the accurate monitoring of soil salinity is crucial for agricultural management and ecological protection. This study combined unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imaging spectroscopy with machine learning algorithms to explore the inversion and spatial mapping of soil salt content (SSC) in coastal areas.【Method】Feature bands were selected using the Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling (CARS) algorithm, and spectral indices were calculated. Spectral indices were selected using the Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) method. Utilizing PLSR, SVR, and RFR, this study developed prediction models for all spectral bands based on six different spectral transformations, and spectral index prediction models were built using SVR, RFR, XGBoost, and BPNN. The best model was chosen for SSC spatial mapping through accuracy evaluation.【Result】The results showed that the measured soil salt content (SSC) in the study area ranged from 1.23 to 8.96 g kg?1, with a mean of 3.12 g kg?1. Among the full-spectrum models, the random forest regression (RFR) model based on raw spectra processed with Savitzky-Golay (SG) smoothing demonstrated the highest accuracy. For the spectral index models, the extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model with feature selection performed the best. The inversion results revealed that low-to-moderate soil salinity was widely distributed across the study area, with high salinity values scattered sporadically. While XGBoost was well-suited for predicting the overall spatial distribution of soil salinity, the RFR model based on SG-smoothed raw spectra was more effective for mapping areas with low salinity.【Conclusion】This study innovatively combined full-spectrum optimized spectral indices with traditional ones to build a SSC prediction model, offering a new technical path for rapid SSC monitoring in coastal regions using UAV imaging spectroscopy.
-
Spatial mapping of effective soil thickness and its surface matrix constraint mechanism in the black soil area of eastern Mongolia
LI Xinye, SHI Pu, LIU Hang, YANG Yong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502150061
Abstract:
Effective soil layer thickness is a decisive indicator for evaluating soil health and productivity, and accurate depiction of the spatial distribution pattern of effective soil layer thickness and its response mechanism to land use change and surface matrix type is of great significance for the sustainable protection of soil resources. In this paper, we selected the black soil area in the eastern part of Inner Mongolia as the study area, and based on the surface matrix survey data and soil-landscape modeling, we carried out the digital mapping and spatial pattern analysis of effective soil layer thickness in this area, identified the main controlling factors of spatial variability of effective soil layer thickness through SHAP analysis, and ascertained the differential distribution pattern of effective soil layer thickness under different land use types and surface matrix zoning. The results showed that the regression model of effective soil thickness based on Cubist had good performance (R2=0.5,RMSE=43.8), and the generated spatial distribution map could accurately reveal its spatial pattern. SHAP analysis revealed that topographic and climatic factors were the main controlling factors determining the spatial variability of the effective soil thickness, which was specifically reflected in the fact that the high elevation areas within the same watershed were affected by the erosion, and the soil layer was thinner; while the monthly average soil thickness was lower than the monthly average soil thickness, and the monthly average soil thickness was lower than the monthly average soil thickness, which was lower than the monthly average soil thickness. The effect of mean monthly temperature extremes on the effective soil layer thickness was positive. Both surface substrate zoning and land use types have important constraints on the spatial characteristics of the effective soil layer thickness, with the overall soil layer thickness in the residual slope deposit area being greater than that in the slope floodplain and slope deposit areas, and the soil layer thickness in cropland being significantly lower than that in woodland and grassland due to soil disturbance by high-intensity cultivation. The mean values of effective soil layer thickness in different surface substrate zones were in the order of residual slope deposits>slope flood deposits>slope deposits. This paper provides a methodological reference for the spatial modeling and characterization of effective soil layer thickness, and the results of the study can provide a data basis for identifying the background conditions of regional natural resources and their response mechanisms to human interactions.
-
Microbial Assimilating Straw-derived Carbon in Response to Nitrogen and Phosphorus Supply in Paddy Soils: From Microbial Necromass Formation and Accumulation Perspective
YANG Dongqiao, Lu Mengya, WANG Zhiquan, DING Xueli
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202508030379
Abstract:
【Objective】Crop straw input and nutrient supply may influence microorganism-mediated formation and transformation of soil organic carbon (SOC). However, the mechanisms by which straw and nutrient supply influence SOC transformation remain unclear. The objective of this study was to explore how and to what extent of straw-derived carbon (C) can be assimilated by microbes into necromass following crop straw amendment combined with nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients supply. 【Method】Using a 13C-labelled rice straw, the 300-day incubation experiment study examined the pattern of microbial assimilating straw-derived C in necromass (indicated by 13C-amino sugar dynamics) and its accumulation efficiency (CAE) as affected by nutrient supply levels. 【Result】The results showed that straw C could be transferred into microbial necromass rapidly as evidenced by the production of 13C-labelled individual and total amino sugars. There were higher amounts of 13C-amino sugars and CAE during the early stage of straw incubation (before 30 days), but a strong decline of total 13C-amino sugars, especially bacterial necromass (decreased by 18%-28% across treatments) was observed during the middle and later stages. The effect of nutrient supply on microbial assimilation of straw C processes was highly time-dependent, that is, no significant effect in the early stage and significant inhibition in the later stage. Specifically, nutrient supply did not have pronounced effects on straw C incorporation into amino sugars but significantly decreased 13C-amino sugars and CAE towards the end of incubation, suggesting an accelerated turnover of newly-formed amino sugars in treatments of straw combined with nitrogen and phosphorus supply. This might be related to potential changes of microbial strategies regarding nutrient acquisition and C allocation, highlighting the complex relationship between extraneous C and nutrient availability. Noteworthy, the total amino sugars (including 13C-labelled and unlabeled) were higher in nutrient supply treatments despite lower amounts of 13C-amino sugars, suggesting that crop straw addition with nutrient supply stimulated microbial transformation of native SOC components into necromass via microbial C pump mechanisms. 【Conclusion】This study highlights that straw input could stimulate microbial-derived C production and accumulation by accelerating microbial anabolisms via microbial C pump. The nutrient supply exerted an overall negative effect on the straw-derived microbial necromass accumulation in the long term, but stimulated native SOC-derived necromass contribution. It is suggested that the microbial necromass accumulation from newly added (fresh organic matter) and old soil carbon (inherent SOC) needs to be further investigated when evaluating the impacts of straw input on SOC formation and transformation. These findings advance the understanding of the mechanisms of microbial control over SOC formation and sequestration following extraneous organic matter input under varying nutrient conditions.
-
Screening of Soil Healthy Microbial Indicators in Rice-Wheat Rotation Areas in Southern Jiangsu
MO Yingping, GENG Tianzhi, WANG Zijing, ZHANG Na, CUI Qinghao, LIU Cuiying, FAN Jianling
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506260313
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil health is essential to achieving sustainable agricultural development. 【Method】 This study selected the soil of a typical rice-wheat rotation area in southern Jiangsu Province as the research object. By measuring physical, chemical, and biological indicators, principal component analysis was used to identify soil health indicators and determine their weights. Combined with the membership function, the soil health index was calculated and subsequently classified. The microbial community indicators were obtained via high-throughput sequencing, and the random forest model was used to screen the indicators and construct a soil health assessment system based on microbial community indicators. 【Result】The results showed that biochar application significantly increased the content of soil available phosphorus (AP), but the content of available potassium (AK) was slightly lower compared to direct straw returning. The impact of different treatments on the alpha diversity index of the fungal community was more significant compared to that of the bacterial community. Also, the minimum dataset for soil health evaluation in the typical rice-wheat rotation area in southern Jiangsu Province, selected based on principal component analysis, consisted of soil organic carbon, AP, AK, and the activities of SUC and urease. The application of nitrogen fertilizer, single straw returning, and straw carbonization returning significantly increased the soil health index, while double straw returning reduced the soil health index in the short term. Moreover, the microbial community indicators selected by the random forest model were the relative abundance of Spirochaetota, Actinobacteriota, Mortierellomycota, bacterial Chao1 index, fungal Shannon index, and the relative abundance of functional genes such as rbcL, nosZ, ureC, and soxA. 【Conclusion】 The results of this study provide a scientific foundation for the formulation of agricultural management measures in the southern Jiangsu region and offer valuable insights into the construction of a soil health system based on microbial community indicators.
-
Mechanism of a Cadmium-Lead Tolerant Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacterium, Bacillus sp. PSB32, in Metal Removal and Plant Growth Promotion in Contaminated Systems
FU Liyuan, LIU Meijing, LI Yang, HE Jianhua, LI Xiaoyi, LIANG Xinran, HE Yongmei, WU Longhua, ZHAN Fangdong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202508030376
Abstract:
【Objective】Phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) are ubiquitous in heavy metal-contaminated soils; however, their impacts on soil heavy metals and crop growth remain inadequately understood. 【Method】This study investigated the mechanisms and efficacy of Bacillus sp. PSB32, a Cd- and Pb-tolerant PSB strain isolated from the maize rhizosphere in the Yunnan Plateau, in removing aqueous Cd and Pb and influencing maize (Zea mays L.) growth in contaminated soils.【Result】Under Cd and Pb stress, strain PSB32 primarily removed Cd via intracellular accumulation(43.7%) and surface precipitation(43.2%), with biosorption playing a secondary role (13.0%). In contrast, Pb removal was dominated by surface adsorption (53.2%), followed by surface precipitation (28.8%) and intracellular accumulation (18.0%). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed the formation of granular precipitates on the bacterial cell surface, which were identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD) as Cd?(PO?)?, Pb?(PO?)?Cl (Pyromorphite), and Pb?(PO?)?OH. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy confirmed the involvement of functional groups (e.g., -COOH, -OH, -NH?) and anionic groups (e.g., PO?3?, SO?2?) in the surface complexation of Cd and Pb. In the pot experiments, the amendment of PSB32 across the three differentially contaminated soils (contaminated farmland, tailings, and slag) led to a consistent increase of 5.90%-9.43% in the residual fraction of Cd, alongside a decrease of 7.20%-18.8% in the reducible fraction of Pb. Concurrently, the soil available phosphorus content was enhanced by 3.00%-18.7%, which contributed to a substantial promotion of maize biomass, ranging from 25.7% to 82.2%. Notably, PSB32 also increased the Cd content in maize shoots by 61.9% and 32.9% in the farmland and tailings soils, respectively, and significantly enhanced the accumulation of Cd and Pb in the roots by 365% and 35.3% in the slag soil.【Conclusion】In conclusion, Bacillus sp. PSB32 demonstrates a dual ecological function: effectively removing aqueous Cd and Pb through multiple mechanisms, and enhancing plant tolerance in contaminated soils by altering metal speciation and improving phosphorus nutrition. This strain presents a promising microbial resource for the bioremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils.
-
Study on the Device and Collection Method for In-situ, Dynamic, Visualized, and Precise Matching Collection of Rhizosphere Soil and Root Exudates
ZHANG Yining, QIN Mingjiao, LU Junjiao, CHEN Tongyao, SHI Xiaoyu, CHEN Xiao, MA Liya, SHI Yu
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501270043
Abstract:
【Objective】The rhizosphere is the interface between plants and soil, and plants affect the composition of soil microbial communities by secreting root exudates, while rhizosphere microorganisms can affect plant physiology and development through multiple mechanisms. Therefore, the development of accurate and applicable root exudate and soil sample collection methods are very important in understanding the ecological process of plant root-soil interface. However, the in-situ collection of rhizosphere soil and root exudates remains understudied. 【Method】This paper introduced a novel device for the in-situ dynamic visualization and accurate collection of rhizosphere soil and root exudates. The device comprises a plant growth compartment, a root growth compartment, a soil compartment, and a root exudate sampling system. The device is designed by partitions, planting seeds or seedlings in the plant growth compartment, allowing the root system to extend into the lower root growth compartment through a slit at the bottom. Also, the nylon membrane isolates the soil from the root system to ensure a two-way pure exchange. On the one hand, it allows soil nutrients to infiltrate, ensuring normal plant growth, and on the other hand, it prevents particle contamination. At the same time, a multi-interface connected sampling system is set up to realize the accurate partition collection of root exudates. The sampling process is automated, with a vacuum pump controlled by a solenoid switch and a program to regularly rinse and extract secretions into the sampling bottle. For soil sampling, the depth and distance from the root system are flexibly selected, and the soil quantity is estimated by the sampling tube scale to ensure the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the experimental data. For validation, root exudates of wheat during the grain-filling stage were collected by both the device collection method and the solution collection method. The content of quercetin in the root exudates was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. A standard curve was prepared using quercetin as the standard substance, and the content of quercetin in the root exudates was calculated. 【Result】This device innovatively integrated the functions of plant growth, root exudates sampling and rhizosphere soil collection. It realized the accurate, in-situ, continuous and dynamic collection of plant root exudates and rhizosphere soil through ingenious design, and the collection range could be accurately concentrated in the root system and the soil environment in the same area, so as to ensure the simultaneous collection of exudates and rhizosphere soil. During collection of root exudates, the content of quercetin obtained by the device collection method was close to that by the solution collection method, and it eliminated the cumbersome operations such as root stripping, supported continuous sampling at multiple time points for the same plant, and significantly improved the research efficiency of individual plants. Moreover, this method ensured the normal growth of plants, and there was no interference with soil components, and provided high accuracy. 【Conclusion】This device, with its comprehensive functions, provides efficient sampling capacity and precise control mechanism, and can serve as a powerful tool in the field of plant physiological ecology, and is conducive for promoting the in-depth development of soil microbiology research.
-
Community Structure of Aerobic Methanotrophs and Environmental Drivers in Coastal Wetlands
lixiaoyong, wanghuan, zhengyue, wuyicheng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503280141
Abstract:
【Objective】 This study investigated the community structure of aerobic methanotrophs in coastal wetlands of southeastern China and the key environmental factors shaping their distribution. 【Method】Sediment samples were collected from four coastal wetlands (Shanghai, Fuzhou, Xiamen, and Dongguan). Methane oxidation rates were determined, physicochemical properties were analyzed, and 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing was performed to resolve community composition. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was applied to assess the influence of environmental factors such as temperature, precipitation, and salinity on community distribution. 【Result】The results showed significant differences in methane oxidation rates among wetlands, with the highest rate observed in Fuzhou (0.11 mmol·L-1·d-1) and the lowest in Dongguan (0.058 mmol·L-1·d-1). Community composition also varied substantially: Methylomicrobium dominated in Shanghai and Xiamen, while Methylobacter and Methylocystis were more abundant in Fuzhou and Dongguan. RDA indicated that temperature, water content, and salinity were the major drivers of community structure, with Methylobacter abundance positively correlated with temperature, and Methylocystis abundance negatively correlated with salinity. These findings demonstrate that the community structure and metabolic activity of aerobic methanotrophs in coastal wetlands are regulated by multiple environmental factors, and regional differences are primarily shaped by the adaptive responses of functional taxa to local conditions. 【Conclusion】This study highlights the spatial heterogeneity and environmental drivers of methanotroph communities in coastal wetlands and provides theoretical insights into wetland carbon cycling processes.
-
Research Progresses and Future Prospects on Soil Pipe Erosion
XU Ximeng, LIANG Wenqian, ZHENG Fenli
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507020322
Abstract:
Soil pipe erosion is a special erosion process caused by the formation and expansion of underground soil pipes, which has an important contribution to the development process of gully erosion and the gravitational erosion processes such as landslide and collapse. It mainly affects the runoff-erosion-sediment transport process of slope and watershed by changing the near-surface soil hydrological conditions. However, due to its concealment and complexity of genesis, related quantification research faces great challenges. Based on the bibliometric analysis method, this paper systematically reviews the development history of soil pipe erosion research, and identifies the hot spots and development directions in the field of soil pipe erosion research. Aiming at the current research focus, this paper overviews the dynamic process of soil pipe formation, summarizes the multiple factors affecting soil pipe erosion, and analyzes the dynamic mechanism and harm of soil pipe erosion. In the future, it is necessary to innovate the monitoring methods of soil pipe erosion, clarify the dynamic mechanism of soil pipe erosion, quantify the contributions of key influencing factors, and develop a water erosion prediction model containing the processes of soil pipe erosion, so as to provide a scientific basis for soil pipe erosion risk assessment and optimization of governance measures.
-
Research Progress on Soil Particulate versus Mineral-Associated Organic Carbon dynamics Mediated by Microorganisms
LIU Lei, ZHANG Yunlong, ZHANG Junling, WANG Ling, SUN Shiyou
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505260240
Abstract:
The turnover and stabilization of soil organic carbon (SOC) play a crucial role in the terrestrial carbon cycle, contributing approximately 25% to natural climate solutions. Particulate organic carbon (POC) and mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC) are pivotal in the soil carbon dynamics. Soil microorganisms are the primary drivers of the carbon cycle, by decomposing plant residues to form POC via the “ex vivo modification” pathway and accumulating microbial residual carbon via “in vivo turnover” pathway, which then combines with soil minerals to form MAOC. However, the role of microorganisms in POC and MAOC formation is constrained by multiple factors, including nutrient management practices, soil properties, and climatic conditions, which limit the microbial regulation of carbon sequestration in agricultural soils. This article systematically introduced the framework of POC and MAOC. The contributions of growth anabolism (living and residual microorganisms) and non-growth anabolism (enzymes and extracellular polymers) to POC and MAOC were described. This study elucidated the regulatory mechanisms governing POC and MAOC through microbial community structure and physiological functions, whilst analyzing the influencing factors. On this basis, the study systematically considered the mechanisms and approaches by which microorganisms regulate and increase SOC, providing an important basis for constructing a theory of SOC increase based on physical-biological synergistic regulation.
-
Green Intelligent Fertilizers: Innovative Approaches to Intelligent Regulation and Industrialization Pathways
ZHANG Fusuo, CHENG Lingyun, HUANG Chengdong, ZHANG Lin, WANG Jianchao, LYU Yang, LU Zhenya, WEI Changzhou, MA Wenqi, Ma Hang, SHEN Jianbo
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202508230411
Abstract:
As global agriculture evolves alongside the increasing demand for environmental protection, green intelligent fertilizers have emerged as a novel approach to enhancing crop productivity and resource use efficiency. This paper reviews the core concepts and development status of green intelligent fertilizers, exploring the principles of intelligent regulation within plant-microbe-environment interactions and the design and application strategies based on the rhizobiont theory. Green intelligent fertilizers operate by maximizing the biological potential of crops and microorganisms to regulate the integrated plant-microbe-soil system, thereby promoting plant growth and minimizing environmental impact. Looking ahead, breakthroughs in material innovation, process optimization, and intelligent fertilizer formulation will enable intelligent fertilizers to drive agricultural green transformation, providing critical support for global food security and environmental sustainability.
-
Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on phosphorus uptake and distribution in rice for multiple generations*
guxinyue, caichuang, yinbin, zhuchunwu
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502280084
Abstract:
Abstract:[Objective] With the intensification of human activities since the Industrial Revolution, there is a continuous rise in carbon dioxide concentration ([CO2]) in the atmosphere, which has become the main feature of global climate change. Rice being an important staple crop, it is important to explore its absorption and distribution of phosphorus under a long-term elevated CO2 environment. [method] In this study, a multigenerational experiment was carried out cultivating Yangdao 6 (indica) and Wuyungeng 23 (japonica) in the Free Atmospheric CO2 Enrichment System (FACE) in Changshu, Jiangsu Province. The experiment was carried out under ambient [CO2] and elevated [CO2] (increased by 200 μmol?mol-1) conditions for seven generations, and the differences in phosphorus concentration, phosphorus uptake, and phosphorus distribution ratio between the single-generation and multigenerational rice plants were evaluated. [Result] (1) Long-term elevated [CO2] had no significant effect on the phosphorus concentration of multigenerational rice plants in Yangdao 6 and Wuyungeng 23. (2) The long-term elevated [CO2] significantly increased the phosphorus uptake of shoots in single-generation and multigenerational rice plants. However, the average increase in phosphorus uptake of the shoot and panicle of the offspring plant of Yangdao 6 was lower than that of the single-generation plant. On the contrary, the average increase in phosphorus uptake of shoot, straw, and panicle of the offspring plant of Wuyungeng 23 was higher than that of the single-generation plant under elevated [CO2]. (3) The average increasing effect of elevated [CO2] on the distribution ratio of phosphorus in the straw of Wuyungeng 23 increased significantly with the increase in generations of maternal seeds under elevated [CO2] treatment. [Conclusion] The results indicate that in the past, based on the single-generation short-term FACE studies, the real effect of long-term elevated [CO2] on phosphorus uptake and distribution in rice plants could not be accurately predicted in the future. Therefore, this study provides guidelines for field-level phosphorus fertilizer management in a future high-CO2 world.
-
The Impact of anoxic Microsites on Soil Respiration and Their Distribution Characteristics in Soil Aggregates
zhang xu sheng, wang xia, zhao yun fei, yuan meng han, wang fei, xia jie yi, li liu jun
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501050008
Abstract:
Anoxic microsites are potential significant contributors to the inhibition of soil organic carbon loss. Soil aggregates, as potential suitable sites for the development of anoxic microsites, are closely related to the accumulation of soil organic carbon. However, few studies have investigated the impact of anoxic microsites on organic carbon within soil aggregates. This study collected dryland soils from four types of vegetation restoration and employed soil incubation and gas chromatography to measure and calculate the extent of anoxic protection. Anaerobic conditions were used to obtain soil samples from the internal and external layers of macroaggregates through the dry dissection method, and their anoxic microsite abundance and organic matter composition were compared. The results indicate that the extent of anoxic protection was 33.5% and 36% of natural shrubland and natural grassland, respectively. Planted forest exhibited a lower protection value at 15.9%, while farmland exhibited the most negligible anoxic protection at ?8.9%. And the internal layer of macroaggregates generally exhibits a high concentration of Fe2+, consequently, this region is characterized by a greater prevalence of hypoxic microenvironments. Organic matter, such as aromatics, lipids, and lignin, protected by anoxic microsites, is relatively abundant in the inner layer of aggregates. Soil respiration rate was significantly negatively correlated with the extent of anoxic protection. The aforementioned results reveal the formation mechanism, stability, and protective role of anoxic microsites within the inner layers of soil aggregates towards organic matter. The extent of anoxic protection is contingent upon a stable soil environment. These microsites selectively conserve the reducing organic matter within macroaggregates, significantly reducing the loss of soil organic carbon. This finding contributes a nuanced understanding of soil carbon cycling and carbon sequestration processes.
-
Soil Health Evaluation of Farmland in Arid Areas Based on Minimum Data Set
JING Yili, HUANG Bin, SU Xinyue, WU Lei, LI Jianhua, XU Minggang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202509010431
Abstract:
【Objective】 Soil health assessment is a critical technical approach for achieving sustainable farmland management. However, existing evaluation systems often suffer from limitations such as indicator redundancy and high operational costs, which hinder their widespread application. This study aims to construct a cost-effective and efficient minimum data set (MDS) for soil health evaluation in the semi-arid farmland regions of the Loess Plateau, and to scientifically validate its reliability and applicability under local ecological conditions. 【Method】A total of 100 soil samples were collected from dryland farmlands in Wuzhai County, Shanxi Province, a representative area of the Loess Plateau. A comprehensive set of 23 soil indicators covering physicochemical and biological properties was analyzed. The MDS was established through an integrated statistical procedure that combined the principal component analysis (PCA), norm value calculation, and Pearson correlation analysis to identify the most representative and non-redundant indicators. The soil health index (SHI) was subsequently calculated using both linear and nonlinear scoring functions based on the MDS and the total data set (TDS). The performance of the MDS was evaluated by comparing SHI values derived from both data sets and further validated through correlation analysis with crop yield data. 【Result】The MDS was successfully established and included six key indicators: soil bulk density, total nitrogen, urease, cellobiohydrolase, bacterial Shannon index, and fungal Shannon index. These indicators accounted for 82.47% of the total variance explained by the TDS. Notably, biological indicators constituted two-thirds of the MDS, underscoring the vital role of microbial processes in soil health within arid regions. The SHI values calculated using the MDS showed a strong and significant positive correlation with those from the TDS under both nonlinear and linear scoring functions (P < 0.001), confirming the MDS’s capability to effectively represent the full data set. Validation with crop yield data further demonstrated that the nonlinear scoring function applied to the MDS provided a better fit (r = 0.70) than the linear function (r = 0.64), indicating its superior suitability for soil health assessment in the regions. The average SHI across the studied area was 0.49, reflecting a moderate overall soil health status. Spatially, soil health exhibited a pattern of lower values in the north and higher values in the south, largely influenced by the high erodibility of loess soils and more pronounced aridity in the northern part. 【Conclusion】This study developed a simplified yet robust MDS for soil health evaluation in semi-arid farmland systems of the Loess Plateau, effectively balancing comprehensiveness and feasibility. The results highlight the essential role of microbial diversity and functional indicators, such as enzyme activities and bacterial/fungal diversity, in evaluating soil health under dryland conditions. The spatial variation in soil health calls for region-specific management strategies, particularly in northern areas where soil erosion and moisture limitation are more severe. It is recommended that future research place greater emphasis on incorporating microbial functional parameters into soil health assessment frameworks. Moreover, integrating emerging technologies such as soil sensing and molecular tools could further enhance the efficiency and predictive power of soil health monitoring in arid and semi-arid agricultural landscapes.
-
Precision and Economic Analysis of Determining Different Forms of Soil Iron Contents Using Spectroscopic Techniques
TANG Yun, GAO Weichang, PAN Wenjie, CAI Kai, ZENG Yuntao, YANG Jing, JIANG Chaoying, ZHENG Gaunghui, LI Decheng, ZENG Rong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503280144
Abstract:
【Objective】Iron (Fe) is an essential micronutrient for plant growth. Accurate monitoring of different forms of iron (Total Fe, Available Fe, Free Fe) is essential for soil health management and agricultural production optimization. Total iron and free iron are also necessary indicators to identify certain soil types. Compared with traditional soil determination methods, spectral technology is rapid, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly, and is gradually becoming an alternative for soil Fe determination in recent years. However, there are few reports on the systematic inversion of different forms of iron by spectral technology.【Method】Based on the color parameter (CP), visible near infrared (VNIR), mid infrared (MIR) , and fusion spectrum (SF) were used to obtain data of 501 typical farmland tillage layer (0~20cm) soil samples in Guizhou Province. The spectrum was smoothed by Savitzky-Golay (SG) denoising, and then the baseline was corrected by the standard normalization (SNV) method. Partial least squares regression (PLSR) and support vector machine (SVM) were used for modeling, respectively. The system compared the predictive performance of single spectra and fused spectra for the three types of iron fractions. Moreover, the relationship between accuracy and cost of different prediction strategies was quantified using two indicators: Cost-Efficiency Ratio (CER) and Efficiency Index (EI).【Result】The results show that: (1) in the single spectral model, VNIR spectrum performed best in the prediction of total iron (determination coefficient R2 = 0.85, relative analysis deviation RPD = 2.59, root mean square error RMSE = 5.48 g·kg-1), while MIR spectrum had the highest accuracy in the prediction of free iron (R2 = 0.80, RPD = 2.23, RMSE = 4.15 g·kg-1). Also, the decision level fusion (SF3) spectrum further improved the prediction accuracy of the three forms of iron, among which the effective iron increased the most, but it was still difficult to achieve effective prediction (RPD = 1.37). Thus, using spectral technology to predict soil available iron is not recommended. (2) The cost accuracy analysis showed that the spectral technology can significantly reduce the cost (by 40%~85%) of soil iron characterization. VNIR and MIR technologies had high accuracy and were cost-effective in the prediction of total iron and free iron, and were suitable for scenarios requiring comprehensive consideration of accuracy and cost. However, the accuracy improvement of fused spectrum (SF) was limited, and the cost increased more, which is suitable for scenarios requiring higher accuracy. 【Conclusion】This study shows that spectral technology can significantly reduce the cost of soil iron content measurement on the basis of ensuring a certain prediction accuracy, and can replace the traditional methods to achieve efficient monitoring of total iron and free iron, so as to provide effective technical support for the implementation of precision agriculture.
-
Advances in Understanding the Interaction Between Soil Iron Oxides and Organic Carbon and its Effect on Carbon Stabilization
TIAN Yihui, XU Yun, HOU Jingtao, HUANG Chuanqin, TAN Wenfeng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502020044
Abstract:
Soil serves as a crucial terrestrial reservoir of organic carbon, plays a significant role in mitigating climate change and ensures sustainable agricultural production. Iron oxides, as important active components in soil, are integral to the stabilization and turnover of soil organic carbon. These oxides interact with organic carbon through processes such as adsorption, co-precipitation, and other mechanisms, forming relatively stable iron-carbon complexes. Additionally, iron acts as a catalyst in the polymerization of organic carbon, facilitating the transformation of organic carbon into more stable forms via the Maillard reaction. However, these protective functions of iron oxides can be modulated by environmental factors, which may reduce their effectiveness under fluctuating conditions. During redox cycling of iron, iron oxides can also accelerate the organic carbon turnover by releasing reactive oxygen species and transferring electrons. This review provides a systematic examination of the mechanisms by which soil iron oxides influence carbon turnover and sequestration, while also exploring the reciprocal effects of organic carbon on iron cycling. This study further evaluates the role of environmental factors and key biological processes in regulating iron-carbon cycling. Particular emphasis is placed on the critical roles of mineral protection and biological activity constraints in maintaining soil carbon pool stability. Finally, the review proposes several directions for future research in the iron-carbon field. These include the verification and quantification of soil organic carbon polymerization reactions, understanding the regulatory role of soil microzone biological processes on iron-carbon coupling, exploring the trade-offs between organic carbon fixation and morphological transformation during iron redox processes, and integrating a cross-scale model for iron-carbon coupling and carbon sink potential assessment. Conducting these studies will facilitate the accurate analysis of physical-chemical-biological mechanisms of soil iron-carbon coupling and furnish insights to promote a more profound understanding of iron-carbon dynamics and formulate strategies for enhancing soil carbon sequestration.
-
Distribution of Photosynthetic Carbon in Corn-soil System and Its Effect on Maize Biomass under Biological Fertilization
GONG Yong-qi, FAN Cong-cong, YIN Chang, ZHU Guo-fan, ZHAO Li-xia, SHEN Ren-fang, WANG Xiao-yue, JIANG Yu-ji
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503060105
Abstract:
【Objective】To investigate the effects of different biological fertilization practices on photosynthetic carbon (C) allocation and maize biomass, a field experiment was conducted at the Red Soil Ecological Experimental Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. 【Method】Four treatments were selected from a long-term biological fertilization trial: ① Chemical fertilizer + Organic manure (FO), ② Chemical fertilizer + Organic manure + Microbial inoculant (FOP), ③ Chemical fertilizer + Organic manure + Nematode inoculation (FON), and ④ Chemical fertilizer + Organic manure + Microbial inoculant + Nematode inoculation (FOPN). After soil samples were collected from the four treatments, a pot experiment using 13CO? pulse labeling was performed to study the allocation of photosynthetically fixed carbon within the maize-soil system. 【Result】The 13C pulse labeling results showed that, compared with the FO treatment, the FOPN treatment significantly increased the total amount of photosynthetic carbon in both aboveground and belowground parts, with a more pronounced increase in the aboveground portion. This led to a reduced belowground-to-aboveground allocation ratio of photosynthetic carbon. Moreover, the trends of maize biomass in aboveground and belowground parts under different treatments were consistent with the trends in carbon allocation. All biofertilization treatments significantly increased total and available soil nutrients, the total abundance of nematodes, and altered nematode community composition, with the most pronounced effects observed under the FOPN treatment. Random forest analysis and structural equation modeling jointly revealed that biofertilization enhances nutrient availability and increases aboveground photosynthetic carbon allocation by elevating nematode abundance and shifting community composition, ultimately promoting maize aboveground biomass.【Conclusion】 This study clarifies the mechanism by which nematode predation influences maize productivity and provides important theoretical guidance for biological fertilization technologies in red soil ecosystems.
-
Plant–soil feedback driven mechanisms and regulation strategies for soil health
Wang Guangzhou, Shen Jianbo, Zhang Junling, Zhang Fusuo
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506290314
Abstract:
A healthy soil is the foundation for ensuring food security and serves as a core pillar for achieving agricultural green development. However, current intensive agricultural systems are primarily focused on maximizing crop yields, relying heavily on high-yielding crop varieties and external inputs such as synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This overreliance often overlooks the impact of crops and field management practices on soil health, leading to various forms of soil degradation that negatively affect crop productivity and food quality. Drawing on the ecological concept of plant-soil feedback (PSF), this paper proposes a new systematic research paradigm that places soil health as the key to the co-improvement of farmland quality and crop productivity. Future sustainable agriculture urgently requires the development of system-based strategies and solutions grounded in PSF theory, integrating aboveground crop management with belowground soil processes in a tightly coupled manner. By elucidating the reciprocal interactions among different components of the soil ecosystem, we can develop soil health management technologies based on positive plant-soil feedback, thereby enhancing the synergy between productivity and other soil multifunctionalities. Specifically, at the individual plant level, modern molecular breeding and functional genomics can be leveraged to modify root architecture, root exudate composition, and signal transduction properties in a targeted way. This enables the precise recruitment of beneficial microbes and suppression of pathogens, triggering cascade amplification effects that reinforce positive feedback loops and mitigate negative ones. At the field management level, integrated strategies such as crop-microbiome holobiont breeding, optimized nutrient management, conservation tillage, and diversified cropping systems can promote beneficial interactions between crops and soils. These approaches reduce dependence on external inputs, improve internal system efficiency, and ultimately achieve the co-enhancement of crop yield and soil health.
-
Differential Responses of Net Nitrogen Transformations in Rhizosphere Soil with Different Root Diameters to Nitrogen Deposition
Lu Lu, Zhou Jiake, Wang Jing, Jing Hang, Cheng Yi
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503200125
Abstract:
【Objective】Under the influence of root, rhizosphere soil has rich nutrients and active microbial biochemical activities, and its nitrogen (N) cycling process is significantly faster than that of non-rhizosphere soil. However, whether rhizospheric N transformation characteristics differ among root diameters, and whether their responses to N deposition are significant remain unclear. 【Method】This study focused on non-rhizosphere and rhizosphere soil with different root diameters of Pinus tabuliformis on the Loess Plateau of China (very fine root, 0-0.5 mm; medium fine root, >0.5-1.0 mm; coarse fine root, >1.0-2.0 mm). Additionally, long-term experimental plots were established with four simulated N deposition levels (N 0, 3, 6, 9 g·m-2·a-1). An indoor incubation experiment was carried out to determine changes in soil net N mineralization and nitrification rates of non-rhizosphere soil and rhizosphere soil with different root diameters, as well as their responses to N deposition. 【Result】The results showed that: 1) The net N transformation rates in rhizosphere soil varied significantly among different root diameters (P<0.05), and the highest rates were observed in rhizosphere soil of very fine root (2.16 mg·kg-1·d-1 for mean net N mineralization rate and 6.67 mg·kg-1·d-1 for mean net nitrification rate). 2) With the increase of N addition, net N mineralization and net nitrification rates decreased first and then increased, peaking at N 6 g·m-2·a-1 or 9 g·m-2·a-1 treatment. In contrast, the net N transformation rates of non-rhizosphere soil were significantly inhibited by N addition (P<0.05). Moreover, net N transformation rate of rhizosphere soil of very fine root was more sensitive to N addition than that of coarse root and non-rhizosphere soil. 3) Correlation analysis and structural equation model showed that low N addition inhibited net N transformation rates through its significant association with soil ammonium content, whereas high N addition enhanced rates via significant linkage to soil carbon-nitrogen ratio. 【Conclusion】N deposition significantly altered the N transformation process of rhizosphere soil, with distinct variations observed among different root diameters. Therefore, strengthening the study of N transformation process in plant rhizosphere soil is helpful to refine the rhizosphere effect and the assessment of forest soil N cycle.
-
Study on the Process of Nitrite-Dependent Anaerobic Methane Oxidation in Rhizosphere and Bulk Soils of Paddy Fields
dailei, wangyanping, baiyanan, shenlidong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503250136
Abstract:
【Objective】Paddy fields are significant anthropogenic sources of methane emissions, and anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM) is an important pathway for mitigating methane emissions from paddy fields. The application of nitrogen fertilizers in paddy fields makes nitrite a primary electron acceptor for AOM. However, existing studies have focused on nitrite-dependent AOM in bulk soils of paddy fields, leaving the activity and functional microbial community characteristics of nitrite-dependent AOM in rhizosphere soils poorly understood. 【Method】Through indoor slurry incubation experiments combined with 13CH4 stable isotope tracing, quantitative PCR, and high-throughput sequencing, this study systematically investigated the nitrite-dependent AOM activity, NC10 bacterial gene abundance, and community structure in rhizosphere soils and bulk soils at different depths (0-10, 10-20 and 20-30 cm) under different fertilization treatments (CF: chemical fertilizer; OF: organic fertilizer combined with chemical fertilizer; SF: straw return combined with chemical fertilizer). 【Result】The results showed that the nitrite-dependent AOM activity in rhizosphere soils ranged from 1.03 to 2.42 nmol·g-1·d-1, which was significantly higher than that in 0-10 cm, 10-20 cm, and 20-30 cm bulk soils, respectively. The pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), and nitrite contents were identified as the main environmental factors influencing nitrite-dependent AOM activity. The NC10 bacterial gene abundance in 0-10 cm bulk soils ranged from 7.44×106 to 2.39×107 copies·g-1, which was significantly higher than that in rhizosphere soils, 10-20 cm, and 20-30 cm bulk soils, respectively. Correlation analysis revealed that SOC was the primary factor affecting NC10 bacterial abundance. Additionally, high-throughput sequencing revealed significant differences in NC10 bacterial community structure between rhizosphere and bulk soils. PCoA analysis indicated that soil water content, pH, and nitrate content were the main environmental factors influencing NC10 bacterial community structure.【Conclusion】These findings demonstrate significant differences in nitrite-dependent AOM activity, NC10 bacterial abundance and community structure between rhizosphere and bulk soils under different fertilization treatments. The findings demonstrate that the rhizosphere serves as an active hotspot for nitrite-driven AOM, providing a deeper understanding of the AOM process and offering theoretical basis for mitigating methane emission from paddy fields.
-
Study on the Community Characteristics and Ecological Functions of Periphyton
ZHANG Zhike, SHI Qing, ZHAO Bin, WEI Yuquan, ZHANG Hao, CAI Linying, SONG Yinan, CHEN Weisheng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502170064
Abstract:
Periphyton (PHT), widely distributed in aquatic ecosystems, function as critical multi-interface carriers across water-sediment-atmosphere boundaries, playing vital ecological roles in energy flow, element cycling, and pollutant remediation. This work reviews recent advancements in the fields of PHT research, both in domestic and international contexts, emphasizing on the analysis of community structures and the corresponding characteristics exhibited under varying environmental conditions. The ecological functions of PHT within aquatic ecosystems are explored, along with the identification of key environmental factors like environmental conditions and media that influence its growth and ecological functions. PHT plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling within aquatic ecosystems. As primary producers, they offer essential nutrients to the ecosystem and serve as effective bioindicators of water quality, with the ability to bioaccumulate heavy metals. Key environmental factors such as temperature, light availability, and pH regulate the growth of PHT, with dominant species in the community shifting in response to changing environmental conditions. Furthermore, anthropogenic activities, nutrient loading, and soil conditions significantly influence the composition, structure, and functional dynamics of PHT communities. Additionally, this work evaluates the potential of the application of PHT-based research to environmental management, sustainable agricultural practices, as well as ecological amendment, with an emphasis on innovative eco-engineering solutions. According to these findings, present study recommends that future work should undertake more in-depth and systematic investigations into the roles of PHT in the degradation and treatment of emerging contaminants, the integration with multidisciplinary approaches and advanced technologies, as well as their applications in other fields. This review aims to provide a theoretical framework and scientific guidance for interdisciplinary research and industrial development on identifying PHT community structures, enhancing ecological functions, and advancing sustainable ecological restoration practices.
-
Distribution Characteristics of Typical Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Different Land Types in Jinji River Basin
Li Yeshan, Feng Shuo, Zhang Zhuoyi, Zhu Changxiong, Zhang Yanrong, Li Hongna
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502130059
Abstract:
【Objective】 The application of antibiotics has significantly advanced animal husbandry and agriculture. However, the resulting contamination by antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) poses a severe threat to the ecological environment and human health. This study aims to systematically investigate the effects of different land use types within the same region on the distribution of ARB and ARGs in soil. 【Method】 This study collected 210 soil samples from six typical land use types (vegetable fields, wheat fields, flower gardens, orchards, nurseries and livestock farms) in the Jinji River basin of Beijing. The abundance of total cultivable bacteria, chlortetracycline-resistant bacteria, sulfamethoxazole-resistant bacteria, and representative ARGs in the soil was measured. Additionally, the structural characteristics of representative soil microbial communities were analyzed using high-throughput sequencing technology. 【Result】 The results indicate that the resistance contamination in Zhang Town and Longwantun Town of the Jinji River basin was the most severe. The abundance of ARB, ARGs, and intI1 in vegetable field soil was significantly higher than that in other land use types (P<0.05). Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Saccharibacteria, and Deinococcus-Thermus were the dominant bacterial phyla in the soil. Also, Lysobacter and Devosia were identified as the main host bacteria for ARGs, and they showed significant positive correlations with sul1, sul2, tetG, tetX, and intI1 (P<0.05). 【Conclusion】 Based on our results, the resistance level of vegetable field soil in the Jinji River sub-basin was significantly higher than that of other land use types. Thus, it is essential to focus on the optimized application of organic fertilizers to reduce the potential risks of soil microbial resistance and ecological health.
-
The Behaviors and Influencing Factors of Reactive Oxygen Species Generation at the Soil-Water Interface Containing Biochar Under Simulated Solar Illumination Conditions
WANG Haowei, HOU Yucheng, YAO Jiayi, LI Mengwei, FANG Jing, SHAN Shengdao
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506200296
Abstract:
【Objective】Reactive oxygen species (ROS) at the soil-water interface play a crucial role in carbon/nitrogen cycling and pollutant transformation. However, it is still unclear how biochar influences the formation of ROS at the soil-water interface. Thus, this study aims to explore the formation behaviors and factors influencing ROS generation at the soil-water interface containing biochar. 【Method】Under simulated solar illumination conditions, the probe capture method was used to quantitatively analyze the generation kinetics and mechanisms of three typical ROS (hydroxyl radical ?OH, hydrogen peroxide H2O2, and superoxide radical (O2??) at the 10 gkg-1 biochar-amended soil-water interface. The effects of biochar pyrolysis temperature, dissolved biochar carbon (DBC), clay minerals (kaolinite), and dissolved organic matter (fulvic acid) on ROS formation were also examined at such interfaces. 【Result】The results showed that under light, substantial ?OH and H2O2 were generated at the biochar-containing soil-water interface, with concentration ranges of 0.43-0.83 μmolL-1 and 21.12-30.93 μmolL-1, respectively, which were 1.39-2.65 times and 1.31-1.91 times higher than those at the biochar-free interface (control group). In contrast, O2?? concentration was low (< 0.2 μmolL-1), significantly lower than that in the control. DBC played an important role in the formation of ROS, and after removing DBC, the generation of H2O2 in the water-soil interface containing biochar was significantly inhibited, but the generation of ?OH was not affected. Also, kaolinite significantly inhibited the capacity of biochar to mediate ROS generation at the soil-water interface under light (except for high-temperature biochar) and reduced the conversion efficiency of H2O2 to ?OH. Fulvic acid significantly enhanced H2O2 generation at the light-irradiated, biochar-containing soil-water interface but decreased ?OH concentration.【Conclusion】Light plays a critical role in mediating ROS formation at the biochar-amended interface: it not only promotes H2O2 generation and transformation, but also facilitates ?OH production and O2?? conversion. However, biochar-mediated ROS generation at the interface is not entirely dependent on light. The generation of ROS at the light-irradiated, biochar-amended soil-water interface is collectively determined by biochar surface persistent free radicals, oxygen-containing functional groups, as well as dissolved organic carbon and Fe2+ contents at the interface. These findings provide an important reference for understanding the formation and distribution of ROS in biochar-amended soils.
-
Interactive Effects of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid and Irrigation Quota on Saline-Alkali Soil Properties and Cotton Yield
WANG Shan, ZHANG Jinzhu, WANG Zhenhua, ZHANG Jihong, LIU Mengjie, MA Zhanli, ZHENG Jiliang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506130284
Abstract:
【Objective】To establish scientifically grounded, synergistic regulatory approaches for the comprehensive mitigation of the persistent challenge of saline–alkali soil degradation in cotton-growing systems, this study conducted a controlled field experiment during the 2024 cotton season on moderately saline–alkali soils in Manas County, Xinjiang. The objective was to elucidate how the integrated application of poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) and regulated irrigation influences soil biochemical processes, cotton physiological performance, yield formation, and fibre quality under field conditions.【Method】A two-factor randomized block design was established, involving three γ-PGA rates (F1: 7.5 kg·hm-2; F2: 15 kg·hm-2; F3: 22.5 kg·hm-2) and two irrigation quotas (W1: 4 000 m3·hm?2; W2: 4 500 m3·hm?2). Comprehensive measurements included soil physicochemical indices (Electrical conductivity (EC) -based salinity and pH variations across growth stages), key enzymatic activities (polyphenol oxidase, catalase, urease, sucrase), root morphological traits (length, diameter, biomass ratios), organ-specific dry matter accumulation, and yield and fibre parameters (boll number, lint percentage, composite quality index).【Result】Compared with F1 and F2, the F3 treatment effectively suppressed peak soil salinity and pH, concurrently elevating enzymatic activity, particularly urease, which increased by 30.13%-35.22 %. Nevertheless, the response plateaued beyond the F3 level, suggesting diminishing returns under higher γ-PGA concentrations. Enhanced enzymatic activity and improved rhizosphere conditions promoted root proliferation and biomass accumulation, resulting in a moderate but statistically significant yield increase (3.02%–27.96 %). Likewise, a higher irrigation quota (W2) alleviated surface salt accumulation and improved enzyme activities by 9.16%-48.33%, although excessive irrigation risked secondary salinization through capillary rise and nutrient leaching. Also, multivariate analyses (Principal component analysis and Pearson correlation) revealed a strong positive correlation (P < 0.05) between enzyme activity and yield traits. At the same time, soil salinity and alkalinity showed negative correlations with fibre quality indices, emphasizing the trade-off between osmotic stress alleviation and fibre maturation under saline conditions.【Conclusion】The combined application of 22.5 kg·hm?2 γ-PGA with 4 500 m3·hm?2 irrigation proved the most efficient configuration within the tested range, primarily by ameliorating the rhizosphere microenvironment (lower EC/pH and enhanced enzymatic turnover) and optimizing photosynthate allocation to reproductive organs. However, the overall improvement remains conditional on soil salinity thresholds, long-term stability, and economic feasibility. Thus, while the integrated γ-PGA–irrigation strategy significantly enhances cotton yield and fibre quality in saline–alkali soils, its scalability and sustainability under variable climatic and hydrological regimes warrant further investigation.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Microplastic Film-Degrading Bacteria from Soil Co-Composting Environments
ZHOU Qian, DAI Guoli, PAN Chennan, JIANG Jiamiao, WEI Ji''an, ZHANG Jun, ZHANG Ming, ZHANG Daoyong, PAN Xiangliang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507050330
Abstract:
【Objective】Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) serves as a crucial alternative to conventional plastic mulch films. However, the presence of aromatic chains renders PBAT more recalcitrant to biodegradation compared to other biodegradable plastics (e.g., polylactic acid). Moreover, there are limited microbial resources exhibiting efficient PBAT degradation capabilities.【Method】This study employed a soil-compost enrichment approach to screen high-efficiency PBAT-degrading microbial strains. Microbial consortia were enriched at 60 ℃ under thermophilic composting conditions using PBAT as the sole carbon source, yielding six candidate strains (designated B1-B6). Degradation efficacy was comprehensively evaluated through mass loss, surface morphology analysis, and water contact angle measurements.【Result】Strain B3 demonstrated superior PBAT degradation efficiency, achieving a 17.85%±11.22% mass loss within 7 days, exceeding currently reported values for PBAT-degrading microorganisms. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis revealed significant surface modification across all treatment groups, with B3-exposed PBAT exhibiting the most pronounced surface roughness (Ra = 44.84±26.48 nm). Concurrent physicochemical characterization showed a 15.6° reduction in water contact angle, collectively indicating substantial polymer matrix alteration. Taxonomic identification through 16S rRNA gene sequencing classified strain B3 as?Parageobacillus toebii.?In addition, characterization of the degradation performance of the mixed microbial consortium (designated as MIX) showed that MIX achieved a PBAT degradation rate of 12.48%±1.11%. Although the impact on surface roughness of PBAT was relatively minor, MIX induced the most significant changes in water contact angle, indicating a pronounced degradation effect. High-throughput 16S rRNA sequencing analysis revealed that, at the species level, the dominant strain within the MIX consortium was Parageobacillus toebii, accounting for 98.50% of the population. Other minor constituents included Aeribacillus pallidus (1.45%), unclassified_g_Lactobacillus (0.01%), unclassified_c_Bacilli (0.02%), unclassified_k_norank_d_Bacteria (0.01%), and unclassified_g_Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 (<0.01%). These findings suggest that the PBAT degradation capability of the MIX consortium is primarily attributed to Parageobacillus toebii. Through whole genome sequencing and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) gene function annotation, it was identified that strain B3 possesses genes encoding enzymes relevant to PBAT degradation, including carboxylesterase, arylesterase, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase, aldehyde dehydrogenase, alcohol dehydrogenase, and catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. Based on the above results, the potential degradation pathway of PBAT microplastics by the degrading microbes could be inferred as follows: (1) Initial hydrolysis: PBAT ester bonds are first cleaved by carboxylesterases, releasing intermediate products such as terephthalic acid and adipic acid. (2) Aliphatic chain metabolism: Adipic acid is activated into its CoA derivative by long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase and subsequently undergoes β-oxidation catalyzed by acyl-CoA dehydrogenase to form acetyl-CoA. Short-chain aldehyde/alcohol byproducts generated during aliphatic chain metabolism are further degraded by aldehyde dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase. (3) Aromatic ring degradation and ring-cleavage: Terephthalic acid undergoes hydroxylation to form catechol, which is then cleaved by dioxygenases, producing intermediates that enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle.【Conclusion】This study successfully isolated Parageobacillus toebii B3 as a high-performance PBAT degrader through multi-parametric characterization (mass loss, surface topography, and hydrophilicity changes). The findings provide both theoretical foundations and practical microbial resources for controlling biodegradable microplastic pollution.
-
Phytic Acid-modified Biochar Reduces Soil Cd Release by Regulating pH and Aggregates Structure
DI Dongliu, XIAO Jiang, GAI Xu, LI Pujun, CHEN Guangcai
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202507010321
Abstract:
【Objective】Phytic acid-modified biochar exhibits excellent adsorption capacity for cadmium (Cd) in aqueous solution; However, its effectiveness and mechanisms in remediating Cd-contaminated soils remain unclear. This study systematically analyzes the dynamic impact of phytic acid-modified biochar on soil properties, investigates its effect on Cd release in soil, and reveals the key mechanisms underlying biochar regulation of Cd movement in soil. 【Method】 Soil incubation experiments were conducted to systematically evaluate the remediation and amelioration effects of bamboo biochar (BBC), phytic acid-modified bamboo biochar (PABC), and sodium phytate-modified bamboo biochar (SPBC) on Cd-contaminated soils over various incubation periods (0, 10, 20, 60, 120, and 180 days). 【Result】The addition of biochar significantly altered the pH of both soil and soil solution and increased the electrical conductivity (EC). SPBC exhibited the highest EC and total carbon concentration in the soil solution, while PABC showed a distinct advantage in supplying total phosphorus, particularly in the short term. During the early and mid-phases (0-120 days), biochar treatment significantly reduced the Cd concentration in soil solution (24.60%-99.35%), with a significant dose-response effect, and SPBC exhibited the most effective remediation. In addition to their inherent adsorption mechanisms, biochar also inhibited Cd release indirectly by affecting the chemical (pH, total phosphorus, and total carbon), physical (aggregate structure), and biological properties (urease and acid phosphatase) of the soil and soil solution, with soil pH and micro-aggregate content identified as key factors influencing Cd release. In the later phase (120-180 days), enhanced soil aggregate stability further facilitated the remediation process, as biochar increased the activity of urease and acid phosphatase. 【Conclusion】 Phytic acid-modified biochar demonstrates strong potential for both Cd remediation and soil improvement in heavily contaminated soils, offering significant application value.
-
Effects of Biochar Application on Organic Carbon Composition of Different Density Fractions in Paddy Soil
ZHU Mengtao, MA Ruiling, CAI Ying, YI Qi, JIANG Shuo, LIU Zhiwei, BIAN Rongjun, ZHANG Xuhui, ZHENG Jufeng, LI Lianqing
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502170063
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration in agricultural ecosystems is critical for mitigating climate change and maintaining soil fertility, with mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC) playing a central role in long-term C stabilization. Paddy soils with higher SOC density exhibit distinct biogeochemical cycles due to periodic flooding and anaerobic conditions, making their SOC dynamics particularly complex. While biochar amendment has emerged as a promising strategy to enhance SOC storage, the specific mechanisms by which biochar interacts with soil mineral fractions and modulates native SOC stability remain poorly understood. Previous studies have primarily focused on total SOC changes, overlooking the differential responses of mineral-bound C pools to biochar input. This knowledge gap hinders accurate assessments of biochar"s long-term C sequestration potential in paddy systems. The present study aimed to address this gap by investigating how biochar amendment affects SOC distribution across density-based mineral fractions and alters native SOC dynamics through advanced spectroscopic and isotopic tracing techniques.【Method】In this study, a field experiment was established in a typical paddy soil in southern China, with two treatments: biochar application at 15 t·ha?1 (C15) and no biochar (C0). After two years of rice cultivation, soil samples were collected from the 0-15 cm depth and subjected to sequential density fractionation using sodium polytungstate solutions with gradient densities (1.65, 1.85, 2.05, 2.25, 2.45, 2.65 g·cm?3). Each fraction was characterized for SOC content, stable isotope composition (δ13C), and chemical functional group via Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) was used to visualize particle morphology and elemental composition, while X-ray diffraction (XRD) identified dominant mineral phases in each fraction. Isotopic mixing models were applied to quantify biochar-derived C versus native SOC contributions across density gradients.【Result】The results showed that (1) Based on SOC content and soil minerals categories, density fractionation successfully separated soil into three functionally distinct pools: particulate organic carbon (POC, <1.85 g·cm?3), clay mineral-associated C (1.85~2.45 g·cm?3), and primary mineral-bound C (>2.45 g·cm?3). XRD analysis confirmed that the 1.85~2.45 g·cm?3 fraction was enriched in 2:1 phyllosilicate (e.g., montmorillonite, illite) and Fe/Al oxides, whereas the >2.45 g·cm?3 fraction contained quartz and feldspars. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) demonstrated that the intensities of O-H stretch (2923 cm–1) for aliphatic structures and C=C stretch (1610 cm–1) for aromatic compounds gradually decrease in both biochar application (C15) and non-application of biochar (C0) treatments with increasing density, while SOC stability progressively increased. (2) SOC content of density-specific changes varied under biochar amendment: Contribution of SOC in the <1.65 g·cm?3 fraction increased by 150.1%, driven by biochar particles, while the 1.65~1.85 g·cm?3 fraction showed a 60.9% increase, due to biochar-derived C adsorption onto clay minerals. Conversely, the 1.85~2.05 g·cm?3 clay fraction exhibited a 37.4% reduction in SOC contribution. δ13C analysis confirmed biochar-C presence across all fractions, with the highest incorporation (64.5%) in the <1.65 g·cm?3 fraction. Native SOC depletion was observed in five density intervals, with the most severe loss (-41.2%) in the <1.65 g·cm?3 fraction, indicating strong positive priming. Notably, priming extended to the 1.85~2.25 g·cm?3 clay fraction (-14.6%), suggesting biochar-induced microbial activity stimulated decomposition of relatively stable mineral-protected C.【Conclusion】This study demonstrates that biochar amendment effectively enhances total SOC content in paddy soil within two years, but its C sequestration efficiency is offset by priming-induced native SOC losses across labile and mineral-protected pools. The findings highlight the need to account for biochar-microbe-mineral interactions when evaluating long-term C sequestration. By linking density fractionation with spectroscopic and isotopic tools, this research advances understanding of mineral-mediated C stabilization in biochar-amended soils, providing a basis for optimizing biochar application strategies (e.g., feedstock selection, application rate) to maximize C sink capacity in rice-based systems. Future work should focus on long-term monitoring of priming effects and microbial community shifts to refine sustainable soil C management practices.
-
Research Progress on the Classification and Application of Life History Strategy in Soil Microbial Community
LIANG Shuxin, SHAO Jiahui, YE Jinru, QI Yuhao, ZHANG Ruifu, SHEN Qirong, XUN Weibing
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502180068
Abstract:
Soil microbial community drives biogeochemical cycles and is crucial for maintaining soil health and ecosystem sustainability. However, the complexity of microbial community composition and the diversity of microbial functions present significant challenges in classifying and understanding microbial community based on functional traits. Life history strategy theory links microbial metabolic characteristics with ecological processes, providing critical insights into the relationship between microbial communities and ecosystem services. This review systematically summarizes the theoretical frameworks and recent advances in soil microbial life history strategy, outlining the original theories and their developmental trajectory. It focuses on the two-way continuum (r-K life history strategy theory and oligotrophic-copiotrophy life history strategy theory) and the three-way continuum (C-S-R and Y-A-S life history strategy theories), highlighting their conceptual foundations and practical applications in soil microbial community researches. However, current studies primarily rely on descriptive analyses of microbial functional composition, lacking investigations into the dynamic expression and regulation mechanisms of microbial functions. Based on this, we propose future research directions on soil microbial life history strategies to support sustainable agriculture. First, integrating multi-omics technologies is essential for assessing the functional dynamics of microbial community. While current sequencing methods (e.g., amplicon and metagenomic sequencing) can identify potential microbial functions based on the genomic information, they fail to capture real-time microbial activity in fluctuating environments. A combined approach incorporating transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and single-cell Raman spectroscopy can provide deeper insights into real-time gene expression, metabolic processes, and other critical aspects of soil microbial communities. Second, elucidating the molecular mechanisms that regulating the microbial life history strategies is crucial. Microbes dynamically reprogram their functional traits in response to environmental changes, yet the signaling networks and genes governing this reprogramming remain largely unknown. Future research should focus on understanding the interactions among environmental factors, microbial gene expression, and microbial functional investments. Additionally, synthetic biology approaches can facilitate the engineering of programmable microbial strains, enabling precise control over microbial functions in complex ecosystems. Third, expanding current life history strategy theories to incorporate species interactions within ecosystems is necessary. Existing frameworks primarily emphasize microbe-environment interactions while neglecting biotic interactions, particularly in agricultural ecosystems. For example, rhizosphere microbes enhance plant stress resistance and growth by producing plant hormones such as cytokinins, yet these functions are not currently integrated into life history strategy frameworks. Future studies should explore how microbial life history strategies regulate soil-microbe-plant interactions and quantify their contributions to ecosystem services. We emphasize the need to establish a multidimensional, dynamic analytical framework for microbial life history strategies, elucidate the driving mechanisms underlying microbial life history transitions, and refine the response framework of soil microbial life history strategies in agricultural ecosystem services. We advocate for developing microbial life history classification into a core theoretical tool for ecosystem function regulation, providing microbiome-based solutions to address global change and food security challenges.
-
Research Progress and Future Perspectives on Soil Nitrogen Cycling in Tropical Croplands of Hainan
JU Xiaotang, ZHANG Chong, ZHANG Limei, SONG Xiaotong, LI Tingyu, LIU Shuoran, LIU Siyi
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503020097
Abstract:
Hainan is the only province in China entirely situated within the tropical region, characterized by abundant light, heat, and water resources, making it the most typical tropical agricultural production base in China. However, restrictive factors such as "poor, acidic, and leaky" soils, coupled with high nitrogen (N) fertilizer inputs in crop cultivation, led to significant risks for N loss in farmlands and severe environmental pollution. The agricultural non-point source pollution situation in Hainan is severe, N and phosphorus discharged from agriculture enter nearshore waters via short transport pathways, leading to serious degradation of coral reefs and seagrass beds. However, the generally weak foundation of research on N cycling in Hainan"s tropical farmland soils hindered the development of scientific and targeted N regulation measures. In response to the characteristics of tropical agricultural resources, we propose that future research should focus on four key areas: the characteristics of N transformation, the fate and loss pathways of N, the mechanisms of efficient N utilization in crops, and the principles and regulation measures for reducing N fertilizer application while enhancing efficiency. More attention should be paid to the effects of organic matter-mediated soil fertility and acidity improvement on soil N transformation in Latosols, the mechanisms underlying high ammonia emissions in acidic soils and nitrate accumulation in deep soil profiles, as well as the impact of organic material inputs on nitrous oxide emissions. We emphasize the need to clarify the relationship between the transformation and migration characteristics of N in farmland soils and crop N use efficiency, and to elucidate the mechanisms by which soil carbon (C) pool expansion affects N transformation, migration, retention, and loss prevention. Thus, to propose a principle for reducing N fertilizer application while enhancing efficiency, centered on "increasing C to retain N, coupling C and N, controlling losses, and coordinating N supply". This approach will form an innovative theory and solution. The finding would provide scientific and technological support for the development of efficient and green tropical agriculture and offer a scientific basis for understanding regional differences in N cycling across global climate-soil zones.
-
Effects of Slope-to-tiered Measure and Crop Type on Soil Organic Carbon Pools and their Compositions in Sloping Cropland in Purple Soil Areas of China
ZHANG Sheng, WANG Guan, WANG Yuehuan, ZHOU Zihe, CHENG Jinhua
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502120058
Abstract:
【Objective】Purple soil is a soil type unique to China, characterized by rapid weathering of the parent material, low permeability, and poor erosion resistance. A large number of slope conversions have been adopted to combat soil erosion, but the synergistic effect of this measure with crop types on the local organic carbon pools of sloping arable land and their composition is not clear. 【Method】In this study, Corn Slope, Corn Terracing, Citrus Slope, Citrus Terracing, Corn-Citrus Terracing in the East River sub-basin in Chongqing were selected as the research objects. Biomarker methods were used to compare the differences in soil microorganisms and organic carbon of plant origin from different types of sloping arable land and to reveal the effects of slope-to-staircase measures on soil organic carbon pools and their compositions.【Results】The results showed that: 1) The contents of SOC, POC, and MAOC in different types of sloping arable land was significantly decreased with the implementation of slope reclamation measures; 2) Slope reclamation significantly decreased the total lignin phenol content in maize sample plots compared to the significant decrease in the degree of oxidation of lignin phenol in citrus sample plots; 3) The main source of microbial organic carbon in all sample plots was fungal residue, which accounted for 74.50%~98.88%, and the slope conversion measures decreased the fungal content in the soil under the monocrop planting mode. 【Conclusion】Although slope conversion measures helped to reduce soil erosion, they had a complex impact on the soil organic carbon pool and its composition in sloping arable land in the purple soil zone. This provides a scientific basis for optimising agricultural management practices and achieving sustainable land use in the purple soil zone.
-
Effects of Different Organic Fertilizers on Rhizosphere Microbial Carbon Source Utilization, Nematode Community, and Nutrient Absorption of Jackfruit
CHEN Hongxing, MO Yuncong, XU Yadong, SU Lanxi, BAI Tingyu, WU Gang, XUN Weibing, XU Zhihui, ZHAO Qingyun
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506120277
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aimed to investigate the regulatory differences of various organic fertilizers on the rhizosphere microorganisms, nematode communities, and nutrient absorption of jackfruit, so as to select suitable organic fertilizers to construct a healthy soil microecology, and provide a theoretical basis for targeted regulation of soil quality.【Method】Malaysian No.1 grafted seedlings were used as experimental materials, and the latosol formed by granite was used as test soil in this study. The experiment was designed to have six treatments: CK (no fertilizer), DF (soybean flour), YF (sheep manure), JF (chicken manure), NF (cow manure), and CF (chemical fertilizer only), for comparing the effects of different fertilizers on the biomass accumulation, nutrient absorption, and soil microenvironment of jackfruit. 【Result】The application of organic fertilizer generally promoted the biomass accumulation and nutrient absorption of jackfruit, and increased the soil pH and organic matter. NF significantly improved the proportion of soil organic matter, available nitrogen, and potassium nutrients, but significantly reduced the proportion of soil available phosphorus compared to other treatments. The application of JF also significantly increased the contents of soil available nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium; however, YF treatment induced the weakest effect among all organic fertilizer treatments. Also, the YF treatment had the highest number of soil nematodes and nematode abundance in each trophic group, followed by the NF treatment. The Shannon-Weiner diversity index and evenness index of soil nematodes in the organic fertilizer treatment were significantly higher than those in the CK and CF treatments. In addition, the soil microbial communities under different fertilization treatments all exhibited relatively active metabolism towards carbohydrates, amino acids and carboxylic acids, while their metabolic capabilities towards polymers, phenolic acids, and amides were weaker. The diversity and evenness index of soil microbial community structure in the DF treatment were significantly higher than those in other organic fertilizer treatments. Mantel analysis showed a significant correlation between plant biomass, nematode community, nematode trophic groups, microbial carbon source utilization, and soil pH. Also, the Mantel analysis of nematode community, bacterial-feeding nematode, and omnivorous/predacious nematode with soil organic matter showed significant correlation. 【Conclusion】The application of organic fertilizer can promote the growth and nutrient absorption of jackfruit, increase soil organic matter, and improve soil microecology. Moreover, organic fertilizers from sheep and cow manure is beneficial for increasing the total number of soil nematodes and the number of nematodes in each trophic group, while soybean flour can enhance the activity of rhizosphere microorganisms and promote carbon source utilization. For practical applications, specific organic fertilizers or their combinations can be selected based on the basic soil conditions for targeted regulation of soil health, providing a theoretical basis for high crop yield and efficient resource utilization.
-
Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of Agricultural Environmental Costs Under Fertilizer Input in Northeast China
ZHANG Xilun, WANG Ping, WANG Jingkuan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505200230
Abstract:
【Objective】Northeast China is an important grain production base, and it is also one of the largest fertilizer consumption markets. Over the years, the application of many chemical fertilizers has led to increasingly prominent negative impacts on the agricultural ecological environment. Using the application rate of chemical fertilizer in Northeast China in the past three decades, it was estimated environmental cost (EC) from different potential pollution, and their comprehensive environmental cost (CEC) and environmental cost load (ECL). This research will provide a scientific basis for realizing agricultural sustainable development in Northeast China and ensuring China "s food security. 【Method】Combining energy analysis and disability-adjusted life year assessment, the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of EC from different potential pollution sources, and their CEC and ECL were analyzed in Northeast China from 1990 to 2022. The EC in different provinces and cities and their potential causes were evaluated, and countermeasures and suggestions for reducing EC were put forward. 【Result】 (1) From 1990 to 2022, the CEC of fertilizer application in Northeast China gradually increased, from 42.12 million yuan to 3 200.55 million yuan, an increase of 76 times, with an average annual growth rate of 14.49%. The growth rates of the 1990s, 2000s, and 2010s were 22.69%, 16.67%, and 7.78%, respectively, which gradually slowed down. (2) In 2022, the total EC of air, water, and soil pollution caused by chemical fertilizer application was 542.37 million yuan, 749.36 million yuan, and 190.88 million yuan, respectively. Ammonia and nitrate, respectively, contributed the most to air, water, and soil pollution. Their ECs respectively were 467.92 million yuan, 691.76 million yuan, and 1 485.17 million yuan, reaching 82.64% of the total EC. (3) The largest change in CEC was mainly concentrated in the line from Jiamusi to Chifeng, while the smaller change was concentrated in the line from Yanbian to Dalian. The largest changes in ECL were mainly concentrated in most areas of Liaoning Province, Tongliao, Shuangyashan and the surrounding areas of Jixi, while the smaller changes were mainly in Siping, Yichun, Daxing"anling, and Xilinguole. 【Conclusion】 In the past three decades, the CEC of chemical fertilizer application in Northeast China has increased year by year, but the growth rate has gradually slowed down, indicating that the impact of chemical fertilizer application on the environment has been significantly alleviated. In addition, the EC and ECL showed obvious spatial distribution characteristics, which indicates that the impact intensity of the southern and southern coastal areas was stronger than the northern inland areas. In future research, it is recommended that the focus should be directed towards typical black, brown, and other types of soil in Northeast China, as well as typical cultivated areas such as the corn belt and miscellaneous grain area in Northeast China, to further explore the spatial differences of CEC. Although chemical fertilizer input can increase grain yield, it also brings high EC, which requires scientific fertilization measures according to local conditions. It is necessary to continue to promote scientific fertilization and reasonable intercropping/rotation to improve the utilization efficiency of chemical fertilizers. Finally, the effect of reducing fertilizer application and being environmentally friendly will be realized to ensure the sustainable development of agricultural production in Northeast China.
-
Screening of Alkali-Producing Strains and Their Amendment Effect on Acidic Soil
LIU Chong, LIU Yang, WANG Dan, LU Yusheng, ZHU Xiaoxuan, WEN Shuheng, WANG Yong, ZHU Zixin, LI Yaying, GU Jun, GU Wenjie
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505230237
Abstract:
【Objective】Managing soil acidification in farmland soils is of great significance to ensure national food security and sustainable agricultural development. Microorganisms have important application value in soil improvement. However, the research on alkali-producing microorganisms and the mechanism of improving acid soil is still lacking. This study aimed to systematically explore the mechanisms of acidified soil remediation by alkali-producing microorganisms, with a focus on overcoming the limitations of functional microbial resource scarcity and field application technology gaps. 【Method】Systematic screening was employed to isolate alkali-producing microorganisms from acidic soils in South China. Indoor simulation experiments evaluated its pH elevation capacity through repeated inoculation. Genomic analysis revealed its urease gene cluster (ureABCEFGD), and field trials assessed the effects of single-dose application on soil pH and crop yield. 【Result】We screened 109 alkali-producing bacterial strains (65% belonging to Bacillus spp.) and 24 fungal strains (33% Trichoderma spp.). The alkali-producing ability and stability of alkali-producing bacteria were generally stronger than those of fungi, with Lysinibacillus fusiformis LW-3 identified as a key strain. Within 15 weeks of continuous culture, repeated inoculation of L. fusiformis elevated soil pH by 1.5 units, reduced exchangeable aluminum by 23.46%, and decreased hydrolytic acid by 31.80%. Genomic analysis revealed that L. fusiformis LW-3 carried a complete urease gene cluster (ureABCEFGD). Lysinibacillus fusiformis LW-3 could ameliorate acid soil by enhancing soil urease and protease activities, metabolizing ammonia, consuming hydrogen ions through bicarbonate, and reducing the content of active and potential acids in soil. Field application confirmed that soil pH stably increased by 0.2 units and enhanced Chinese cabbage yield by 11.6%. 【Conclusion】This study elucidated a multi-pathway synergy mechanism for acidified soil remediation, including alkali production, enzymatic activity regulation, and acid speciation transformation. These findings indicate that the strain L. fusiformis LW-3 has good application prospects in acid soil amendment, providing technical support for alkaline-producing microbiome-driven soil acidification management.
-
Improved Diffusion Method for Determination of Natural Abundance and Low-Concentration Labeled NH4+-15N in Soil Extracts
YOU Zhijie, YE Ping, ZHANG Siwei, DAI Shenyan, WEN Teng, ZHANG Jinbo
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505080209
Abstract:
【Objective】The 15N isotope ratio of NH4+-N plays a crucial role in nitrogen transformation research and is widely applied to soil, water, and other samples with sufficient inorganic nitrogen content. While the diffusion method is the most effective technique for isolating and transforming soil NH4+-N, its application remains limited for low-concentration and natural abundance NH4+-N. 【Method】In this study, it is aimed to evaluate the feasibility of using the diffusion method alone for transforming and measuring low-concentration (≤1 mg·L-1) labeled and natural abundance NH4+-15N. To establish a diffusion system for rapid and accurate determination, this study improved the acid trap material and production method, incubation time, reaction volume, and incubation temperature. 【Result】The results demonstrated that: (1) The envelope diffusion packet acid trap exhibited higher nitrogen recovery?(95.0%) and better precision (standard deviation <0.010 atom%) compared to suspended acid traps. Envelope packets fabricated from domestic high-purity polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) could replace imported Merck Millipore PTFE, reducing costs by >90%.?The improved diffusion packet not only reduced the cost, simplified the operation and also increased N recovery to 99.8%. (2) The diffusion method accurately and sensitively measured the labeled NH4+-15N concentrations as low as 0.2 mg·L-1 with an error <0.006 atom%, and the difference between the corrected and the expected value was <0.020 atom%. In addition, diffusion method further exhibited robust performance in natural abundance NH4+-15N (≥1 mg·L-1), with an error ≤0.30‰ and a deviation from the expected less than 0.38‰. (3) Expanding the sample volume to 100 mL for low-concentration labeled samples and employing envelope packet acid traps for 8-day diffusion at 25 ℃ not only significantly enhanced recovery, measurement accuracy and precision, but also enabled accurate quantification of low-concentration NH4+-N (≥0.2 mg·L-1) with minimal isotopic deviation (Δ15N<0.020 atom%) after correction with standards. For even lower concentrations of labeled or natural abundance NH4+-N, it is advisable to combine diffusion method with additional methods. While heating can effectively shorten the incubation time and improve recovery, it also amplified interference from exogenous nitrogen impurities.?And heating may lead to increase the interference of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in natural soil or water samples, necessitating cautious application during practical measurements. 【Conclusion】Overall, diffusion remains a powerful method for transforming and measuring NH4+-15N in soil. This study enhances the concentration threshold and accuracy of labeled sample diffusion methods while significantly reducing experimental duration. The improved diffusion protocol can be used for measuring NH4+-15N at different concentrations and abundances, providing a theoretical foundation for accurate soil inorganic nitrogen analysis.
-
Effects of Soil Microbial Diversity on Soil Multifunctionality Under Sustained Intensive Forest Management
HUANG Cheng, WU Lin, LI Xu, FU Songling, FENG Chun, WANG Zhaocheng, LIU Hua
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505240239
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil microorganisms serve as crucial mediators, bridging organic and inorganic environmental factors. They play a significant role in regulating multiple soil functions. Forest management represents the primary anthropogenic disturbance to forest soils, yet the mechanisms through which soil microorganisms influence soil multifunctionality (SMF) under continuous intensive management remain unclear. 【Method】This study investigated Carya cathayensis var. dabeishansis secondary forests in the Dabie Mountains to explore the mechanisms by which soil microbial diversity affects SMF under sustained intensive forest management. The authors analyzed 45 plots under varying management durations (0, 3, 8, 15, 20 years) and management metods (CK: no management; EM: extensive management; IM: intensive management) in Jinzhai County, Anhui Province. The soil microbial diversity (amplicon sequence variant, ASV) number, Simpson index, Shannon-Wiener index, and Chao1 richness index for bacterial and fungal communities) and 15 indicators related to four soil functions: nutrient supply (alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), available potassium (AK), microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN), microbial biomass phosphorus (MBP)); nutrient storage (total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), total potassium (TK)); nutrient cycling (acid phosphatase (ACP), urease (UE), sucrase (SC), β-1,4-glucosidase (BG), protease (Pro)); and carbon storage (soil organic carbon, SOC), microbial biomass carbon (MBC)) were measured. SMF was calculated using both the single-function approach and the averaging method. Two-way ANOVA was employed to compare management effects, while Pearson correlation, Mantel tests, and random forest models identified key functional indicators. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was constructed to analyze regulatory pathways. 【Result】The results indicated that short-term management (3 years) significantly enhanced soil microbial diversity and SMF (bacterial Shannon index peaked under IM at year 3; SMF increased by 0.94 compared to CK). However, both declined significantly with prolonged management, with bacterial ASV number and Shannon index decreasing by 19.63% and 3.46% after 20 years of intensive management, respectively. Management duration exerted a significantly greater impact on microbial diversity and SMF than management regime (P < 0.001), and IM amplified this temporal effect (e.g., carbon storage, nutrient cycling, and supply functions under IM-15 were significantly lower than CK). Random forest analysis identified SOC, TP, MBC, AN, TK, MBN, SC, and BG as key indicators of SMF (P < 0.05). SEM revealed that microbial diversity influenced SMF by indirectly regulating soil nutrients and enzyme activities (explaining 57.4% of the variation): bacterial diversity positively drives nutrient and carbon storage. In contrast, fungal diversity governed nutrient cycling and carbon storage. Nutrient supply and storage functions were the core contributors to SMF, where TP and TK indirectly affected SMF by regulating AN, MBN content, and SC/BG enzyme activities. Moreover, long-term management induced soil acidification, SOC loss, and phosphorus limitation (TP significantly decreased after 15 years), impairing microbial community function. This subsequently reduced enzyme activities (e.g., SC, BG) and nutrient turnover efficiency, ultimately leading to SMF degradation.【Conclusion】 This study revealed that the loss of soil microbial diversity is a key factor in SMF degradation under long-term intensive forest management. Thus, optimizing management strategies (supplementing carbon/phosphorus fertilizers, reducing nitrogen fertilizer application, decreasing understory vegetation clearance frequency) to maintain soil ecological functions is highly recommended. These findings provide a theoretical basis for the sustainable management of economic forests in mountainous regions.
-
Effects of Low Temperature-Acclimatized Rhizosphere Soil Microorgasims of Sphagneticola trilobata on the Cold Tolerance of Different Geographical Populations
LI Yifan, GONG Zongzhi, LIU Junzhen, QI Shanshan, CHENG Pengfei, DAI Zhicong, DU Daolin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202504040158
Abstract:
【Objective】 The invasive plant Sphagneticola trilobata has been expanding to higher latitudes and colder regions since it invaded China due to its rapid adaptability to the environment. As a part of the rhizosphere environment, the rhizosphere microbial community plays an important role in plant invasion and resistance to abiotic stress. However, the effect of rhizosphere microorganisms on the cold tolerance of invasive plants remains to be elucidated. It is therefore hypothesized that rhizosphere microorganisms of S. trilobata acclimated to cold stress play an important role in the improved cold resistance of S. trilobata populations to spread to high latitudes (colder regions).【Method】In this study, two populations of S. trilobata from the southernmost (Sanya ) and northernmost (Wenzhou ) regions of China were used as the research objects, and the cold-acclimatized rhizosphere soil microorganisms of these two populations of S. trilobata were used as microbial agents. Afterwards, the feedback effects of rhizosphere soil microorganisms on the cold tolerance of host plants after low temperature acclimation was explored through soil feedback experiments.【Result】 Under low temperature stress, the inoculation of rhizosphere microbial community significantly increased the biomass, root growth, chlorophyll and leaf nitrogen content of S. trilobata. The maximum photochemical efficiency and photosynthetic performance index of S. trilobata were significantly enhanced by inoculation of rhizosphere soil microbial agents domesticated by the northern (Wenzhou) population, and the relative content of anthocyanins was significantly reduced, indicating that it was less affected by low temperature stress. 【Conclusion】 The results showed that S. trilobata could improve its tolerance to low temperature stress by recruiting rhizosphere microorganisms, and the effect of northern populations was better. This indicates that domestication and recruitment of cold-tolerant rhizosphere microorganisms could promote the expansion of S. trilobata to higher latitudes. Moreover, this study provides an explanation for the possible reasons for differential cold tolerance in different populations of S. trilobata from the perspective of rhizosphere microorganisms, and emphasizes the necessity and urgency of strengthening the supervision of the current invasion boundary regions of S. trilobata.
-
A Rheological Approach to Study the Effects of Biochar Addition on the Mechanical Stability of Soil Structures
HE Bing, LI Jiangwen, ZHOU Lin, SUN Jian, XU Chenyang, DU Wei, HU Feinan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502220080
Abstract:
[Objective] Biochar plays an important role in improving soil physicochemical properties and enhancing soil structural stability. It achieves this by increasing soil organic matter content, enhancing nutrient retention and availability, and improving soil structure changes that further promote soil aeration, water infiltration, and root penetration, thereby strengthening soil structural stability. Soil structural stability is critical for sustainable agricultural production, as it influences soil erosion resistance, water-holding capacity, and overall soil health. However, few studies have explored the effects of biochar addition on the mechanical stability of soil structure from the perspective of rheological methods. [Methods] To address this research gap, a two - year field experiment was conducted. Soil samples with different biochar addition rates (0%, 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%) were tested for basic physicochemical properties. Additionally, amplitude sweep tests were used to measure soil shear strength and viscoelastic parameters under varying water contents (30%, 37.5%, 45%, and 60%), aiming to analyze how biochar addition levels affect the shear strength and viscoelastic properties of the soils. The amplitude sweep mode is a robust rheological technique that allows for the assessment of soil behavior under different deformation conditions, providing valuable insights into soil mechanical stability. [Results] The results showed that biochar addition significantly improved soil structural mechanical stability by enhancing soil basic physicochemical properties, such as increasing soil cation exchange capacity and organic carbon content, which in turn increased soil energy storage modulus and shear strength This effect was particularly pronounced at lower water contents ranging from 30% to 37.5%. At these water contents, the soil structure was more stable and better able to resist external forces. Furthermore, biochar addition also resulted in an increased range of the linear viscoelastic zone and higher soil yield stress, thereby improving its structural stability. Notably, at a 10% addition rate, the soil maintained strong stability even under high water content conditions. [Conclusion] Biochar addition enhances the mechanical stability of soil structure by improving soil shear strength and viscoelasticity. These findings clarify the mechanical mechanism underlying soil structure improvement via biochar application, and thus provide a scientific basis for formulating targeted soil structure optimization measures in the Loess Plateau region.
-
Effects of Mixed Planting Rare Tree Species on Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Communities in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations
WU Qinqin, YE Zihao, HU Hanwen, HU Zhaogui, WU Jiasen
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503300148
Abstract:
【Objective】Cunninghamia lanceolata is a significant timber species in subtropical China with a long cultivation history. However, persistent monoculture management has triggered multiple ecological issues, including soil nutrient depletion, biodiversity loss, and declining forest productivity. To enhance ecological functions and economic returns while achieving sustainable development of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations, precious tree species were introduced through interplanting and their effects on soil chemical properties and microbial communities were investigated.【Method】Soil samples were collected from pure Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations (PC) and four mixed forests: Taxus wallichiana-C. lanceolata (MTC), Ormosia hosiei-C. lanceolata (MOC), Phoebe chekiangensis-C. lanceolata (MPC), and Houpoea officinalis-C. lanceolata (MHC) in Qingyuan Forest Farm, Zhejiang Province. Soil chemical properties were analyzed via standard protocols. Microbial community composition was characterized using 16S rRNA and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) high-throughput sequencing, while co-occurrence network analysis and partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM) were employed to decipher microbial interactions and functional linkages.【Result】(1) Interplanting significantly improved soil chemical properties. The MPC treatment increased soil pH by 11.2% (P<0.05), while the MTC treatment elevated soil organic carbon (SOC) content to 31.8 g·kg-1, a 26.2% increase compared to PC (P<0.05). The MOC treatment significantly boosted available phosphorus (AP) content by 3.96 times relative to PC (P<0.01). (2) The bacterial co-occurrence networks in mixed forests exhibited increased nodes, edges, and path lengths. Significant differences (P<0.05) were observed in degree centrality, closeness centrality, and eigenvector centrality among the treatments. Notably, the MTC treatment resulted in the highest degree centrality and eigenvector centrality within the soil bacterial co-occurrence network, indicating the formation of a more efficient and stable bacterial community structure. (3) Functional gene analysis revealed distinct metabolic pathways: PC treatment was dominated by nitrogen respiration and nitrogen fixation functions, whereas MTC and MPC treatments activated xylanoly and nitrate reduction functions, respectively. (4) PLS-PM demonstrated that soil chemical properties indirectly influenced the expression of carbon and nitrogen cycling genes by regulating key microbial taxa, such as those within the Actinobacteria phylum.【Conclusion】Interplanting valuable tree species significantly enhances the stability of Cunninghamia lanceolata forest ecosystems by optimizing soil physicochemical properties and strengthening the complexity and functional redundancy of microbial networks. The improvements in soil chemistry (pH, SOC, AP), the formation of more complex and stable bacterial co-occurrence networks (particularly under MTC), and the shift towards specific functional genes (carbon decomposition, nitrate reduction) collectively underpin this increased ecosystem resilience. Based on the superior performance in fostering stable microbial structures and activating beneficial functional genes, the Taxus wallichiana-C. lanceolata mixed model (MTC) is prioritized for future promotion in southern China. Supplementing this with interplanting Phoebe chekiangensis is recommended to synergistically optimize overall soil quality.
-
Responses of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Characteristics to Organic Materials Application in Urban Green Soils
Niu Yuhui, Wang Qingfeng, Ma Xiang, He Xiaoli, Liang Jing
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412230502
Abstract:
【Objective】Adding organic waste materials into soils significantly affects microbial characteristics, however, the responses of bacterial and fungal diversity, community compositions and their interactions to the addition of different types of organic materials in urban green soils remain poorly understood.【Method】Using mesh bag method, six types of organic materials including green waste (GW), green waste compost (GWC), biogas residue (BR), biogas residue compost (BRC), peat (PT) and biochar (BC) were selected to investigate the effects of organic materials addition on soil properties, microbial communities and co-occurrence network in urban green soils through a 16-month in situ experiment.【Result】The addition of organic materials greatly increased soil electrical conductivity, soil organic carbon, and soil total nitrogen content by 12.7%-49.0%, 34.1%-87.0%, and 4.2%-14.7%, respectively. Soil bacterial alpha (?) diversity did not change among all the treatments, while soil fungal ? diversity was obviously increased after organic materials addition, which was mainly regulated by soil electrical conductivity. The dominant fungi were Ascomycota in urban green soils. Fungal communities in GW and GWC treatments obviously differed from other treatments, which was significantly influenced by soil pH and microbial biomass carbon. In contrast, Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi and Fimicutes were abundant in urban green soils. Bacterial communities in BR and BRC treatments were distinctly separated from other treatments, which was primarily driven by the aromaticity index of organic materials. Further analysis of occurrence-network revealed six main ecological clusters. The relative abundances of microbe in each module were different among all the treatments and were significantly correlated with soil nutrients and aromaticity index of organic material. Specifically, the highest relative abundance of bacteria community in module 2, 3 and 4 was observed in BR and BRC treatments, which was positively correlated with dissolved organic carbon, microbial biomass carbon, and soil total nitrogen, indicating that addition of biogas residue and biogas residue compost might enhance soil nutrient availability and subsequently facilitate microbial activity.【Conclusion】This study concludes that adding different types of organic materials can regulate urban green soil microbial community composition and interaction patterns by influencing soil physicochemical properties, thereby altering soil carbon cycling. Organic materials with low aromaticity index, which are more easily decomposed by microorganisms, may accelerate soil carbon cycling, whereas organic materials with high aromaticity index may favor carbon retention in soils. These findings hold significant implications for accurately assessing the resource utilization of urban organic wastes and the improvement of microbial diversity and ecological function in green space soils.
-
Microbial Multi-kingdom Interaction Mechanism Underlying the Control of Tomato Bacterial Wilt by Reductive Soil Disinfestatio
XU Shunan, XIE Yi, LU Zhiyu, LI Ruimin, YAN Yuanyuan, REN Yi, ZHOU Xing, CAI Zucong, HUANG Xinqi
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202506070264
Abstract:
【Objective】The interrelationships within soil microbial communities play a crucial role in maintaining plant health. As an efficient ecological regulation measure for controlling crop soil-borne diseases, the impacts of reductive soil disinfestation (RSD) on the interrelationships of soil microbial communities and its contribution to plant disease control efficacy remain unclear. 【Method】Based on two field experiments, this study systematically investigated the effects of RSD on the intra-kingdom and cross-kingdom interactions within soil bacterial, fungal, and protist communities, as well as the associations between community interactions and tomato growth. 【Result】The results showed that compared with the control, the incidence of tomato bacterial wilt significantly decreased by 90.2% after RSD treatment, while the plant height of surviving plants and tomato yield increased by 13.5% and 57.4%, respectively. RSD treatment significantly reduced the diversity indices of soil bacterial and fungal communities, and significantly altered the community structures of bacteria, fungi, and protists. The microbial groups enriched by RSD treatment included the bacterial phyla Proteobacteria and Acidobacteria, the fungal phyla Ascomycota and Mortierellomycota, and the protist groups Rhizaria and Archaeplastida. Following RSD treatment, the total cohesion within soil bacterial communities, protist communities, and cross-kingdom communities significantly increased. Correlation analysis revealed that compared with community diversity and compositional structure, the total cohesion of bacterial communities, bacteria-fungi communities, and bacteria-fungi-protist communities exhibited stronger and more stable relationships with plant disease incidence, shoot length, and yield, and was significantly negatively correlated with plant disease incidence, and significantly positively correlated with yield and shoot length.【Conclusion】This study highlights the critical role of bacterial and cross-kingdom community interactions in determining plant growth and provides new insights into the disease-suppressive mechanisms of RSD treatment.
-
Ecological Intensification Enhance Soil Multifunctionality: A Review
Xue Wenfeng, Cheng Saisai, Hu Feng, Liu Manqiang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202505040204
Abstract:
With the exacerbation of global food demand and climate change, there is an urgent need for agricultural systems to deliver multiple ecosystem functions and services. However, conventional agriculture, with its emphasis on yield maximization, has often exacerbated ecological issues such as biodiversity loss, soil degradation, and environmental pollution. Ecological intensification, grounded in nature-based solutions, aims to harmonize agricultural production with ecosystem functioning while enhancing soil multifunctionality at minimal environmental cost, thereby driving the transition of agricultural systems toward more sustainable production models. This review synthesizes the mechanisms through which ecological intensification enhances soil multifunctionality and elucidates the regulatory pathways of key management practices, including conservation tillage, diversified cropping, organic amendments, and the inoculation of beneficial organisms. Furthermore, we identified the major challenges, including the absence of a comprehensive evaluation framework for soil multifunctionality, limited understanding of trade-offs and synergies among functions, and insufficient insights into the mechanisms underlying the synergistic effects of multiple practices, and proposed targeted solutions to address these gaps. Finally, this review outlines future research priorities, emphasizing the need to establish dynamic, multi-scale research frameworks of soil multifunctionality that incorporate spatial and temporal dimensions; to deepen mechanistic understanding through theoretical and methodological innovation; and to promote regionally adaptive, context-specific management strategies through the integration of multiple ecological practices. By bridging scientific research and practical application, ecological intensification offers significant potential to simultaneously enhance agricultural productivity and ecosystem services, thereby supporting the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems.
-
Cultivated Land Soil Security Evaluation Based on the Earth
fengzhe, wangyixin, kanglong, peiwei, liangmeng, chen''anqi, wukening
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503250139
Abstract:
【Objective】 Ensuring the security of soils in the Northeast Black Soil Region, a critical commodity grain production base in China, is essential for safeguarding the national food supply and promoting sustainable resource utilization. However, existing evaluation systems lack a comprehensive integration of multi-sphere interaction mechanisms within the Earth’s critical zone, making it difficult to quantify the synergistic effects of natural substrates and human activities. Thus, this study aims to address this gap by developing a systematic decision-making tool for the sustainable management of cultivated land resources in the Northeast Black Soil Region. 【Method】This study focused on Suihua City, a typical black soil region, and constructed a four-dimensional evaluation system of "Condition (C1)-Capability (C2)-Capital (C3)-Connectivity (C4)" guided by the Earth""s critical zone theory. Seventeen indicators (such as black soil layer thickness, cation exchange capacity, soil organic matter content, etc.) were selected from aspects including soil physical, chemical, and biological properties to characterize the cultivated land soil security pattern of Suihua City. Also, the influencing mechanism of Earth""s critical zone elements on soil security was evaluated by combining with the Random Forest model. 【Result】The results showed that: (1) The C1 state scores exhibited a spatial variation with higher values in the northeast and lower values in the southwest; C2 scores were generally high; C3 capital scores showed an opposite spatial pattern to C1, with lower values in the northeast and higher values in the southwest; and C4 scores did not display a clear spatial pattern. (2) The comprehensive soil security scores ranged from 54.3 to 88.4 (average of 77.7), with 84.9% of cultivated land classified as moderately secure or higher. Higher security regions (56.5%) were concentrated in Beilin District, Anda City, and Hailun City, while critical and insecure regions (15.1%) were mainly distributed in Qing’an County and Mingshui County. (3) The average means square error increase (%IncMSE) for the 17 indicators was 1.3%, with black soil layer thickness and soil organic carbon content having %IncMSE values of 10.7% and 3.7%, respectively, significantly higher than other indicators. 【Conclusion】The results of the study demonstrate that the four-dimensional evaluation framework rooted in the Earth""s critical zone theory effectively quantifies the interplay between natural substrates and anthropogenic activities. This approach elucidates the response mechanisms of soil security within the multi-layered structure of the critical zone, offering a systematic decision-making tool for sustainable management of cultivated land resources in black soil regions. These findings provide actionable insights for balancing agricultural productivity with ecological sustainability in ecologically fragile agroecosystems.
-
Responses of soil nutrients and microbial communities to elevated ozone concentrations across different rice cultivars
JI Yang, DU Yiming, ZHAO Mengying, ZHANG yijia, Li Yuxin, SHANG Bo, FENG Zhaozhong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502060048
Abstract:
【Objective】Elevated near-surface ozone (O3) concentrations are an increasing threat to rice production, but the mechanisms and dose effects on below-ground ecosystems, including soil nutrient cycling and microbial communities, remain poorly understood. 【Method】This study targeted three major rice cultivars (HuaiDao 5, NanJing 5055, and WuYunJing 27) in the Yangtze River Delta. Using open-top chambers, we conducted an 84-day fumigation experiment with four ozone concentration gradients, including [NF (ambient air), NF20 (ambient air + 20 nmol·mol-1 O3), NF40 (ambient air + 40 nmol·mol-1 O3), and NF60 (ambient air + 60 nmol·mol-1 O3)], to systematically analyze the dose-response effects of elevated O3 concentration on soil nutrients and microbial communities in paddy fields. 【Results】The results showed that increasing O3 concentration significantly altered soil NO3--N and available phosphorus (AP) contents, as well as the abundances of methanotrophs (pmoA gene) and archaea during the rice filling stage, whereas no significant effects were observed for soil DOC, total carbon (TC), available potassium (AK), bacterial or methanogen (mcrA gene) abundances. The interaction between O₃ fumigation and rice cultivar significantly affected soil NH4⁺-N, NO3⁻-N, and AP contents. Specifically, O3 fumigation significantly reduced NO3⁻-N contents in HuaiDao 5 and WuYunJing 27, although the inhibitory effect weakened with increasing O3 concentration. In contrast, NH4⁺-N content in NanJing 5055 significantly increased under the highest O3 treatment (NF60). Similarly, NH4⁺-N in HuaiDao 5 decreased under O3 stress but the effect weakened at higher concentrations, whereas NH4⁺-N in WuYunJing 27 increased under NF60. AP content in HuaiDao 5 exhibited a negative correlation with O3 concentration, whereas no significant effects were observed in the other two cultivars. O3 fumigation significantly increased the abundance of pmoA gene in NanJing 5055 and WuYunJing 27, with the promoting effect intensifying under higher O3 concentrations. Soil bacterial community analysis revealed cultivar-specific responses, the relative abundance of Bacteroidota in WuYunJing 27 and Chloroflexi in NanJing 5055 was positively correlated with O3 concentration, while the relative abundance of Bacteroidota in NanJing 5055 and Desulfobacterota in HuaiDao 5 showed significant negative correlations. Moreover, the abundance of carbon and nitrogen metabolic pathways in NanJing 5055 and WuYunJing 27 exhibited nonlinear dose-response relationships with increasing O3 concentrations. 【Conclusion】Our findings demonstrate that soil nutrient dynamics and microbial community responses to O3 stress are highly cultivar-specific, with evidence suggesting the existence of threshold concentrations for O3 sensitivity. However, accurately quantifying the mechanisms underlying O3-induced alterations in below-ground elemental cycling and identifying key ecological thresholds will require long-term in situ observations. These findings offer critical insights for assessing the ecological risks of ozone pollution in rice paddies and guiding the selection of ozone-tolerant cultivars.
-
Mechanisms of High Cadmium Accumulation by Wheat Grown in Alkaline Soils and Prospects for Mitigation Strategies
GAO Yan, FAN Guangping, LI Yuntao, SHI Gaoling, TONG Fei, LI Jiangye, CHEN Wei, GE Chenghao, ZHOU Dongmei
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502060046
Abstract:
Wheat, serving as a staple food for one-third of the global population, has long been overlooked in terms of its grain cadmium (Cd) accumulation capacity and the resulting dietary exposure risks. By integrating analyses of global literature and our recent research findings, this study preliminarily clarified that wheat grown in contaminated alkaline soils exhibited high Cd accumulation capacity with elevated risks of exceeding food safety thresholds. In rice-wheat rotation farmland systems, the Cd enrichment factor of wheat grains at the same sampling points was significantly higher than that of rice. Remarkably, wheat grains exceeded China"s food safety standard in alkaline soils even when the Cd concentrations remained below the national risk screening threshold. Elevated soil pH levels induced a pronounced increase in wheat"s contribution to adult daily dietary cadmium intake, while concurrently reducing rice"s contribution, demonstrating that alkaline soil conditions amplify Cd exposure risks specifically through wheat-derived dietary pathways. The article further discussed the Cd speciation in alkaline soils and their influencing factors, analyzed the mechanisms related to Cd migration and its chemical binding forms at the root-soil interface, and explored the interaction effects between Cd and trace elements during uptake and translocation by wheat. In order to develop wheat-safe production technologies adapted to the characteristics of alkaline Cd-contaminated soils, future research should strengthen investigations into the molecular mechanisms of Cd interface processes in the wheat rhizosphere and Cd-trace elements interactions on uptake and translocation by roots.
-
Spatial Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Factors of the Silica Neoformation Accumulation Layer in Northeast Black Soil Region: A Case Study of Liaoning Province
LIU Siwei, SUN Zhongxiu†, GUO Long, DUAN Siyi, WANG Qiubing
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503210129
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aims to systematically investigate the spatial distribution and driving factors of silica neoformation accumulation layers in the Northeast Black Soil Region, which significantly affect soil physical properties, impede plant root penetration and water transport, and exacerbate slope erosion. 【Method】Taking Liaoning Province as a representative region, a total of 333 soil profile samples were integrated, and advanced machine learning techniques were used to quantitatively analyze the spatial distribution and characteristics of silica neoformation accumulation layers.【Result】The results indicate that silica neoformation accumulation layers were predominantly distributed across Shenyang, Tieling, Fushun, Benxi, Dandong, and Chaoyang, encompassing a total area of approximately 4,261 km2 with a model prediction accuracy of 0.42. Notably, the layers exhibited deep accumulation in the central terrace and hilly regions, whereas they were relatively shallower in the eastern mountainous areas. Specifically, the was an abundance of silica neoformation peaks in the central region (6.66% to 27.35%), with higher densities observed in the central and western regions (132.70–611.94 g·dm-3). The depth of occurrence was greater in the central and northern regions (21.06–74.06 cm), whereas the thickness was thinner in the eastern region (31.78–97.71 cm). Furthermore, the distribution of silica neoformation accumulation layers was significantly influenced by annual mean ground temperature, relative humidity, and precipitation. In the eastern part of Shenyang, frequent groundwater activities and favorable climatic conditions contributed to the formation of profound silica neoformation accumulation layers. Conversely, in mountainous areas such as Fushun, limited groundwater influence, higher terrain, affected by biological enrichment processes and precipitation patterns, resulted in limited silicon leaching. Furthermore, the depths of leaching and deposition were shallow, and the silica neoformation accumulation layer remains superficial. 【Conclusion】This study provides an important solid scientific basis for understanding the spatial distribution and influencing factors of silica neoformation accumulation layers. It also offers practical guidance for developing effective soil improvement strategies, highlighting the importance of addressing the issues related to enhancing soil health and sustainability in the Northeast China Black Soil Region.
-
Response of Soil Properties and Productivity to Application of Calcium Carbonate and Organic Matter in Acidic Vegetable Fields
GENG Jinzhao, LI Zhenlun, ZHANG Min, CHEN Fuhui, MA Zheng, LIANG Kang, LUAN Huilin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503130114
Abstract:
【Objective】Vegetable production is frequently associated with high nitrogen fertilizer application and intensive crop rotation, resulting in soil acidification, structural degradation, and proliferation of harmful microorganisms. These factors significantly impede the sustainable development of vegetable farming. 【Method】Therefore, this study investigated the short-term effects of organic fertilizer, potassium humate, calcium carbonate, and their combinations on soil properties, organic carbon components, and microbial community structure in acidic vegetable fields with an untreated control (CK). 【Result】(1) Results showed that the sole application of full-dose organic fertilizer significantly increased total nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium in non-rhizosphere soil, while significantly increasing easily oxidizable organic carbon (EOC) in non-rhizosphere (by 22.70%) and rhizosphere (by 9.76%) soils. The sole application of full-dose calcium carbonate significantly raised soil pH but reduced available phosphorus in non-rhizosphere soil and alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, available potassium, and organic carbon (SOC) in rhizosphere soil. Most notably, the combined application of all three amendments significantly increased soil pH and Chinese cabbage yield, compared to CK, while also increasing SOC, EOC, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), and the abundance of soil bacteria, fungi, Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and actinomycetes. (2) Correlation analysis between soil physicochemical properties and microbial community structure revealed that alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen and EOC were significantly positively correlated with all measured microbial groups in the non-rhizosphere, where DOC correlated positively with bacteria. Also, in the rhizosphere, DOC correlated positively with bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. Redundancy analysis showed that in non-rhizosphere soil, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen had the greatest influence on microbial communities. In rhizosphere soil, available potassium and DOC were the main factors affecting microbial communities. (3) Correlation analysis between soil properties and Chinese cabbage yield indicated that yield correlated positively with non-rhizosphere pH and rhizosphere exchangeable Ca2? and Mg2?, but negatively with rhizosphere alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen. Structural equation modeling revealed that exchangeable Ca2+, available phosphorus, and alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen had significant positive effects on cabbage yield, with Gram-negative bacteria indirectly influencing yield through available phosphorus. 【Conclusion】Based on these results, it can be concluded that the combined application of calcium carbonate and organic amendments effectively mitigated soil acidity, enhanced soil organic carbon sequestration, increased microbial biomass, and stabilized soil productivity. This study provides an important reference for research aimed at managing soil acidification and improving crop yields in acidic soils.
-
Information Statistics and Property Analysis of Commercially Acidic Soil Amendments
YU Junfeng, Guo Xinyi, LI Zhongyi, Fu Dengwei, WANG Yuanpeng, ZHOU Jia, WANG Shuai
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503290145
Abstract:
【Objective】Direct application of soil amendments represents a crucial approach for ameliorating acidic soils. Grasping the fundamental properties of commercially available acidic soil amendments is vital for developing strategies to improve acidic soils in China. 【Method】In this study, detailed information regarding product registration and patent applications for acidic soil amendments in China was gathered and systematically organized. Subsequently, the basic properties; including particle size distribution, pH, contents of CaO and MgO, crystalline minerals, and functional groups, of 24 randomly selected commercial soil amendments were determined. The crystalline minerals and functional groups of soil amendments were identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses. 【Result】The results indicate that a substantial number of acidic soil amendments exist in China, accounting for 78% of all types of soil amendments. Driven by market demand, raw material availability, and agricultural development characteristics, the manufacturers of acidic soil amendments are predominantly located in Guangdong and Shandong provinces. The authorization rate of patents for acidic soil amendments in China is less than 10%. Among the authorized patents, the primary raw materials are organic matter and by-products from industry and agriculture, followed by natural minerals and chemical products. Specifically, the main raw materials listed in product registrations were carbonate minerals and oyster shells and most of the amendments were available in powder and granular forms, with a product registration ratio of approximately 2:1. However, the adoption of the powder products face challenges in promotion due to dust generation during application. The pH value, CaO content, and MgO content are the core indicators that most effectively reflect the ability of acidic soil amendments to mitigate soil acidity and replenish soil base nutrients. Even though some of the soil amendments did not fully disclose these three parameters on their packaging, the experimental evidence indicated that they were highly alkaline and exhibited high pH values and CaO contents, and most products also contained small amounts of MgO. These measured indicators aligned with their labeled values or ranges and the XRD and FTIR analyses further demonstrated that the predominant component in the commercially available amendments was CaCO₃. In addition, other alkaline constituents such as Ca(OH)₂, CaO, CaMg(CO₃)₂, and MgO were also present in some of the soil amendments, depending on their raw materials and production technologies. Moreover, most of the amendments also contained silicate minerals or SiO₂. 【Conclusion】The results of this study revealed that the primary function of the commercially available amendments for acidic soils in China is the amelioration of soil acidity. However, due to the single functionality of these products, there are significant challenges in market promotion. To meet the diversified needs of agricultural production, it is necessary to further develop multi-functional acidic soil amendment products that can both regulate soil acidity and enhance soil fertility, thereby improving product practicability and market competitiveness. In addition, acidified soil amelioration is a systematic project. Besides strengthening the development of new products, it is also necessary to simultaneously advance various aspects of work such as soil acidification monitoring and early warning, and integration of acidified soil improvement technologies and models, in order to effectively promote the improvement and sustainable utilization of China""s acidic cultivated land.
-
Origins of Mineral-associated Organic Carbon (MAOC) Under Long-term Fertilization in a Vertisol
YU ZiZhou, GUO ZiChun, DING TianYu, WANG DaoZhong, HUA KeKe, GUO ZhiBin, GAO Lei, PENG XinHua
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503120112
Abstract:
【Objective】Mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC) constitutes the largest and most stable fraction of soil organic carbon (SOC), and increasing its proportion is essential for improving soil quality. Although long-term fertilization has significantly increased the MAOC proportion in SOC in Shajiang black soil, the accumulation patterns of plant- and microbial-derived carbon within MAOC, as well as their relative contributions to SOC, remain unclear. Therefore, this study aims to explore the accumulation characteristics of plant- and microbial-derived carbon and their contribution to MAOC in the 0-20 cm soil depth of Shajiang black soil under long-term fertilization. 【Method】Based on a 34-year field experiment, four treatments were established (no fertilizer and wheat straw return as CK, mineral fertilizer as NPK, mineral fertilizer with half amount of wheat straw return as NPKLS, and mineral fertilizer with full amount of wheat straw return as NPKHS). Biomarkers and chemometric methods were used to investigate the effects of long-term fertilization on plant and microbial-derived carbon in MAOC. 【Results】The results reveal that compared to CK treatment, NPKHS and NPKLS treatments significantly increased the content of MAOC by 29.6% to 54.3% (P < 0.05), with MAOC exhibiting a significant linear positive correlation with SOC (R² = 0.95, P < 0.05) and carbon input (R² = 0.98, P < 0.01). In terms of plant-derived components, the NPKHS treatment induced an increase of 14.8% and 13.3% in the contents of Vanillyl (V) and Syringyl (S) phenols, respectively, while the S/V and C/V ratios decreased by 1.27% to 9.46%. However, the differences in the acid-to-aldehyde ratios (Ad/Al)V and (Ad/Al)S were not significant (P > 0.05). For microbial-derived components, NPKHS treatment significantly elevated the amino sugar content, with an increase of up to 91.4% compared to the control (P < 0.05). Specifically, the contents of fungal residual carbon (FNC) and bacterial residual carbon (BNC) increased by 92.7% and 48.5%, respectively, with fungal necromass dominating (FNC/BNC=4.39). Biomarker analysis indicated that the microbial-derived carbon contribution rate was as high as 72.6% to 73.4%, whereas chemometric methods suggested that the plant-derived carbon contribution ranged from 74.0% to 82.6%. Compared to previous studies on grassland/forest ecosystems (53% to 65%), this proportion appears somewhat unreasonable, suggesting that the chemometric method may have overestimated the contribution from plant sources. 【Conclusion】Our findings indicate that long-term fertilization enhances the accumulation and stability of MAOC in Shajiang black soil primarily by increasing microbial-derived carbon content. This study provides an important reference for the efficient utilization of straw resources and for improving the quality of cultivated land in the Shajiang black soil region.
-
Effects of Sheep Manure Combined with Wood Vinegar on Nutrients in Saline-alkali Soil and Salt Tolerance of Winter Wheat
QIE Ying, LI Yihong, WANG Guangen, JIANG Longgang, LI Dongxiao, ZHANG Yuechen, GUO Li
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503030099
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aimed to explore the effects of applying different amounts of wood vinegar in combination with sheep manure on the improvement of saline-alkali soil in the low plain of Hebei and the salt tolerance of winter wheat from 2022 to 2024. 【Method】There were five treatments including conventional fertilization (CK), sheep manure at 27 t?hm-2 (T0), T0 + wood vinegar at 270 kg?hm-2 (T1), T0 + wood vinegar at 540 kg?hm-2 (T2), and T0 + wood vinegar at 810 kg?hm-2 (T3). The effects of the combined application of sheep manure with different amounts of wood vinegar on soil nutrients, salt tolerance characteristics of winter wheat, nutrient absorption and utilization, and yield were analyzed. 【Result】The results showed that at soil depth of 0-20 cm, the soil bulk density and electrical conductivity value under T2 treatments were significantly reduced by an average of 8.03% and 13.17% compared with CK (P < 0.05), while the total porosity, organic matter and available potassium contents significantly increased. The nitrate nitrogen content and available phosphorus under T2 were significantly increased compared with CK and T0. At a soil depth of 20-40 cm, the content of available phosphorus under T2 was significantly increased compared with CK. Compared with CK, T0, and T1, the content of soluble sugar and the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) at each filling stage, the soluble protein content and the activity of peroxidase at the early and middle filling stages, and the free amino acid content at the early filling stage in the flag leaf of T2 were significantly increased. Also, the content of superoxide anions radicals showed an opposite trend to the SOD activity while the total accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium under T2 in the aboveground part was significantly increased by 8.30% to 25.79% compared with CK, T0, and T1. The stomatal characteristic parameters of the flag leaf under T2 were significantly increased compared with CK, among which the stomatal size of the flag leaf under T2 was significantly increased by 21.23% compared with CK. Moreover, the yield of winter wheat under T2 treatment was significantly increased by 5.93% to 17.29% compared with CK, T0, and T1. Using mathematical modeling, it was observed that the optimal dosage of wood vinegar liquid following a simulation for a two-year period was close to the application amount of 540 kg?hm-2 of wood vinegar. 【Conclusion】Based on these results, it was recommended that the optimal amount of sheep manure to be applied should be 27 t?hm-2 while the amount of wood vinegar should be in the range of 535.46-551.03 kg?hm-2. This, could contribute to mitigating the negative impacts of saline-alkali soils and enhance winter wheat productivity in this region.
-
Revealing the Interaction Characteristics Between Selenomethionine and Iron Oxides over Surface Spectroscopy - Energy Spectrum Technique
WANG Rui, LIU Xin, HOU Ruicheng, YANG Hui, YANG Shunping, SHEN Xuele, LONG Ting, XIANG Wenjun, WEI Shiyong, TAN Wenfeng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503240131
Abstract:
【Objective】Organic Se is an important component of total Se in soil, and selenomethionine exists as one of the most common species among the organic Se. Given that the interfacial interaction between iron oxides in soil and organic Se species remains elusive, this study provides an avenue for understanding the migration and transformation of Se coupling with Fe-cycling in soil. 【Method】 In this study, the interfacial interaction between selenomethionine and iron oxides, ferrihydrite, goethite, and hematite was investigated through the analysis of surface species, coordination structure of iron atom (Fe) and adsorption configuration over the X-ray photoelectron spectrum (XPS), X-ray absorption fine structure spectrum (XAFS), and attenuated diffuse reflection infrared spectrum (DRIFTS-IR). 【Result】The results revealed that the binding energy (B.E.) of N1s was decreased to 399.7 eV and it was maintained for the main Se species adsorbed on ferrihydrite. The coordination structure of first- and second-sphere for Fe atom of ferrihydrite before and after interacting with selenomethionine did not change, while there was an adsorbed carboxyl-species with bidentate coordination mode. This result suggested that selenomethionine could be adsorbed on ferrihydrite through the bidentate coordination mode with a vertical adsorption configuration over carboxyl on the surface of ferrihudrite. After interacting with selenomethionine, the B.E. of Fe for bulk FeO6 at the goethite sub-surface was reduced by 0.4 eV. Also, the distance of first-sphere and coordination number of outer spheres for Fe atom in goethite showed an obvious change, compared to that of the fresh goethite. It indicated that goethite had undergone an obvious dissolution accompanied by obvious reduction effect after interacting with selenomethionine. Moreover, the Se atom mainly existed as the oxidized species on goethite. There was a monodentate coordination mode for the adsorbed selenomethionine on goethite with a horizontal adsorption configuration. For hematite, the B.E. of Fe both at sub-surface and surface were reduced to 0.4 eV, while the coordination structure of Fe atom for the Fe-sphere did not change but shortened in the first-sphere. This phenomenon revealed a characteristic weak dissolution interaction and a strong reducibility for hematite interacted with selenomethionine. Owing to the reduction by selenomethionine, there was a strong surface-enhanced infrared absorption effect for the adsorbed selenomethionine. Besides, the amino N and Se atoms might directly participate in the chemical adsorption of selenomethionine on hematite. Among the three iron oxides, there was a similar oxidization pattern for Se during the interaction process and this observation can be summarized as: 1) the complete oxidization of selenomethionine into selenite and 2) the incomplete oxidization species of selenomethionine. 【Conclusion】The interaction characteristic and mechanism of selenomethionine with ferrihydrite, goethite, and hematite was carefully revealed through surface analysis. The results revealed a differential response for the surface structure of mineral and change of selenomethionine when it interacted with iron oxides with different surface structure and properties. These findings provide an important reference for understanding the migration and transformation of organic Se in soil under different Fe-cycling processes. It also provides guidance for the unitization of Se resource and remediation of Se pollution in Se-rich area.
-
The Theoretical Framework and Technical Pathway of
LI Guangjie, YU Zhen, WANG Chong, SHI Weiming, WANG Zhaoyue, LI Yan, ZHANG Lin, LIU Zhaohui
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503050101
Abstract:
Saline-alkali land is an important agricultural land resource, and in recent years, China has adopted various improvement measures for the management of saline-alkali soil. However, the improvement and utilization of saline-alkali land still face challenges, including high costs, severe water resource constraints, poor stability of improved saline-alkali land with a tendency to revert, and the need for enhanced low-water-consumption and high-efficiency technical support. To address these significant issues, this study proposes the concept of "rhizosphere suitable microzones" (RSM) for crops in saline-alkali soils. Focusing on the problems of "difficult emergence and establishment" of crops in saline-alkali land, as opposed to the overall soil improvement strategy, it expounds the theoretical framework of RSM. RSM refers to creating a specific local environment with unique physical, chemical, and biological characteristics within the small space of plant root systems, which differs from the surrounding environment and can support specific biological communities or life activities. This study proposes the technical path construction concept centered around "activating soil to promote root growth, using ions to nourish roots, acidification to regulate roots, and biological agents to protect roots". This will be achieved through cross-innovation of multiple theories, including soil fertility enhancement with carbon addition and salt reduction, balanced nutrient supply for salt inhibition, physical structure optimization to eliminate compaction, and enhancement of rhizosphere biological functions. Thus, it depicts the exploration of the construction principles and technical paths of RSM from a systematic perspective. This study outlines the key directions and contents of research on RSM and saline-alkali land improvement, aiming to break through the technical bottlenecks of saline-alkali soil improvement and promote the development of related disciplines. Specifically, the study considers salt-tolerant high-value crop varieties as pioneers, promotes the migration of sodium ions in the rhizosphere through water regulation, and considers the research and development of the technical path of RSM for crops in saline-alkali soils. This is centered on new slow and controlled-release fertilizers supplemented by anti-salt, growth-promoting, and biological strengthening factors.
-
Cover Crop Rotations Enhance Biopore Structure in Shajiang Black Soil: A Multi-scale Investigation
DING Tianyu, GUO Zichun†, HUA Keke, ZHANG Hongxia, PENG Xinhua
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202504260193
Abstract:
【Objective】Biopores constitute a critical component of the soil pore network, exhibiting significantly greater efficiency in facilitating the transport of water, solutes, and gases compared to nonbiopores. However, quantitative analysis of biopores at a single scale exhibits significant limitations in resolving morphological characteristics, elucidating developmental dynamics, and evaluating functional attributes. 【Method】To comprehensively characterize soil biopores distribution patterns, this study integrated a 5-year rotational field experiment on lime concretion black soil with high-resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanning. The investigation was conducted at three distinct scales: (1) large column scale (10 cm diameter × 20 cm height soil columns), (2) small column scale (5 cm diameter × 5 cm height soil cores), and (3) aggregate-scale (3-5 mm aggregates). We systematically examined the effects of different cropping systems - conventional wheat-maize rotation (WM) versus cover crop rotations (wheat-Cassia occidentalis: WY, and wheat-Cassia tora Linn.: WJ) - on biopore characteristics within the 0-20 cm soil layer. Furthermore, we critically evaluated the applicability of each scale for biopore network analysis. 【Results】This study developed an improved biopores segmentation protocol comprising three key steps: (1) initial classification of pores into connected and isolated networks, (2) application of 3D distance transform watershed algorithms to separate biopores and nonbiopores, and (3) implementation of a Random Forest classifier leveraging morphological feature parameters (blobness, sphericity, compactness, and plateness) for scale-specific biopores segmentation across all three observational scales. Compared to the WM treatment, the WY treatment significantly increased bioporosity by 237%, 243%, and 119% at the large column, small column, and aggregate scales (P<0.05), respectively. Similarly, the WJ treatment resulted in an increase of bioporosity by 111%, 217%, and 114% at the large column, small column, and aggregate scales (P<0.05), respectively. At the large column scale, biopores exhibited significantly larger diameters than those at small column and aggregate scales, with mean diameters ranging from 1,444-3,374 μm and maximum diameters reaching from 4,792-8,854 μm (P<0.05). This scale effectively captured the biopores network architecture and directly revealed vertical continuity patterns throughout the 0-20 cm plow layer. However, large column scale analysis showed limited detection capability for fine biopores (<60 μm in diameter), reflecting inherent resolution constraints of the methodology. The small column effectively identified medium-to-fine biopores (>30 μm) and primarily correlates with soil physical properties governing hydraulic conductivity and gas transport. Microscale aggregate analysis can resolve ultra-fine biopores (>6 μm in diameter), with quantitative characterization revealing these biopores occupy 21.6-34.4% of total aggregate porosity. Aggregate scale analysis provides critical insights into root-soil architecture interactions and reveals fundamental mechanisms of soil organic carbon physical protection within microhabitats. 【Conclusion】This study demonstrated that cover cropping significantly enhanced soil biopore networks across multiple scales. We propose that future research adopt integrated multiscale approaches to fully unravel the spatial distribution and temporal evolution of these biopore systems.
-
Study on the Potential of Manure Application for Carbon Sequestration in Cropland Soil Profiles
LI Tiantian, ZHU Qi, SHEN Lidong, ZHU Tianshen, ZHANG Jiakai, MA Yuchun, XIA Longlong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502260087
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil organic carbon (SOC) in cropland is an important component of the terrestrial ecosystem carbon pool. The application of organic manure, as a critical agricultural management practice, has been extensively validated to significantly enhance soil organic carbon (SOC) content and stock. However, Current research mainly focuses on the SOC fixation and mechanisms in the 0~20 cm surface soil layer, with little attention given to the carbon sequestration potential of deeper soil layers. 【Method】This study used a meta-analysis method to systematically analyze the impact of animal manure application on SOC distribution and stock in the soil profile of global croplands. 【Result】The results showed that the application of animal manure increased SOC stock in different soil layers. In the surface layer (0~20 cm), SOC stock increased from 28.3 t·hm-2 to 36.4 t·hm-2, with an increase of 28.6%. In the 20~40 cm layer, SOC stock increased from 23.6 t·hm-2 to 27.5 t·hm-2, with an increase of 16.5% while in the >40 cm layer, SOC stock increased from 45.6 t·hm-2 to 48.7 t·hm-2 (6.8%). The new SOC sequestration efficiency (NCE) was highest in the 0~20 cm layer (146.0%), significantly higher than in the 20~40 cm layer (117.2%) and the >40 cm layer (64.3%). Also, it was observed that soil carbon sequestration efficiency was co-regulated by both natural factors (annual mean temperature, annual mean precipitation) and anthropogenic factors (fertilizer type, nitrogen application rate, land use type, and application duration). Specifically, the impacts of annual mean temperature and annual mean precipitation on sequestration efficiency vary across different soil layers. Moreover, the combined application of animal manure and an appropriate amount of nitrogen fertilizer significantly enhanced SOC stock in the surface soil layer. 【Conclusion】This study provides a theoretical basis for developing differentiated carbon sequestration strategies based on soil profile characteristics. Furthermore, the study highlights the significance of optimizing agricultural management to enhance soil carbon stock, mitigate climate change, and achieve sustainable agricultural development.
-
Microbial Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Elevated Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations on Nitrogen Fixation Potential in Paddy Soils
WU Yanlin, HUANG Wei, HU Zhenghua
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412250509
Abstract:
【Objective】?Biological nitrogen fixation?, which converts inert nitrogen into plant-available nitrogen, is a critical process for maintaining the soil nitrogen cycle and supporting the productivity of agroecosystems. However, the effect of atmospheric CO2 on biological nitrogen fixation in paddy fields remains poorly understood. Thus, this study aims to elucidate the microbial-driven mechanism of biological nitrogen fixation in paddy soils affected by elevated atmospheric CO2. The findings of this study will provide a scientific basis for the optimization of nitrogen cycling in paddy fields and sustainable nitrogen management in agriculture under climate change scenarios.【Method】In this study, we investigated the microbial-driven mechanism of biological nitrogen fixation in paddy fields by elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration. Two treatments, CK (ambient CO2 concentration) and EC (elevated ambient CO2 concentration by 200 μmol·mol?1) were set up by using an open-top chamber (OTC)-based platform for the automated control of CO2 concentration. Soil physicochemical properties, nitrogen fixation potential (NFP), and the abundance and community composition of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (nifH gene) of paddy soils were analyzed by microcosmic cultivation, real-time quantitative PCR, and high-throughput sequencing.【Result】The results showed that across the whole rice plant growth period and compared with CK, EC treatment significantly increased the microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) content by 3.3% and significantly decreased the NH4+?N content by 11.6%. Also, the NFP and nifH gene abundance were significantly increased by EC treatment. At the maturity stage, the community structure of the nifH gene in the EC treatment changed significantly compared with CK. In addition, the TN content was positively correlated with NFP, which was regulated by soil MBN content, SOC content, and nifH gene abundance.【Conclusion】This study reveals that elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration increased soil MBN content and nifH gene abundance, enhanced NFP, and increased the nitrogen content of paddy soils.
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Biochar and Diatomite on Nitrification Processes and Ammonia-Oxidizing Microorganisms in Coastal Saline Soils
Ma Lan, Wang Jie, Shan Yan, Wang Xiangyu, Song Yanjing, Li Junlin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501170036
Abstract:
【Objective】 Biochar and diatomite have gained considerable attention as soil amendments; however, their effects and underlying mechanisms on nitrification processes as well as ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in coastal saline soils remain poorly understood. 【Method】 A 42-day indoor incubation experiment was conducted using typical coastal saline soil from the Yellow River Delta. Five treatments were applied: control without fertilizer (CK), urea (U), urea with dicyandiamide (DCD), urea with diatomite (DE), and urea with biochar (BC). The effects of these treatments on soil nitrification were evaluated, and the abundance and community structure of AOA and AOB were analyzed using quantitative PCR and high-throughput sequencing. 【Result】 The results demonstrated that DCD significantly inhibited nitrification in the short term, with an inhibition rate of 73.1%, however, its inhibitory effect diminished over time. Biochar also showed short-term nitrification inhibition but subsequently promoted AOA abundance. In contrast, diatomite did not significantly inhibit nitrification but notably enhanced AOB abundance. Correlation analysis revealed that the amoA gene abundances of AOA and AOB exhibited significantly opposite regulatory effects on the nitrification process. AOA showed significant positive correlations with ammonium nitrogen (NH??-N) content and nitrification inhibition rate (NIR), but a significant negative correlation with nitrate nitrogen (NO??-N) content. Conversely, AOB demonstrated significant negative correlations with NH??-N content and NIR, but highly significant positive correlations with NO??-N content and net nitrification rate (NNR). Notably, the correlation between AOB and NNR was significantly stronger than that of AOA. Cluster analysis indicated that the community structures of AOA and AOB in the BC and DCD treatments were more similar, which may be related to the fact that both regulate the soil nitrogen transformation process and microbial activity. 【Conclusion】 This study elucidates the differential regulatory mechanisms of biochar and diatomite on ammonia-oxidizing microbial communities in coastal saline soils, offering a novel theoretical foundation for the amelioration of saline soils.
-
Polarization‐Induced Covalent Bonding between H+ and Surface O Atoms Promotes Clay Mineral Dissolution
TANG Yuting, XIAO Shuang, DING Wuquan, LI Hang, LIU Xinmin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501090018
Abstract:
【Objective】Dissolution reactions of clay minerals are one of the essential processes contributing to natural soil acidification and mineral weathering. However, the surface reaction mechanism of mineral dissolution remains unclear. 【Method】The strong electric field generated by the surface charges of minerals induces a new type of covalent bonding between the oxygen (O) atoms on the mineral surface and the hydrogen (H+) ions, a phenomenon known as polarization-induced covalent bonding (PICB). In this study, we selected montmorillonite (MMT), illite (ILI), and kaolinite (KLI) to explore the interfacial reaction mechanisms promoting the dissolution of clay minerals by PICB using mineral dissolution analysis and hydrothermal experiments. 【Result】The dissolution density of mineral elements increases with decreasing pH, and the initial stage of mineral dissolution aligns with three processes of chemical weathering: desalination, desilicification, and ferrallitization. The PICB significantly enhanced the H+ adsorption energy density (γH(0)), and the absolute value of γH(0) increased with the decrease of pH, indicating an interaction between H+ and the mineral. Also, the surface was stronger under low pH conditions, and a consistent critical pH of 3.0 was observed based on both the theoretical analyses of γH(0) and the dissolution density of mineral elements as a function of pH. At a pH < 3.0, the PICB was significantly enhanced, resulting in a notably weakened Si-O bonding energy and a substantial increase in the dissolution efficiency of silicate minerals. Although the dissolution behaviors of various minerals exhibited significant variations in response to pH, they can be described as a function of γH(0), indicating that γH(0) has an important influence on the structure of clay minerals. Moreover, the enhancement of γH(0) resulted in a higher content of SiO2 in the hydrothermal reaction products of MMT, accompanied by a subsequent reduction in the residual products represented by Al2O3. 【Conclusion】This study quantified the impact of H+-mineral bonding on the chemical weathering of minerals and revealed that the PICB between H+ and surface O atoms of minerals enhanced the γH(0) of H+ on the mineral surface and weakened the Si-O bond energy, thus significantly affecting the dissolution reactions of clay minerals. The results of this study provide theoretical insights for proposing targeted modulation techniques aimed at enhancing the structural stability of minerals.
-
Variation Characteristics and Accumulation Mechanism of Organic Matter Molecular Components in Soil Aggregates Under Long-Term Rice Cultivation
Liu Tao, Wang Ping, Liu Yalong, Wang Jingkuan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202408270343
Abstract:
Abstract: 【Objective】 As important carbon sources and sinks in terrestrial ecosystems, the accumulation process of paddy soil organic matter (SOM) is relatively well understood. However, changes in the molecular composition of SOM within soil aggregates and the mechanisms underlying SOM accumulation remain unclear.【Method】This investigation employed a paddy soil chronosequence in Cixi, utilizing Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy (3D-EEM). These methods were implemented to elucidate the variation patterns of SOM molecular components across different aggregate sizes and their contributions to SOM sequestration processes within the paddy chronosequence.【Result】Our findings revealed distinct temporal patterns in soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics. Both macroaggregates (>250 μm) and microaggregates (<250 μm) exhibited rapid SOC accumulation within the initial century, followed by a gradual stabilization. Aliphatic SOM components demonstrated a substantial decrease from 12%-13% to 1% within the first 100 years of rice cultivation, while aromatic SOM components showed a progressive increase from 16%-17% to 30%-38%. In dissolved organic matter (DOM) fractions, tryptophan-like DOM increased from 16%-17% to 33%, whereas fulvic acid and humic acid components decreased from 41%-42% to 36%-37% and 31%, respectively, subsequently maintaining relative stability. The fluorescence index (FI) and autochthonous index (BIX) of DOM displayed an initial increase followed by a decrease, while the humification index (HIX) showed the opposite trend. These observations suggest an initial period of microbial activity characterized by high metabolic substance content, followed by microbial community stabilization and continuous production of complex humic substances during prolonged rice cultivation.【Conclusion】Despite relatively minor differences in SOC molecular components across various aggregate sizes under extended rice cultivation, our results substantiate that SOC accumulation in paddy fields is influenced not only by chemical adsorption and physical protection within soil aggregates but also significantly by microbial transformations. These findings contribute to a comprehensive understanding of SOC accumulation mechanisms in paddy soils and provide valuable insights for enhancing soil fertility sustainability.
-
Sustainable Utilization of Cadmium-Contaminated Soil: Safe Utilization Strategies Based on Mechanisms of Plant Cadmium Accumulation
HUANG Jiu, HU die, GAO Yongqiang, CHEN Changzhao, JIANG Mengmeng, WANG Haoyu, ZHONG Chongwei, ZHENG Lu, SHEN Rengfang, ZHU Xiaofang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202502260089
Abstract:
Objectives: Cadmium contamination poses a significant threat to agricultural production and human health due to its persistence, toxicity, and potential to accumulate in crops and the food chain. However, there is a need for a comprehensive review that provides scientific guidelines for understanding Cd soil-solution chemistry, decreasing Cd levels in the food chain, and bridging the gap between laboratory research and field applications. Methodology: This study conducted an in-depth literature analysis of both laboratory and field research to provide a comprehensive analysis of the soil chemistry of cadmium, which is crucial for understanding its bioavailability and mobility. Results: The chemical behavior of Cd in soil is influenced by various factors, such as soil pH, organic matter content, and redox conditions. These factors determine the speciation of Cd, which in turn affects its uptake by plants and its potential to enter the food chain. The phytotoxic effects of Cd are manifold, impacting plant growth, physiological functions, and metabolic processes. Cd can suppress plant growth by inhibiting root and shoot development, reducing chlorophyll content, and disrupting photosynthesis. It also induces oxidative stress by increasing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA. The review also sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying plant responses to Cd stress. Two major molecular systems are highlighted: metal transporter families and regulatory transcription factor families. Metal transporters, including Nramp, HMA, ZIP, ABC, and YSL, play essential roles in Cd uptake from the soil, translocation from roots to shoots, and detoxification within plant cells. These transporters facilitate the movement of Cd through cellular membranes and into subcellular compartments, such as vacuoles, where it can be sequestered to reduce its toxicity. On the other hand, transcription factors like WRKY, MYB, bHLH, and NAC regulate the expression of genes involved in Cd tolerance and detoxification. They activate defense mechanisms that help plants mitigate Cd-induced oxidative damage and maintain cellular homeostasis. Based on the understanding of these molecular mechanisms, the review proposes innovative strategies for the sustainable utilization of Cd-contaminated soils. These strategies integrate molecular design approaches, such as engineering transporters to limit Cd uptake and enhance its sequestration, with phytoremediation techniques that utilize metal-tolerant plant species. By providing scientific guidelines for reducing Cd levels in agricultural products and enhancing food safety protocols, this study bridges the gap between laboratory research and field applications. It offers valuable insights for developing environmentally sustainable agricultural practices in regions affected by Cd pollution, thereby contributing to global food security and environmental protection. The proposed approaches not only aim to decrease Cd accumulation in crops but also seek to improve the overall health and productivity of plants grown in contaminated soils, ensuring safer food supplies for the growing global population. Furthermore, the review emphasizes the importance of these strategies in mitigating the adverse effects of Cd contamination on soil fertility and ecosystem health. By reducing Cd levels in soil and crops, these strategies can help maintain soil fertility, protect biodiversity, and promote the overall health of ecosystems. Conclusion: The integration of different approaches can lead to the development of more resilient agricultural systems that can withstand the challenges posed by Cd contamination and other environmental stresses. This comprehensive review thus provides a foundation for future research and practical applications aimed at addressing the complex issue of Cd pollution in agricultural environments.
-
Change characteristic of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Fractions during the Natural Restoration of Cultivated Black Soil
wuyanan, ZOU Wenxiu, WANG Shouyu, LU Xinchun, Han Xiaozeng
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503140117
Abstract:
【Objective】The restoration of cultivated land to natural grassland can increase soil organic carbon (SOC) content. This study aimed to investigate the changes in black soil organic carbon during vegetation restoration.【Method】Based on a 19-year long-term field experiment, the temporal dynamics of SOC and its fractions were examined during the restoration of cultivated black soil to natural grassland vegetation (GL), with comparisons made to continuous cultivated land (CL) and bare land (BL) without vegetation cover.【Result】The results showed that: (1) Compared to the initial soil, the SOC content in the topsoil (0-20 cm) increased by 26.19% in the GL treatment, with an annual growth rate of 1.38% (0.41 g·kg-1·a-1). In contrast, the SOC content decreased by 7.99% in the BL treatment, while no significant change was observed in the CL treatment; (2) Across the entire 0-100 cm soil profile, GL not only significantly increased the SOC content in the topsoil (0-20 cm), but also increased the SOC content in the subsoil layers (20-60 cm). The increments in the 0-20, 20-40 and 40-60 cm layers were 26.19%, 12.08% and 8.70%, respectively. However, no significant changes in SOC content were observed below 20 cm in the CL and BL treatments; (3) Compared to the initial soil, the GL treatment increased the carbon contents of free light fraction (fLFC), occluded light fraction (oLFC) and heavy fraction (HFC) by 199.45%, 112.83% and 12.00%, respectively. Additionally, GL increased the proportions of fLFC and oLFC while reducing the proportion of HFC in the SOC; (4) For humus fractions, the GL treatment increased the contents of fulvic acid (FA), humic acid (HA) and humin (HM) by 74.82%, 29.69% and 11.46%, respectively, and decreased the HA/FA ratio, indicating a reduction in the humification degree of soil organic matter.【Conclusion】In conclusion, long-term restoration of cultivated land can effectively increase the organic carbon content of black soil and promote the accumulation of labile SOC fractions.
-
The Impact of Cover Crops on Organic Carbon and Microbial Community in Biopore Sheaths of Shajiang Black Soil
Xiewanyu, Liushuai, Guozichun, Gaolei, Chenyan, Shenxintao, Zhangzhongbin, Pengxinhua
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412300513
Abstract:
【Objective】Cover crops are very important for regulating soil structure and enhancing soil organic carbon. Cover crops can improve soil pore structure by creating biopores through root penetration and subsequent decomposition. However, the effects of different cover crops on organic carbon accumulation and microbial communities in biopore sheaths remain unclear. 【Method】A field experiment was conducted in a typical Shajiang black soil, including four winter cover crop treatments (fallow, alfalfa, rapeseed, and a mixture of radish + hairy vetch) in rotation with summer maize. Soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN) contents in the biopore sheaths of the 20–40 cm soil layer under different treatments were determined, while bacterial and fungal community structures were analyzed via high-throughput sequencing. 【Result】The results showed that, compared with bulk soil, SOC content in the biopore sheaths increased significantly by 33.4% under the alfalfa treatment, while TN content increased significantly by 24.6% and 18.5% under the alfalfa and radish + hairy vetch treatments, respectively. However, no significant differences in SOC and TN contents of the biopore sheath were observed among different cover crops. The microbial community structure varies significantly with the interaction between cover crop species and soil habitats. The bacterial α-diversity indices and niche breadth indices in biopore sheaths were significantly higher than those in bulk soil, particularly in the radish + hairy vetch treatment, whereas no significant differences were observed in fungal communities between the two soil compartments. Furthermore, microbial communities within biopore sheaths exhibited a shift toward copiotrophic taxa compared with bulk soil. The relative abundance of Pseudomonas and Bacillus was higher in alfalfa-derived biopore sheaths than in other treatments. Correlation analysis indicated that the relative abundance of core microbial taxa involved in carbon decomposition and transformation was significantly positively correlated with SOC content. 【Conclusion】In summary, SOC and TN contents in the biopore sheaths under the alfalfa treatment significantly increased. SOC content may regulate microbial community structures within biopore sheaths by influencing bacterial α-diversity indices, niche breadth indices, and the relative abundance of core microbial taxa.
-
Effects of Different Biomass Materials on the Physicochemical Properties and Water-Salt Transport Characteristics of Saline-Alkali Soil
sunyan, liujianqi, wujianxin, fengzhenlong, liuxianhe, huzifu, ye jin hao
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202409300379
Abstract:
【Objective】Salinization leads to a decline in soil fertility and reduced agricultural productivity, significantly limiting the high-quality development of arid region agriculture. Bioorganic materials have shown promising effectiveness in land reclamation for salt-alkali-affected areas. 【Method】The effects of adding different biomass materials (8‰ biochar (B), 8‰ biochemical fulvic acid (BF), and a mixture of 4‰ biochar and 4‰ biochemical fulvic acid (BBF)) on the physicochemical properties and water-salt transport characteristics of soda saline-alkali soil was investigated, through one-dimensional vertical infiltration experiments. Each layer of soil was completely mixed with bioorganic materials and subjected to an equal volume treatment. 【Result】The results showed that the application of biochar and biochemical fulvic acid both significantly reduced soil bulk density and increased porosity, with significant differences between treatment B and other treatments (P<0.05). Under the same infiltration time,the wetting front depth of B, BF, and BBF treatments was significantly smaller than that of the CK, with the BF treatment showing the smallest wet front migration depth. Both the Kostiakov and Philip models could effectively simulate the infiltration process, and the infiltration rate (S) showed a variation pattern of CK > B > BBF > BF. The B, BF, and BBF treatments significantly increased the soil volumetric water content in the 0-15 cm soil layer, with significant differences among the treatments (P<0.05). At the 15 cm soil depth, the soil salt content in the B, BF, and BBF treatments was higher than that in the CK, and the soil salt content in the 20-30 cm soil layer gradually increased with depth. The BF treatment showed the most significant effect on salt content. Also, the soil pH in all treatments was lower than the initial pH, but in the 0-15 cm soil layer, the pH of the B, BF, and BBF treatments was higher than that of the CK. Additionally, the concentration of soil salt ions in the 0-15 cm soil layer was higher compared to CK, especially the water-soluble Na+ concentration, which significantly increased. 【Conclusion】The result indicates that bioorganic materials, such as B and BF, exhibit significant effects in land reclamation for salt-alkali affected areas by significantly reducing soil bulk density and increasing porosity. Additionally, these materials decreased infiltration rates while enhancing cumulative infiltration, though increased Na? concentrations may affect long-term outcomes. Therefore, when improving salt-alkali soils, emphasis should be placed on considering the physical properties of bioorganic materials. It is recommended to select materials with suitable physical properties and low sodium content, followed by salt leaching treatments, to optimize land reclamation efforts.
-
Effects of Improvement Measures on Aggregate Stability and Humus Composition of Soda Saline Meadow Soil
lisiyan, liangxiaoyan, wangchen, wangyuqing, xiewei, yangdi, zhangmingcong
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501060011
Abstract:
【Objective】This study was aimed to investigate the regulation mechanisms of different improvement measures on soil structure and humus characteristics of soda saline-alkali land.【Method】A field comparative experiment was conducted to study the effects of conventional (CK), biochar (T1), organic fertilizer (T2), and structural modifier (T3) on aggregate stability, humus composition, and soybean yield in soda saline meadow soil.【Result】The results showed that compared with CK, T1, T2 and T3 treatments significantly promoted the transformation of microaggregates to macroaggregates. The effect of T3 treatment was the most significant, and the mass fraction of >2 mm aggregates increased by 12.66% (P<0.05), which was significantly higher than that of T1 and T2. T3 treatment significantly improved nutrient availability by reducing soil pH by 3.02% and simultaneously increasing available phosphorus (67.84%) and alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (7.98%) content. The average weight diameter and geometric mean diameter of soil increased by 7.99% and 2.39%, respectively, and the organic carbon content of microaggregates (0.053-0.25 mm) increased by 24.58%-31.14%, which was significantly higher than other treatments. In terms of humus components, the contents of humic acid, fulvic acid, and humin in each particle size of T3 treatment increased by 19.95%-29.62%, 3.64%-6.48%, and 7.33%-36.92%, respectively, which were better than those of T1 and T2 treatments. T3 treatment significantly increased the complexity of humus, and the ratio of E4/E6 significantly increased by 84.84%. The PLS-PM structural equation model revealed that soil organic carbon (path coefficient 0.96) significantly affected aggregate stability by regulating total humic acid (1.13) and humin (1.29). Yield analysis showed that T3 treatment achieved a soybean yield of 2653.97 kg·hm-2 by increasing plant height (61.32%) and pod number per plant (11.96%), with an increase of 42.67%.【Conclusion】The results showed that the compound modifier (T3) complicated the molecular structure of large-grained aggregates by reconstructing the molecular structure of humus, promoted the increase of cementing materials, increased the content of organic carbon, significantly increased the mass fraction of aggregates with >2 mm particle size and the stability of soil aggregates, and effectively improved the soil structure of the plough layer of soda-saline meadow soil. This provides a theoretical basis for the improvement of soda saline-alkali land and the synergistic improvement of production capacity.
-
Effects of Bridge Construction on Mangrove Soil Fungal Diversity and Co-Occurrence Networks
GAO Guifeng, MA Cheng, YAN Subo, SONG Luyao, CHU Haiyan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412090480
Abstract:
【Objective】Bridge construction strongly affects the structure and function of soil microbial communities in coastal wetlands. However, its specific impacts on mangrove soil fungal communities have not been given much attention. This study aimed to investigate the impacts of bridge construction on mangrove soil fungal communities, focusing on two common construction methods (Steel casing pipe, SC; Sheet pile cofferdam, SP) compared to undisturbed areas (UD), providing insights for ecological conservation and sustainable management.【Method】Soil fungal communities across SC, SP, and UD habitats were investigated using high-throughput sequencing, functional guild annotation, and co-occurrence network analysis. Key soil properties were measured to identify environmental drivers.【Result】The results showed that the main fungal biomarkers in the soils of the UD and SC habitats were Ascomycota, whereas the SP habitat was dominated by Basidiomycota. Also, the species richness of the soil fungi in the SP habitat was significantly (P < 0.01) higher than that in the SC and UD habitats. In addition, the species richness of saprotrophic fungi was significantly (P <0.05) higher in SP than in SC and UD, and the relative abundance of saprotrophic fungi was significantly (P < 0.05) higher in SC than in UD. The soil C/N ratio, TN, and pH were the main environmental drivers affecting fungal guilds. Fungal co-occurrence network analysis showed that the network complexity (avgK = 1.94) was higher in the UD habitat than in the SC and SP habitats.【Conclusion】This study reveals that bridge construction methods differentially alter mangrove soil fungal communities through soil physicochemical alterations. These findings highlight the need for method-specific environmental assessments and offer a scientific basis for balancing coastal wetland conservation with construction activities.
-
Effect of Organic Substitution on Crop-Soil-Microbial Stoichiometric Characteristics and Soil Phosphorus Morphology
HUA Mingxiu, HU Can, CHEN Hao, CHEN Guanglei, WANG Lei, WANG Shenqiang, WANG Yu
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412120486
Abstract:
【Objective】To address the limited understanding of the nutrient stoichiometric relationships among crops, soil, and microorganisms under different proportions of organic fertilizer substitution for chemical fertilizers in a rice-wheat rotation system.【Method】 This study utilized a five-year field experiment at the Yixing experimental site of the Changshu Agro-Ecological Experimental Station, Chinese Academy of Sciences, five treatments were established: no phosphorus fertilizer (CK), conventional chemical phosphorus fertilizer (CF), 30% substitution of chemical phosphorus fertilizer with organic fertilizer (TM), 50% substitution (FM), and 100% substitution (HM). The aim was to investigate the effects of organic fertilizer substitution on crop-soil-microorganism stoichiometric ratios and phosphorus availability under equivalent nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium inputs. 【Result】Results from ten consecutive cropping seasons over five years revealed no significant differences in the grain and straw yields of rice and wheat or in the total carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric ratios among treatments. The stoichiometric ratios of available nutrients in soil, including dissolved organic carbon: available nitrogen, dissolved organic carbon: available phosphorus, and available nitrogen: available phosphorus, ranged from 7.08-7.39, 23.1-26.8, and 3.59-4.06, respectively, under the TM, FM, and HM treatments. Compared with CF, these treatments did not significantly alter the total nutrient stoichiometric ratios in the soil but significantly increased the soil organic phosphorus fractions (by 49.7%-58.2%, dominated by moderately labile organic phosphorus, NaOH-Po). Additionally, soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC), nitrogen (MBN), and phosphorus (MBP) in soil increased by 14.3%-61.1%, 4.37%-36.2%, and 46.4%-50.8%, respectively. The microbial stoichiometric ratios under all treatments were as follows: MBC:MBN (11.6-14.5), MBC:MBP (68.3-106), and MBN:MBP (5.32-7.32). The TM and FM treatments significantly reduced the stoichiometric ratio of enzyme activity (EEA(C:N)) but did not affect the overall soil-microorganism stoichiometric balance. 【Conclusion】These findings demonstrate that substituting 30% of chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers can maintain crop yields while effectively enhancing soil available phosphorus content. This study underscores the critical importance of scientifically regulating the substitution ratio of organic fertilizers to optimize soil nutrient management, improve soil fertility, and promote sustainable agricultural development.
-
Effects of Biological Fertilization on the Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacterial Community and Maize Productivity in Upland Red Soil
Peng Ziyi, Zheng Jie, Zhu Guofan, Shi Guangping, Wang Xiaoyue, Ding Yanghuiqin, Zhou Shungui, Jiang Yu-ji
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202412310518
Abstract:
【Objective】Phosphorus solubilizing bacterial communities in the rhizosphere are critical functional components in soil phosphorus cycling. Their abundance, community composition, and diversity determine the activity of soil alkaline phosphomonoesterase (ALP) and phosphorus availability. Thus, this study aimed to explore the impact of different bio-fertilization regimes on phosphorus-solubilizing bacterial communities in red soil and maize productivity. 【Method】Based on a long-term (11-year) bio-fertilization experiment at the Yingtan Red Soil Ecological Experiment Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, four treatments were selected: chemical fertilizer + organic fertilizer (FO), FO + phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (FOP), FO + nematodes (FON), and FO + phosphate-solubilizing bacteria + nematodes (FOPN). Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and high-throughput sequencing technologies were employed to elucidate the mechanisms through which biological amendments affect rhizosphere phosphorus solubilizing bacterial communities, ALP activity, and maize productivity. 【Results】(1) Compared with the FO treatment, bio-fertilization treatments (FOP, FON, FOPN) significantly improved soil fertility and maize yield, with the combined inoculation treatment (FOPN) showing the most pronounced effects. Soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), and maize yield increased by 8.08%, 24.2%, 30.5%, 20.2%, and 39.7%, respectively. (2) Bio-fertilization significantly increased the abundance of rhizosphere phosphorus solubilizing bacteria, showing notable interactive effects, while the Shannon index remained consistently lower than that in the FO treatment. The abundance of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria exhibited significant positive correlations with TN and AN. (3) AN, phosphorus solubilizing bacterial abundance and ALP activity were identified as the key drivers of maize yield. Structural equation modeling revealed that AN not only directly promoted maize yield but also indirectly enhanced yield by increasing phosphorus-solubilizing bacterial abundance and ALP activity. 【Conclusion】Bio-fertilization significantly increased phosphorus solubilizing bacterial abundance, suggesting that microbial population dynamics may regulate phosphorus uptake in maize. These amendments enhanced upland red soil fertility by indirectly promoting phosphorus solubilizing bacterial abundance and ALP activity, thereby facilitating organic phosphorus mineralization and maize growth.
-
The spatiotemporal variation characteristics of soil enzyme activity in alpine meadow after adding yak dung
SUBINUER·wubuli, YIN Xiaoyue, FENG Jingying, SUONAN Jiangcai, WANG Changting[†]
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202501160033
Abstract:
Yak dung is an important factor affecting the nutrient cycling of soil in alpine grassland ecosystems, and changes in soil enzyme activity can effectively measure the soil nutrient cycling processes. To explore the temporal and spatial variations in soil enzyme activity under the addition of yak dung in alpine meadows, a fluorescence analysis method using 96-well microplate enzyme assays was employed. Key enzymes involved in soil carbon and nitrogen transformation processes in the alpine meadow soils of the eastern Tibetan Plateau:β-glucosidase (BG), peroxidase (PER), phenol oxidase (PPO), β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG), and protease (LAP)—were studied to analyze the potential impacts of yak dung decomposition over different periods in warm and cold seasons. Also, the effect of the yak dung on the determined properties was considered at varying distances from the dung pile (under the dung (D0), 10 cm away (D10), and 20 cm away (D20)). The results indicate that (1) The decomposition of yak dung in both warm and cold seasons significantly increased the activities of BG, PER, PPO, NAG, and LAP, with the highest enzyme activity observed under D0. As the decomposition time progressed from warm to cold seasons and the distance from the dung increased, soil enzyme activity gradually decreased; (2) The decomposition of yak dung in both seasons significantly enhanced the total soil nutrients (total carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus) and available nutrients (ammonium nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, available phosphorus), soil moisture, and pH, although the impacts of decomposition time on these soil environmental factors varied between seasons. The correlation between soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activity in the cold season was significantly stronger than in the warm season, with the C/N ratio in the cold season having the most pronounced effect on enzyme activity. The addition of exogenous nutrients led to the redistribution of nutrients and organic matter, with changes in enzyme activity exhibiting spatial and temporal gradient distribution characteristics, which were significantly correlated with the distance from the dung (radiating outward) and soil depth (extending downward).
-
Impact Characteristics and Mechanisms of Warming on the Decomposition of Soil Organic Carbon Three Pools in Grasslands of the Loess Plateau
Feng Junhao, Liu Xiaowei, Jing Yudu, Liang Ke, Yu Qiang, Guo Liang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411150440
Abstract:
【Objective】Grasslands, as one of the most extensive ecosystems, play an important role in regulating the global carbon cycle through the decomposition of soil organic carbon (SOC) pools. However, the effects of global warming on SOC decomposition dynamics, and the underlying microbial and enzymatic regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we investigated how warming alters the decomposition dynamics of active, slow, and passive SOC pools, with a focus on microbial community composition and extracellular enzyme stoichiometry. 【Method】This study was conducted using surface soil collected from semi-arid grasslands on the Loess Plateau in a long-term incubation experiment. Soil samples were incubated at two controlled temperatures (15 °C and 25 °C) under constant temperature and humidity for 553 days (~1.5 year). During the incubation, soil respiration rates, microbial biomass carbon (MBC), extracellular enzyme activities, and microbial community compositions were systematically monitored. 【Result】The results showed that incubation at 25 °C significantly increased soil respiration rates, cumulative carbon emissions, and the decomposition rates of the three SOC pools (active, slow, and passive) compared to 15 °C. However, the magnitude of this enhancement diminished over time. Among the SOC pools, the active pool exhibited the most rapid decline in respiration rate, followed by the slow pool, with the passive pool showing the slowest decline. Additionally, microbial biomass carbon and bacterial diversity decreased more rapidly at 25 °C, accompanied by significant shifts in microbial community composition. The relative abundance of copiotrophic microorganisms, such as Proteobacteria and Ascomycota, decreased during the incubation, whereas oligotrophic microorganisms, including Actinobacteria and Ascomycota, increased. Notably, copiotrophic microorganisms were more dominant at 15 °C, while oligotrophic microorganisms were more prevalent at 25 °C. Microbial oxidative metabolism, nitrogen demand, and phosphorus demand increased progressively throughout the incubation, with overall higher levels observed at 25 °C compared to 15 °C. Furthermore, the response of the three carbon pool decompositions to temperature increase was regulated by extracellular enzymes and microbial community composition. Stepwise linear regression showed that under 15 °C incubation, MBC and oxidases were positive regulatory factors for the decomposition of the active and slow carbon pools, respectively. Under 25 °C incubation, NAG (β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase), and AKP (alkaline phosphatase) were positive regulatory factors for the decomposition of the passive carbon pool. The partial least squares path model analysis indicated that incubation temperature and time significantly regulated microbial community composition. The microbial community composition positively regulated extracellular enzyme activity and exerted negative and positive regulation on the decomposition of the slow and passive carbon pools, respectively. Also, extracellular enzymes, as key regulatory factors for the decomposition of the active and passive carbon pools, exerted negative and positive regulation on the decomposition of these pools, respectively.【Conclusion】This study reveals that shifts in microbial community composition, particularly the shift in species with different ecological strategies, play a key role in regulating extracellular enzyme activities and stoichiometry, thereby mediating temperature-induced changes in SOC decomposition dynamics. These findings provide critical insights into the microbial and enzymatic mechanisms that drive SOC turnover under warming conditions, offering valuable evidence to enhance our understanding of global carbon cycling and its feedback to climate change.
-
Vertical Differentiation Characteristics and Main Controlling Factors of Acid Buffering Capacity in the Strongly Acidic Red Soil Regoliths
CUI Zixiao, WU Huayong, SONG Xiaodong, YANG Shunhua, ZHANG Ganlin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503090107
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aimed to investigate the vertical variation characteristics and controlling factors of acid buffering capacity (pHBC) of strongly acidic red soil regoliths.【Method】The strongly acidic red soil regoliths with pH values less than 5.0 were selected as the study objects, which are developed from Quaternary red clay (including an upper uniform red clay layer and a lower reticulate red clay layer) underlain by sandstone bedrock located at a small agricultural watershed in Yujiang District, Yingtan City, Jiangxi Province. Approximately 8-meter-deep soil-rock core samples were collected from two upland boreholes using drilling, which were classified into four layers, including a uniform red clay layer, reticulate red clay layer, weathered sandstone layer, and sandstone bedrock layer. Regolith pHBC and other related physicochemical properties were measured. Multiple linear regression and random forest modeling as well as acid-base equilibrium theory analysis were used to quantify the relative contributions of regolith organic matter, mechanical compositions, mineral compositions, iron and aluminum oxides, exchangeable base cations, exchangeable acidity, and pH to pHBC variations across different layers.【Result】The red soil regoliths exhibited layer-specific acid buffering characteristics. The regolith pHBC were 2.53 ± 0.41 cmol·kg-1·pH unit-1, 1.93 ± 0.59 cmol·kg-1·pH unit-1, and 1.39 ± 0.22 cmol·kg-1·pH unit-1 in the uniform red clay layer, the reticulate red clay layer, and the weathered sandstone layer, respectively. The regolith pHBC increased with depth in the uniform red clay layer, decreased with depth in the reticulate red clay layer and the weathered sandstone layer, and increased from the weathered sandstone layer to the sandstone bedrock layer. Interestingly, the exchangeable base cations of the Quaternary red clay layer at a strongly acidic state were exhausted and played a limited role in the changes of pHBC. Moreover, the pHBC depended on the protonation process of crystalline iron oxide and organic matter in the uniform red clay layer, the dissolution of amorphous and crystalline aluminum oxides and the protonation of amorphous and crystalline iron oxides in the reticulate red clay layer, and on feldspar dissolution and exchange of exchangeable calcium and magnesium ions in the weathered sandstone layer. Also, the dissolution of carbonates plays a key role in the pHBC in the sandstone bedrock layer.【Conclusion】The acid buffering mechanism in the strongly acidic red soil regoliths primarily centers around the protonation and dissolution processes of iron and aluminum oxides. These research findings provide support for the acidification assessment and improvement of the red soil ecosystems.
-
Response of Dissolved Organic Matter Content and Quality in Greenhouse Soils to the Application of Organic Fertilizers with Various Carbon Components
Xu Yehong, Ba Wenwen, Wang Xuanqing, Lu Chao, Luo Jia, Ma Yan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411190446
Abstract:
【Objective】Dissolved organic matter (DOM) is the most active functional component in the soil carbon pool, and the application of organic fertilizer is an effective measure for carbon sequestration and soil fertility improvement in greenhouse soils. However, the response of DOM content and quality in greenhouse soils to organic fertilizer is still unclear, which hinders the elucidation of the regulation mechanisms of the active carbon pool in greenhouse soils and the development of precise application technologies for organic fertilizers.【Method】This study was conducted in situ and five treatments were included: no fertilization as control (CK), chemical fertilizer only (F), and three organic fertilizers with different carbon components replacing 30% of chemical N fertilizer (composted straw replacing 30% of chemical N, FMs; chicken manure replacing 30% of chemical N fertilizer, FMc; and spent mushroom replacing 30% of chemical N fertilizer, FMm). The content of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) were studied in the surface and subsurface layers of greenhouse soils under vegetable cultivation. Combined with three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy technology and parallel factor analysis method, the fluorescence spectral characteristic parameters and chemical composition of DOM in soil were analyzed.【Result】Compared with CK, the F treatment had no significant effect on the DOC content in both the surface and subsurface soil; it only significantly increased the DON content in the subsurface soil, with an increase of 1.22-folds. The results showed that compared with F, the FMc organic fertilizer with the highest content of labile carbon components significantly increased the DOC and DON content by 44.2% and 78.1%, respectively, in the surface soil. However, only the DON content in the surface soil significantly increased under the FMs and FMm treatments. Compared with CK, the application of chemical and organic fertilizers significantly reduced the DOC/DON ratio in the surface and subsurface soils, and the humification index (HIX) of DOM in the surface soil significantly increased by 1.06 to 2.07-folds, reaching the highest in the FMc treatment. Also, the fluorescence spectral characteristics of DOM in the subsurface soil did not significantly respond to fertilization. In addition, the content of DOC and DON were significantly negatively correlated with fulvic acid-like components with low molecular weight, while significantly positively correlated with humic acid and aromatic components with high molecular weight.【Conclusion】In summary, the application of chicken manure rich in labile carbon components can more effectively increase the content of DOC and DON and the humification degree of DOM in the surface soil, and increase the proportion of refractory components of DOM in the subsurface soil. Thus, it is more beneficial to apply chicken manure to achieve the "double improvement" of the content and quality of labile carbon pools in the entire tillage layer of greenhouse soils under vegetable cultivation.
-
Study on Colloidal Properties of Purple Soil and Its Aggregation Kinetics under Different Fertilization Treatments
Zhang Yiwei, Tian Rui, Wu Wenfei, Bi Linna, Lv Runze, Li Hang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202411010420
Abstract:
【Objective】The aggregation and dispersion of soil colloids influence macroscopic phenomena such as soil structure, soil erosion, soil nutrients, and pollutant transport. This study aims to explore the process of purple soil colloid aggregation and its ion-specific effects under different fertilization treatments. Specifically, the study aims to elucidate the interactions and microscopic mechanisms from the perspective of the effect of fertilization on mineral composition, surface properties, and aggregation kinetics of purple soil colloids. 【Method】In this study, four fertilization treatments, no fertilizer (CK), urea alone (N), organic fertilizer replacing 10% urea nitrogen (LM), and organic fertilizer replacing 30% urea nitrogen (HM) were set up on a purple soil in Southwest China. After 60 d of incubation, the effect of fertilization on the colloid aggregation kinetics of purple soils and their causes were investigated by determining the colloid quantity, clay mineral composition and surface properties, and soil colloid aggregation process. 【Result】The colloids used in this study contained mainly hydromica, chlorite, montmorillonite, vermiculite, and kaolinite, and the short-term fertilization treatments had no significant effect on the colloid content and mineral composition. Compared to CK, the N treatment induced the highest surface charge density to the purple soil colloids, with the greatest electrostatic repulsion between particles whereas LM and HM treatments decreased the surface charge density, and the degree of decrease was directly proportional to the amount of organic fertilizer added. The aggregation kinetics of soil colloids differed under different fertilizations and the critical coagulation concentration (CCC) decreased in the order of N > CK > LM > HM. Under the same fertilization treatment, the CCC values of purple soil colloids showed an ion-specific effect, decreasing in the order of Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. Also, correlation analysis showed that there was a strong positive correlation between the CCC values of purple soil colloids and the surface charge density and a strong negative correlation with the specific surface area and organic matter content. 【Conclusion】Different fertilization treatments affect the interaction force between soil particles mainly by influencing the surface chemical properties of purple soil colloids, thus, affecting the aggregation and dispersive behaviors of the colloids.
-
Elemental Geochemical Characteristics and Chemical Weathering Intensity of Soils in the Shergyla Mountain, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
ZHANG Chu, YANG Jinling, YANG Fei, YE Mingliang, GU Jun, CHEN Yamin, ZHANG Ganlin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503130113
Abstract:
【Objective】This study aimed to unravel the weathering intensity and elemental geochemical characteristics of soils in the southern mountainous regions of the Tibetan Plateau. 【Method】 Shergyla Mountain in Linzhi City was selected as the study area. Fifteen typical soil profiles were sampled across different landscapes and altitudes, and the geochemical characteristics of soil elements were analyzed, with weathering intensity estimated for different soil horizons. 【Result】The results indicate that the soils of Shergyla Mountain, influenced by the alpine climate, are weakly developed, with the soil types dominated by Gelic Cambosols. For the studied soils, primary minerals were predominant in soil minerals while secondary minerals were present in low abundance. The Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA) ranged from 47 to 62, suggesting that most soils were in a state of weak weathering. The low temperatures at high altitudes restricted chemical weathering of soil minerals, resulting in insignificant impacts of precipitation, temperature, altitude, slope, and parent material on soil chemical weathering. The weathering intensity indicators (CIA, weathering leaching coefficient ba, Weathering Index of Parker WIP) across soil profiles exhibited different distribution patterns from the surface layer downwards, primarily influenced by transportation and deposition processes driven by external forces such as wind, gravity, and runoff. Nevertheless, the results indicate that chemical weathering had a relatively small impact on soil formation. 【Conclusion】The alpine environment controls overall soil development thus weakening the difference between other soil forming factors. The findings of this study provide theoretical support for the evolution of pedogenesis and soil classification on the Tibetan Plateau and offer pedological insights into the rational utilization of land resources.
-
The Relationship Between Microbial Necromass Carbon and Soil Aggregate Stability on a Global Scale
Kuang Yanyun, Hu Han, Li Sen, Liang Yuting
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202409030355
Abstract:
【Objective】 The soil organic carbon (SOC) pool is the largest carbon reservoir in terrestrial ecosystems, playing an essential role in mitigating climate change and maintaining soil fertility. Among the various components of SOC, microbial necromass carbon (MNC) constitutes a significant proportion, contributing approximately 30-80% to the total SOC, and playing a crucial role in stabilizing soil carbon stocks. Accumulation and stabilization of MNC in soil are closely linked to the formation and stability of soil aggregates, which provide physical protection against microbial decomposition. Despite the known connection between MNC and soil aggregation, no comprehensive studies have systematically explored the relationship between MNC and soil aggregate stability. This study aims to further explore the global association between MNC and soil aggregate stability.【Method】 To assess the relationship between MNC and soil aggregate stability, we compiled global observational datasets on soil amino sugars (biomarkers of MNC) and soil aggregates. Using machine learning techniques, we predicted the global distribution of MNC and analyzed its correlation with the stability of soil aggregates. The PLS-PM was employed to further investigate the pathways through which soil aggregate stability influences MNC sequestration, takin into account factors such as soil physical properties, nutrient availability. 【Result】 The results revealed that MWD is a key predictor of MNC, with a significant positive correlation between MNC and MWD on a global scale (P < 0.05). Further correlation analysis of global prediction data confirmed this relationship and showed that it is consistent across different ecosystems. The Partial Least Squares Path Model (PLS-PM) analysis revealed that soil aggregates protect MNC directly by forming physical barriers and indirectly by regulating soil physical properties and nutrient availability, which in turn influence MNC accumulation and stabilization. In particular, soil nutrients had the most significant positive impact on MNC (path coefficient = 0.67, P < 0.05). The process through which MWD influences MNC shows significant differences across different ecosystems, specifically in terms of the direction and strength of the pathways. For example, in agricultural ecosystems, the indirect effects through soil physical properties and nutrients are more pronounced, while in forest ecosystems, the direct effect is stronger. 【Conclusion】The findings of this study underscore the significant role of soil aggregates in stabilizing MNC, and highlight the potential of soil aggregation as a key factor in enhancing soil carbon storage. Also, the positive correlation between MNC and aggregate stability suggests that strategies aimed at improving soil structure; eg., practices that enhance aggregation and optimize nutrient management, can effectively contribute to greater carbon sequestration. By fostering more stable soil aggregates, we can improve MNC sequestration, mitigate climate change, and sustain soil fertility. Furthermore, these findings can inform the development of predictive models for MNC sequestration and the integration of soil aggregate stability as a critical indicator for assessing the carbon sequestration potential of soils.
-
Effects of Different Organic Materials on the Stability of Saline-alkali Soil Colloid
SUN Yuliang, LI Qirui, Li Wei, Wang Xiang, SHANG Jianying
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202408300349
Abstract:
【Objective】Soil colloid stability plays an important role in soil nutrient retention, structure formation and crop growth. The application of organic materials is an effective method for improving saline-alkali soil, but their effects on soil colloid stability in these conditions remain unclear.【Method】In this study, we investigated the effects of biochar (BC), cattle manure (CM), and maize straw (MS) on soil colloid stability at different salinity-alkalinity levels (non-saline-alkali, mild saline-alkali and moderate saline-alkali) through soil incubation and sedimentation experiments in the laboratory.【Result】(1) The addition of organic materials significantly reduced the diameter of saline-alkali soil colloidal particles, making it similar to the diameter of non-saline-alkali soil colloid. In mild saline-alkali soil, the effect of MS treatment was most effective, and the colloidal particles size decreased from 785.7 nm to 360.2 nm. In moderate saline-alkali soil, the effect of CM treatment was most effective, decreasing the colloidal particles size from 675.8 nm to 393.6 nm. (2) The stability of soil colloid is related to the degree of soil salinity. Compared with non-saline-alkali soil and mild saline-alkali soil, moderate saline-alkali soil colloid exhibited significantly high stability, likely due to elevated high pH and high alkalinity. (3) Organic materials had minimal effect on the colloid stability of non-saline-alkali soil and mild saline-alkali soil. However, CM and MS treatments significantly reduced the colloid stability of moderate saline-alkali soil, causing colloidal particles agglomerated. Therefore, in moderate saline-alkali soil, the application of cow manure and maize straw may be more effective than biochar for stability improvement.【Conclusion】The application of organic materials ameliorates the basic physicochemical properties of saline-alkali soil and optimizes the state of soil colloid. Compared with biochar, cattle manure and maize straw, due to their rich functional groups and nutrients, significantly reduced the colloid stability of moderate saline-alkali soil upon application, thereby inducing colloidal aggregation and promoting the formation of microaggregates.
-
Response Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon to Reduced Chemical Fertilizers or Organic Fertilizer Substitution
Wu Nengxiang, Wang Ping, Liu Yalong, Wang Jingkuan
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202408190332
Abstract:
Delving into the impacts of reduced chemical fertilizers (RCF) and organic fertilizer substitution (OFS) on soil organic carbon (SOC) is crucial for understanding the response processes of agricultural SOC pools to fertilization and achieving sustainable agricultural development early. This study aims to explore the impacts of RCF and OFS on SOC under different climatic conditions, initial soil properties, and land use patterns. Furthermore, it endeavors to estimate the key influencing factors and clarify the natural and anthropogenic conditions conducive to SOC accumulation.【Method】After collecting and sorting out 142 published literature, we analyzed the variation characteristics of SOC content under RCF and OFS using meta-analysis. Thereafter, the influence degrees of various factors on SOC were systematically investigated by the Random Forest Model.【Result】The results revealed that SOC decreased by 2.61% on average under RCF. Notably, greater SOC losses were observed in temperate regions (with annual mean temperature < 10°C and annual mean precipitation < 1000 mm), whereas SOC losses were not significant with changes in altitude. Soils with high initial SOC content favored SOC retention. With soil’s initial pH and available phosphorus content increasing, the overall loss of SOC tended to intensify, with the highest SOC reduction reaching 6.91%, however, the effect of initial available potassium was the opposite. The declines in SOC under RCF were similar in farmland and orchards, while changes in SOC in vegetable fields were not significant. In contrast, SOC significantly increased by 14.39% under OFS, with subtropical regions at low to medium altitudes and annual precipitation < 600 mm being more conducive to SOC accumulation. Except for low levels of initially available nitrogen (50 mg·kg-1), no significant differences in SOC were observed among soils with different initial SOC, total nitrogen, and available nitrogen contents. With initial pH and available phosphorus content increasing, the cumulative effect of SOC enhanced, whereas the effect of initially available potassium was the opposite. Among different land use types under OFS, paddy-upland rotation and vegetable field utilization were most favorable for SOC accumulation.【Conclusion】Under the two fertilization systems, the climatic and environmental conditions in subtropical regions are more conducive to SOC sequestration. Compared to the subsurface soil, the impact of RCF and OFS on SOC in the surface soil was more significant. The decline in SOC of RCF was similar in both farmland and orchards, while the change of SOC in vegetable fields was not significant. In contrast, paddy-upland rotation and vegetable fields were the most favorable practices for SOC accumulation under OFS. Additionally, pH and initially available nitrogen were the most critical factors influencing the changes in SOC with RCF and OFS, respectively. These research results are of great significance for achieving carbon neutrality and sustainable development in agriculture as soon as possible.
-
Progress of soil temperature prediction equation
Zhang Jianbin, Gao Zhi Qiu, Tong Bing, Wang Linlin
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202210220581
Abstract:
Soil temperature (especially surface temperature) is a key physical quantity in the interaction between land and atmosphere, and plays a very important role in the earth system. Soil temperature prediction technology has always been the core scientific problem in land surface model, numerical weather prediction and climate prediction. This paper systematically reviews the research progress of soil temperature prediction equation, from the classical heat conduction equation to the heat conduction convection equation that takes into account the physical process of vertical movement of soil moisture, from the single sine wave approximation to the Fourier series approximation of the daily change of surface temperature, from the assumption that the diurnal change of convection parameters is constant to the consideration of its diurnal change, and emphatically summarizes the creation, improvement and solution of the soil heat conduction convection equation. Finally, this paper reviews the application of heat conduction convection equation in the study of surface energy balance, vertical movement of soil moisture, water flux, earthquake and frozen soil heat transfer. At the same time, it is pointed out that the influences of soil water phases and plant roots on the heat conduction-convection equation is warranted for the future research of soil temperature prediction equation.
-
Characteristics and prediction of soil-sodium adsorption ratio in Hebei coastal saline-alkali soil
Chen TianMing, Zhang Chong, Gao Hui, Wang Feng, Shang BaiJun, Fu YuHang, Chen HuiZe, Liu JinTong, Fu TongGang
DOI: 10.11766/trxb202503020095
Abstract:
The Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) is a critical indicator for characterizing the hazard of sodium ions and the degree of soil sodification in saline-alkali soils. However, in the coastal region of Hebei, the characteristics and key influencing factors of soil SAR remain unclear due to unique processes of salt formation and accumulation, as well as complex physicochemical interactions, which hinders its accurate prediction.【Objective】This study aims to elucidate the spatial distribution and profile variation patterns of SAR in representative coastal saline-alkali soils of Cangzhou, Hebei; to identify and quantify the key soil physicochemical factors influencing SAR dynamics. Also, the study seeks to develop and select an optimal machine learning model for accurately predicting SAR based on easily measurable parameters.【Method】Taking typical coastal saline-alkali land in Cangzhou City, Hebei Province as the research area, soil samples were collected from two layers (0–20 cm and 20–40 cm). A comprehensive set of properties was measured, including ionic composition, bulk density (BD), soil water content (SWC), soil organic matter (SOM), total porosity (STP), capillary porosity (SCP), saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks), electrical conductivity (EC), and pH. The characteristics of SAR were analyzed, its main influencing factors were explored, and four machine learning models: Linear Regression (LR), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), were used to predict SAR. Model performance was evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R2) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE).【Result】The mean SAR values in the upper (0–20 cm) and lower (20–40 cm) layers were 22.23 and 28.02, respectively, with no significant difference (P = 0.126). The soil in the study area was classified as moderately saline-sodic soil. Correlation analysis revealed that SAR was significantly correlated with K?, Cl?, SO?2?, EC, pH, BD, HCO??, SOM, SWC, STP, SCP, and Ks. Among these, the correlations with Cl?, SO?2?, and EC were the strongest, identifying them as the primary influencing factors. In the comparison of SAR prediction models, a model using both EC and pH as predictors achieved higher accuracy, and the RF model demonstrated the best predictive performance, with soil EC being the most significant feature.【Conclusion】The RF model can achieve robust prediction of SAR in the coastal saline-alkali soils of Hebei based on easily measurable indicators such as EC and pH. This study identified the key driving factors of SAR in the region and developed an effective predictive framework, providing a scientific basis and practical tools for the precise reclamation and sustainable utilization of local saline-alkali lands.
 About
About
Supervisor: Chinese Academy of Sciences
Sponsor:Soil Science Society of China
Editor-in-Chief:Xu Renkou
Address:71 East Beijing Road, Nanjing 210008, P. R. China
Zip Code:210008
Phone:+86-25-86881237
Email:actapedo@issas.ac.cn
ISSN:0564-3929
 Qr Code
Qr Code
-

WeChat